上一章<windows下flink示例程序的执行> 简单介绍了一下flink在windows下如何通过flink-webui运行已经打包完成的示例程序(jar),那么我们为什么要使用flink呢?
flink的特征
官网给出的特征如下:
1、一切皆为流(All streaming use cases )
- 事件驱动应用(Event-driven Applications)
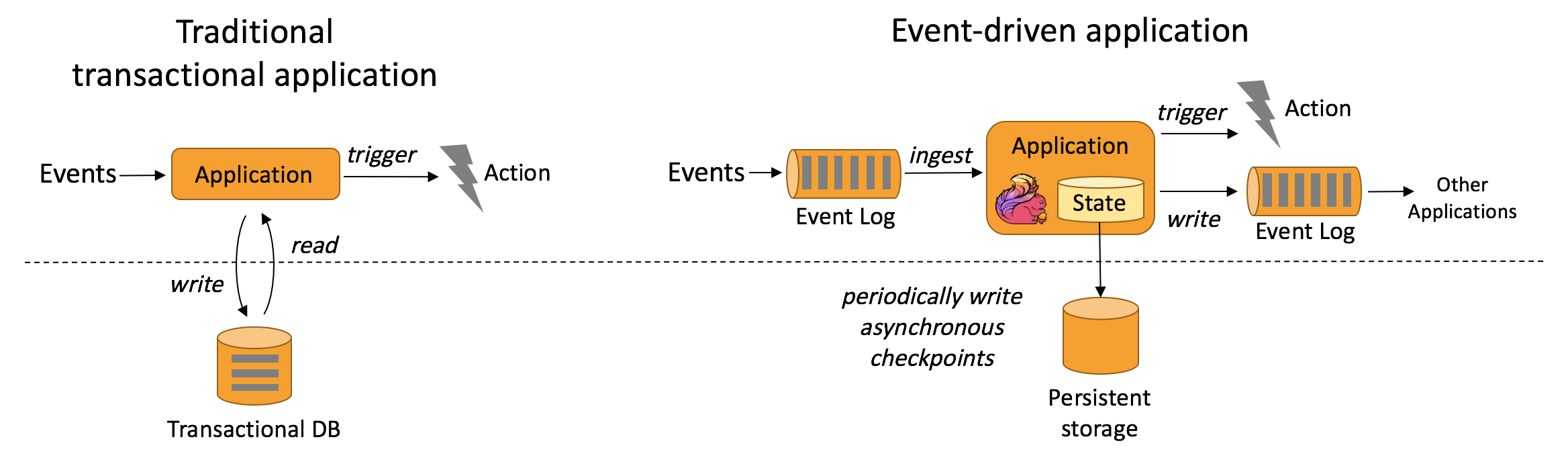
- 流式 & 批量分析(Stream & Batch Analytics)

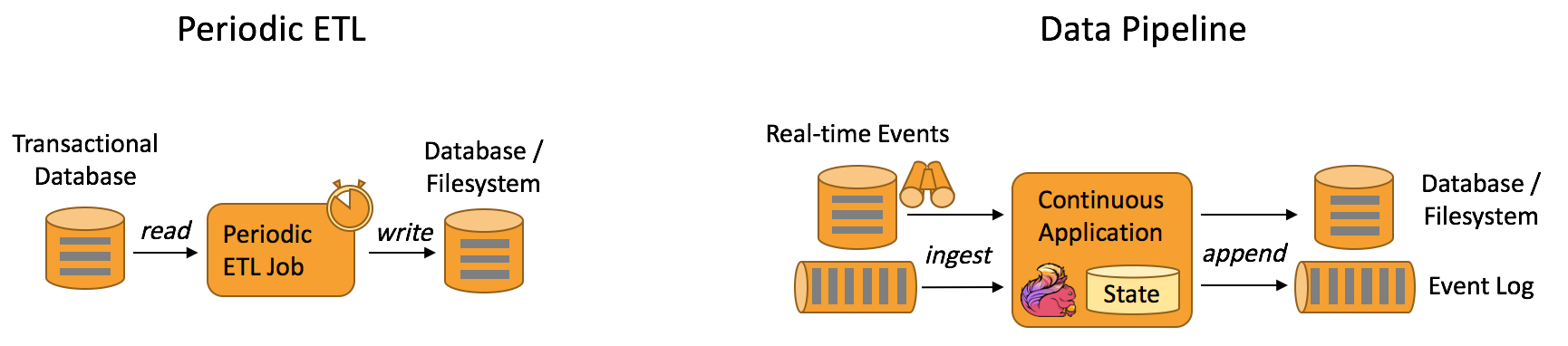
- 数据管道&ETL(Data Pipelines & ETL)
2、正确性保证(Guaranteed correctness)
- 唯一状态一致性(Exactly-once state consistency)
- 事件-事件处理(Event-time processing)
- 高超的最近数据处理(Sophisticated late data handling)
3、多层api(Layered APIs)
- 基于流式和批量数据处理的SQL(SQL on Stream & Batch Data)
- 流水数据API & 数据集API(DataStream API & DataSet API)
- 处理函数 (时间 & 状态)(ProcessFunction (Time & State))

4、易用性
- 部署灵活(Flexible deployment)
- 高可用安装(High-availability setup)
- 保存点(Savepoints)
5、可扩展性
- 可扩展架构(Scale-out architecture)
- 大量状态的支持(Support for very large state)
- 增量检查点(Incremental checkpointing)
6、高性能
- 低延迟(Low latency)
- 高吞吐量(High throughput)
- 内存计算(In-Memory computing)
flink架构
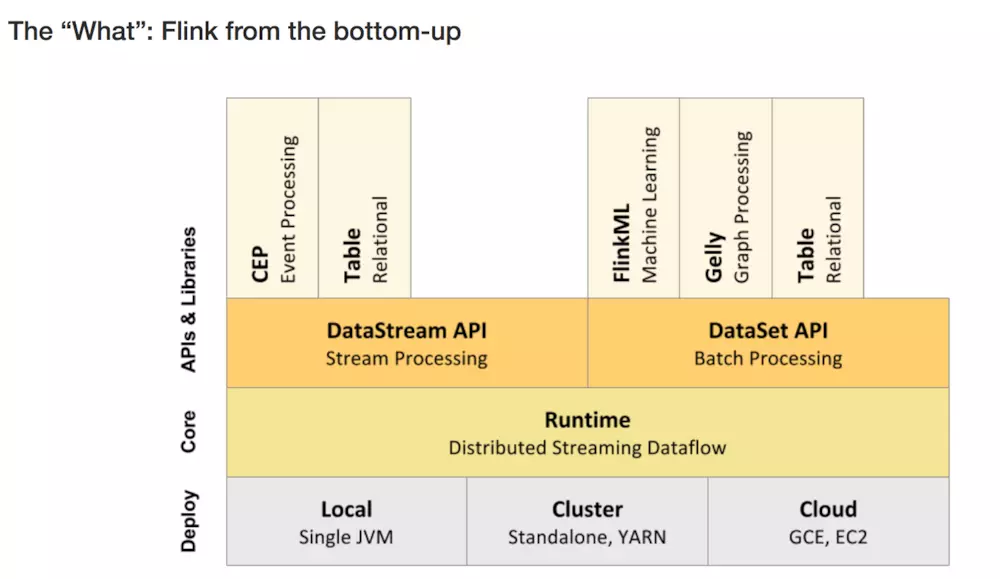
1、层级结构
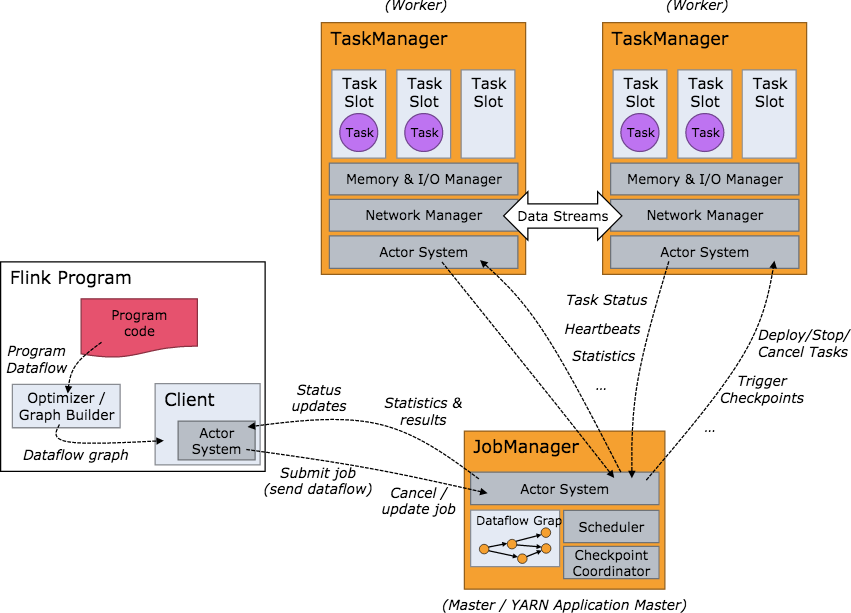
2.工作架构图
flink实战
1、依赖文件pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>flinkDemo</groupId> <artifactId>flinkDemo</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId> <artifactId>flink-java</artifactId> <version>1.5.0</version> <!--<scope>provided</scope>--> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId> <artifactId>flink-streaming-java_2.11</artifactId> <version>1.5.0</version> <!--<scope>provided</scope>--> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.flink/flink-connector-kafka-0.10 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId> <artifactId>flink-connector-kafka-0.10_2.11</artifactId> <version>1.5.0</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.flink/flink-hbase --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId> <artifactId>flink-hbase_2.11</artifactId> <version>1.5.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId> <artifactId>kafka-clients</artifactId> <version>0.10.1.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId> <artifactId>hbase-client</artifactId> <version>1.1.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <version>1.16.10</version> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.google.code.gson</groupId> <artifactId>gson</artifactId> <version>2.8.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.github.rholder</groupId> <artifactId>guava-retrying</artifactId> <version>2.0.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.5.1</version> <configuration> <source>1.8</source> <target>1.8</target> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
2、java程序
public class WordCountDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { final ParameterTool params = ParameterTool.fromArgs(args); // create execution environment final ExecutionEnvironment env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); env.getConfig().setGlobalJobParameters(params); // get input data DataSet<String> text; if (params.has("input")) { // read the text file from given input path text = env.readTextFile(params.get("input")); } else { // get default test text data System.out.println("Executing WordCount example with default input data set."); System.out.println("Use --input to specify file input."); text = WordCountData.getDefaultTextLineDataSet(env); } DataSet<Tuple2<String, Integer>> counts = // split up the lines in pairs (2-tuples) containing: (word,1) text.flatMap(new Tokenizer()) // group by the tuple field "0" and sum up tuple field "1" .groupBy(0) .sum(1); // emit result if (params.has("output")) { counts.writeAsCsv(params.get("output"), "\n", " "); // execute program env.execute("WordCount Example"); } else { System.out.println("Printing result to stdout. Use --output to specify output path."); counts.print(); } } // ************************************************************************* // USER FUNCTIONS // ************************************************************************* /** * Implements the string tokenizer that splits sentences into words as a user-defined * FlatMapFunction. The function takes a line (String) and splits it into * multiple pairs in the form of "(word,1)" ({@code Tuple2<String, Integer>}). */ public static final class Tokenizer implements FlatMapFunction<String, Tuple2<String, Integer>> { @Override public void flatMap(String value, Collector<Tuple2<String, Integer>> out) { // normalize and split the line String[] tokens = value.toLowerCase().split("\\W+"); // emit the pairs for (String token : tokens) { if (token.length() > 0) { out.collect(new Tuple2<>(token, 1)); } } } } }
3、单步调试分析
第一步:获取环境信息ExecutionEnvironment.java
/** * The ExecutionEnvironment is the context in which a program is executed. A * {@link LocalEnvironment} will cause execution in the current JVM, a * {@link RemoteEnvironment} will cause execution on a remote setup. * * <p>The environment provides methods to control the job execution (such as setting the parallelism) * and to interact with the outside world (data access). * * <p>Please note that the execution environment needs strong type information for the input and return types * of all operations that are executed. This means that the environments needs to know that the return * value of an operation is for example a Tuple of String and Integer. * Because the Java compiler throws much of the generic type information away, most methods attempt to re- * obtain that information using reflection. In certain cases, it may be necessary to manually supply that * information to some of the methods. * * @see LocalEnvironment * @see RemoteEnvironment */
创建本地环境
/** * Creates a {@link LocalEnvironment} which is used for executing Flink jobs. * * @param configuration to start the {@link LocalEnvironment} with * @param defaultParallelism to initialize the {@link LocalEnvironment} with * @return {@link LocalEnvironment} */ private static LocalEnvironment createLocalEnvironment(Configuration configuration, int defaultParallelism) { final LocalEnvironment localEnvironment = new LocalEnvironment(configuration); if (defaultParallelism > 0) { localEnvironment.setParallelism(defaultParallelism); } return localEnvironment; }
第二步:获取外部数据,创建数据集 ExecutionEnvironment.java
/** * Creates a DataSet from the given non-empty collection. Note that this operation will result * in a non-parallel data source, i.e. a data source with a parallelism of one. * * <p>The returned DataSet is typed to the given TypeInformation. * * @param data The collection of elements to create the data set from. * @param type The TypeInformation for the produced data set. * @return A DataSet representing the given collection. * * @see #fromCollection(Collection) */ public <X> DataSource<X> fromCollection(Collection<X> data, TypeInformation<X> type) { return fromCollection(data, type, Utils.getCallLocationName()); } private <X> DataSource<X> fromCollection(Collection<X> data, TypeInformation<X> type, String callLocationName) { CollectionInputFormat.checkCollection(data, type.getTypeClass()); return new DataSource<>(this, new CollectionInputFormat<>(data, type.createSerializer(config)), type, callLocationName); }
数据集的继承关系
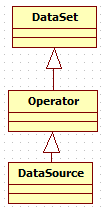
其中,DataSet是一组相同类型数据的集合,抽象类,它提供了数据的转换功能,如map,reduce,join和coGroup
/** * A DataSet represents a collection of elements of the same type. * * <p>A DataSet can be transformed into another DataSet by applying a transformation as for example * <ul> * <li>{@link DataSet#map(org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.MapFunction)},</li> * <li>{@link DataSet#reduce(org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.ReduceFunction)},</li> * <li>{@link DataSet#join(DataSet)}, or</li> * <li>{@link DataSet#coGroup(DataSet)}.</li> * </ul> * * @param <T> The type of the DataSet, i.e., the type of the elements of the DataSet. */
Operator是java api的操作基类,抽象类
/** * Base class of all operators in the Java API. * * @param <OUT> The type of the data set produced by this operator. * @param <O> The type of the operator, so that we can return it. */ @Public public abstract class Operator<OUT, O extends Operator<OUT, O>> extends DataSet<OUT> {
DataSource具体实现类。
/** * An operation that creates a new data set (data source). The operation acts as the * data set on which to apply further transformations. It encapsulates additional * configuration parameters, to customize the execution. * * @param <OUT> The type of the elements produced by this data source. */ @Public public class DataSource<OUT> extends Operator<OUT, DataSource<OUT>> {
第三步:对输入数据集进行转换
DataSet<Tuple2<String, Integer>> counts =
// split up the lines in pairs (2-tuples) containing: (word,1)
text.flatMap(new Tokenizer())
// group by the tuple field "0" and sum up tuple field "1"
.groupBy(0)
.sum(1);
>>调用map DataSet.java
/** * Applies a FlatMap transformation on a {@link DataSet}. * * <p>The transformation calls a {@link org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.RichFlatMapFunction} for each element of the DataSet. * Each FlatMapFunction call can return any number of elements including none. * * @param flatMapper The FlatMapFunction that is called for each element of the DataSet. * @return A FlatMapOperator that represents the transformed DataSet. * * @see org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.RichFlatMapFunction * @see FlatMapOperator * @see DataSet */ public <R> FlatMapOperator<T, R> flatMap(FlatMapFunction<T, R> flatMapper) { if (flatMapper == null) { throw new NullPointerException("FlatMap function must not be null."); } String callLocation = Utils.getCallLocationName(); TypeInformation<R> resultType = TypeExtractor.getFlatMapReturnTypes(flatMapper, getType(), callLocation, true); return new FlatMapOperator<>(this, resultType, clean(flatMapper), callLocation); }
>>调用groupby DataSet.java
/** * Groups a {@link Tuple} {@link DataSet} using field position keys. * * <p><b>Note: Field position keys only be specified for Tuple DataSets.</b> * * <p>The field position keys specify the fields of Tuples on which the DataSet is grouped. * This method returns an {@link UnsortedGrouping} on which one of the following grouping transformation * can be applied. * <ul> * <li>{@link UnsortedGrouping#sortGroup(int, org.apache.flink.api.common.operators.Order)} to get a {@link SortedGrouping}. * <li>{@link UnsortedGrouping#aggregate(Aggregations, int)} to apply an Aggregate transformation. * <li>{@link UnsortedGrouping#reduce(org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.ReduceFunction)} to apply a Reduce transformation. * <li>{@link UnsortedGrouping#reduceGroup(org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.GroupReduceFunction)} to apply a GroupReduce transformation. * </ul> * * @param fields One or more field positions on which the DataSet will be grouped. * @return A Grouping on which a transformation needs to be applied to obtain a transformed DataSet. * * @see Tuple * @see UnsortedGrouping * @see AggregateOperator * @see ReduceOperator * @see org.apache.flink.api.java.operators.GroupReduceOperator * @see DataSet */ public UnsortedGrouping<T> groupBy(int... fields) { return new UnsortedGrouping<>(this, new Keys.ExpressionKeys<>(fields, getType())); }
>>调用sum UnsortedGrouping.java
/** * Syntactic sugar for aggregate (SUM, field). * @param field The index of the Tuple field on which the aggregation function is applied. * @return An AggregateOperator that represents the summed DataSet. * * @see org.apache.flink.api.java.operators.AggregateOperator */ public AggregateOperator<T> sum (int field) { return this.aggregate (Aggregations.SUM, field, Utils.getCallLocationName()); } // private helper that allows to set a different call location name private AggregateOperator<T> aggregate(Aggregations agg, int field, String callLocationName) { return new AggregateOperator<T>(this, agg, field, callLocationName); }
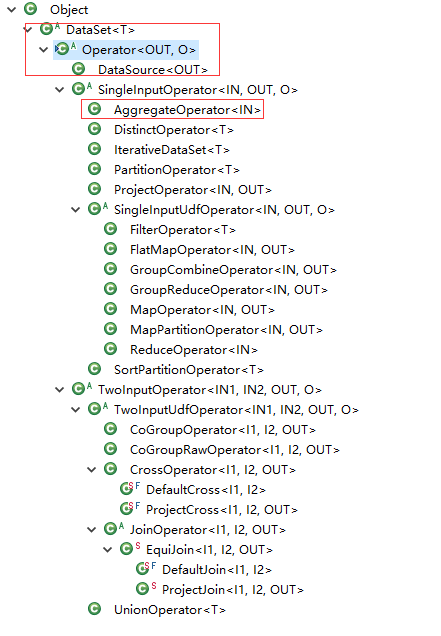
UnsortedGrouping和DataSet的关系
UnsortedGrouping使用AggregateOperator做聚合
第四步:对转换的输入值进行处理
// emit result if (params.has("output")) { counts.writeAsCsv(params.get("output"), "\n", " "); // execute program env.execute("WordCount Example"); } else { System.out.println("Printing result to stdout. Use --output to specify output path."); counts.print(); }
如果不指定output参数,则打印到控制台
/** * Prints the elements in a DataSet to the standard output stream {@link System#out} of the JVM that calls * the print() method. For programs that are executed in a cluster, this method needs * to gather the contents of the DataSet back to the client, to print it there. * * <p>The string written for each element is defined by the {@link Object#toString()} method. * * <p>This method immediately triggers the program execution, similar to the * {@link #collect()} and {@link #count()} methods. * * @see #printToErr() * @see #printOnTaskManager(String) */ public void print() throws Exception { List<T> elements = collect(); for (T e: elements) { System.out.println(e); } }
若指定输出,则先进行输入转换为csv文件的DataSink,它是用来存储数据结果的
/** * An operation that allows storing data results. * @param <T> */
过程如下:
/** * Writes a {@link Tuple} DataSet as CSV file(s) to the specified location with the specified field and line delimiters. * * <p><b>Note: Only a Tuple DataSet can written as a CSV file.</b> * For each Tuple field the result of {@link Object#toString()} is written. * * @param filePath The path pointing to the location the CSV file is written to. * @param rowDelimiter The row delimiter to separate Tuples. * @param fieldDelimiter The field delimiter to separate Tuple fields. * @param writeMode The behavior regarding existing files. Options are NO_OVERWRITE and OVERWRITE. * * @see Tuple * @see CsvOutputFormat * @see DataSet#writeAsText(String) Output files and directories */ public DataSink<T> writeAsCsv(String filePath, String rowDelimiter, String fieldDelimiter, WriteMode writeMode) { return internalWriteAsCsv(new Path(filePath), rowDelimiter, fieldDelimiter, writeMode); } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private <X extends Tuple> DataSink<T> internalWriteAsCsv(Path filePath, String rowDelimiter, String fieldDelimiter, WriteMode wm) { Preconditions.checkArgument(getType().isTupleType(), "The writeAsCsv() method can only be used on data sets of tuples."); CsvOutputFormat<X> of = new CsvOutputFormat<>(filePath, rowDelimiter, fieldDelimiter); if (wm != null) { of.setWriteMode(wm); } return output((OutputFormat<T>) of); } /** * Emits a DataSet using an {@link OutputFormat}. This method adds a data sink to the program. * Programs may have multiple data sinks. A DataSet may also have multiple consumers (data sinks * or transformations) at the same time. * * @param outputFormat The OutputFormat to process the DataSet. * @return The DataSink that processes the DataSet. * * @see OutputFormat * @see DataSink */ public DataSink<T> output(OutputFormat<T> outputFormat) { Preconditions.checkNotNull(outputFormat); // configure the type if needed if (outputFormat instanceof InputTypeConfigurable) { ((InputTypeConfigurable) outputFormat).setInputType(getType(), context.getConfig()); } DataSink<T> sink = new DataSink<>(this, outputFormat, getType()); this.context.registerDataSink(sink); return sink; }
最后执行job
@Override public JobExecutionResult execute(String jobName) throws Exception { if (executor == null) { startNewSession(); } Plan p = createProgramPlan(jobName); // Session management is disabled, revert this commit to enable //p.setJobId(jobID); //p.setSessionTimeout(sessionTimeout); JobExecutionResult result = executor.executePlan(p); this.lastJobExecutionResult = result; return result; }
这一阶段是内容比较多,放到下一篇讲解吧
总结
Apache Flink 功能强大,支持开发和运行多种不同种类的应用程序。它的主要特性包括:批流一体化、精密的状态管理、事件时间支持以及精确一次的状态一致性保障等。Flink 不仅可以运行在包括 YARN、 Mesos、Kubernetes 在内的多种资源管理框架上,还支持在裸机集群上独立部署。在启用高可用选项的情况下,它不存在单点失效问题。事实证明,Flink 已经可以扩展到数千核心,其状态可以达到 TB 级别,且仍能保持高吞吐、低延迟的特性。世界各地有很多要求严苛的流处理应用都运行在 Flink 之上。
其应用场景如下:
1、事件驱动型应用
典型的事件驱动型应用实例:
反欺诈
异常检测
基于规则的报警
业务流程监控
(社交网络)Web 应用
2、数据分析应用
典型的数据分析应用实例
电信网络质量监控
移动应用中的产品更新及实验评估分析
消费者技术中的实时数据即席分析
大规模图分析
3、数据管道应用
典型的数据管道应用实例
电子商务中的实时查询索引构建
电子商务中的持续 ETL
参考资料
【2】https://blog.csdn.net/yangyin007/article/details/82382734
【3】https://flink.apache.org/zh/usecases.html

微信公众号: 架构师日常笔记 欢迎关注!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号