要深入理解spring mvc的工作流程,就需要先了解spring mvc的架构:
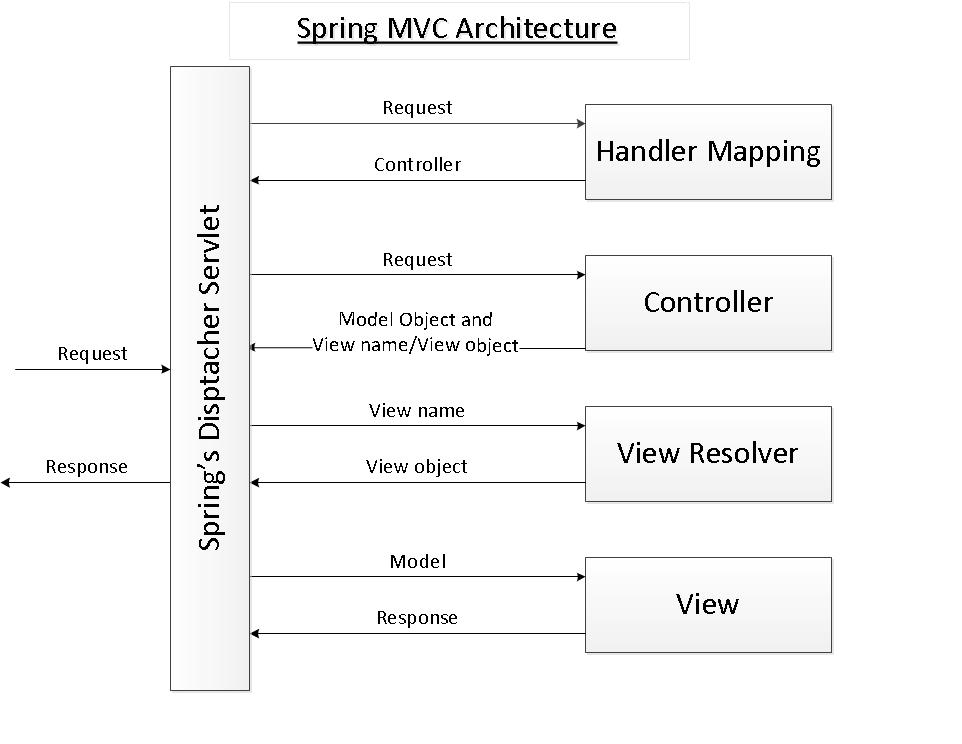
从上图可以看到 前端控制器DispatcherServlet在其中起着主导作用,理解了DispatcherServlet 就完全可以说弄清楚了spring mvc。
为了加深对spring mvc的整个工作流程的理解,本文从分析DispatcherServlet的工作过程来一窥spring mvc的整个面貌。
1. 初始化
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context); //文件上传解析,如果请求类型是multipart将通过MultipartResolver进行文件上传解析;
initLocaleResolver(context); //本地化解析
initThemeResolver(context); //主题解析
initHandlerMappings(context); //通过HandlerMapping,将请求映射到处理器
initHandlerAdapters(context); //通过HandlerAdapter支持多种类型的处理器
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); //如果执行过程中遇到异常将交给HandlerExceptionResolver来解析
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); //直接解析请求到视图名
initViewResolvers(context); //通过ViewResolver解析逻辑视图名到具体视图实现
initFlashMapManager(context); //flash映射管理器
}
单个resolver
initMultipartResolver,initLocaleResolver,initThemeResolver,initRequestToViewNameTranslator,initFlashMapManager 这五个初始化方法流程相同,都是使用
context.getBean(String name, Class<FlashMapManager> requiredType)的方式获取到相应的Resolver。以initMultipartResolver为例,见如下:
/** * Initialize the MultipartResolver used by this class. * <p>If no bean is defined with the given name in the BeanFactory for this namespace, * no multipart handling is provided. */ private void initMultipartResolver(ApplicationContext context) { try { this.multipartResolver = context.getBean(MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, MultipartResolver.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Using MultipartResolver [" + this.multipartResolver + "]"); } } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // Default is no multipart resolver. this.multipartResolver = null; if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Unable to locate MultipartResolver with name '" + MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME + "': no multipart request handling provided"); } } }
多个resolver
initHandlerMappings,initHandlerAdapters,initHandlerExceptionResolvers,initViewResolvers 获取方式相同,使用:
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(ListableBeanFactory lbf, Class<HandlerMapping> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit)
的方式获取到相应的Resolver。以initHandlerMappings为例,见如下:
/** * Initialize the HandlerMappings used by this class. * <p>If no HandlerMapping beans are defined in the BeanFactory for this namespace, * we default to BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping. */ private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) { this.handlerMappings = null; if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) { // Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts. Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false); if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<HandlerMapping>(matchingBeans.values()); // We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order. OrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings); } } else { try { HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class); this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later. } } // Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering // a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found. if (this.handlerMappings == null) { this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("No HandlerMappings found in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default"); } } }
那么深入看一下BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors 究竟做了什么?返回指定类型和子类型的所有bean,若该bean factory 是一个继承类型的beanFactory,这个方法也会获取祖宗factory中定义的指定类型的bean。
/** * Return all beans of the given type or subtypes, also picking up beans defined in * ancestor bean factories if the current bean factory is a HierarchicalBeanFactory. * The returned Map will only contain beans of this type. * <p>Does consider objects created by FactoryBeans if the "allowEagerInit" flag is set, * which means that FactoryBeans will get initialized. If the object created by the * FactoryBean doesn't match, the raw FactoryBean itself will be matched against the * type. If "allowEagerInit" is not set, only raw FactoryBeans will be checked * (which doesn't require initialization of each FactoryBean). * <p><b>Note: Beans of the same name will take precedence at the 'lowest' factory level, * i.e. such beans will be returned from the lowest factory that they are being found in, * hiding corresponding beans in ancestor factories.</b> This feature allows for * 'replacing' beans by explicitly choosing the same bean name in a child factory; * the bean in the ancestor factory won't be visible then, not even for by-type lookups. * @param lbf the bean factory * @param type type of bean to match * @param includeNonSingletons whether to include prototype or scoped beans too * or just singletons (also applies to FactoryBeans) * @param allowEagerInit whether to initialize <i>lazy-init singletons</i> and * <i>objects created by FactoryBeans</i> (or by factory methods with a * "factory-bean" reference) for the type check. Note that FactoryBeans need to be * eagerly initialized to determine their type: So be aware that passing in "true" * for this flag will initialize FactoryBeans and "factory-bean" references. * @return the Map of matching bean instances, or an empty Map if none * @throws BeansException if a bean could not be created */ public static <T> Map<String, T> beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors( ListableBeanFactory lbf, Class<T> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit) throws BeansException { Assert.notNull(lbf, "ListableBeanFactory must not be null"); Map<String, T> result = new LinkedHashMap<String, T>(4); result.putAll(lbf.getBeansOfType(type, includeNonSingletons, allowEagerInit)); if (lbf instanceof HierarchicalBeanFactory) { HierarchicalBeanFactory hbf = (HierarchicalBeanFactory) lbf; if (hbf.getParentBeanFactory() instanceof ListableBeanFactory) { Map<String, T> parentResult = beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors( (ListableBeanFactory) hbf.getParentBeanFactory(), type, includeNonSingletons, allowEagerInit); for (Map.Entry<String, T> entry : parentResult.entrySet()) { String beanName = entry.getKey(); if (!result.containsKey(beanName) && !hbf.containsLocalBean(beanName)) { result.put(beanName, entry.getValue()); } } } } return result; }
2. 提供服务
我们来看看这个servlet是如何提供服务的?
@Override protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : ""; logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'" + resumed + " processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]"); } // Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include, // to be able to restore the original attributes after the include. Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null; if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) { attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<String, Object>(); Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames(); while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) { String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement(); if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith("org.springframework.web.servlet")) { attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName)); } } } // Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects. request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext()); request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource()); FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response); if (inputFlashMap != null) { request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap)); } request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap()); request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager); try { doDispatch(request, response); } finally { if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } // Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include. if (attributesSnapshot != null) { restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot); } } }
从上面我们可以看到,提供服务只要分4步:
1. 保存现场。保存request 熟悉的快照,以便能在必要时恢复。
2. 将框架需要的对象放入request中,以便view和handler使用。
3. 请求分发服务.
4. 恢复现场。
其中最重要的是请求分发服务:
/** * Process the actual dispatching to the handler. * <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order. * The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters * to find the first that supports the handler class. * <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers * themselves to decide which methods are acceptable. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure */ protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; Exception dispatchException = null; try { processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // Determine handler for the current request. mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // Determine handler adapter for the current request. HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified); } if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } try { // Actually invoke the handler. mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } } applyDefaultViewName(request, mv); mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Error err) { triggerAfterCompletionWithError(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, err); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); return; } // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } }
分发过程如下:
1. 判断是否设置了multipart resolver,设置的话转换为multipart request,没有的话则继续下面的步骤。
2. 根据当前request,获取hangdler。
3. 根据当前request,获取HandlerAdapter。
4. 如果支持http请求头,处理 last-modified header请求头。
5. 应用已注册interceptor的preHandle方法
6. HandlerAdapter处理请求。
7. 设置默认视图。
8. 应用已注册interceptor的postHandle方法。
9. 处理异常或者视图渲染。
小结:
DispatherServlet整个过程的细节一章之内很难描述的面面俱到,只能分析部分流程,想了解更具体的实现需要从源代码中去寻找。

微信公众号: 架构师日常笔记 欢迎关注!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号