1. Spring WebFlux是什么?
Spring WebFlux是Spring Framework 5.0中引入的新的反应式Web框架。 与Spring MVC不同,它不需要Servlet API,完全异步和非阻塞, 并通过Reactor项目实现Reactive Streams规范。 并且可以在诸如Netty,Undertow和Servlet 3.1+容器的服务器上运行。
Reactor 也是 Spring 5 中反应式编程的基础,它一个新的反应式编程库。
2. Reactor是什么?
Reactor offers non-blocking and backpressure-ready network runtimes including local TCP/HTTP/UDP client & servers based on the robust Netty framework.
Reactor提供了一个非阻塞的,高并发的基于健壮的Netty框架的网络运行API,包括本地tcp/http/udp 客户端和服务端。
重要的两个概念
Flux 和 Mono 是 Reactor 中的两个基本概念。Flux 表示的是包含 0 到 N 个元素的异步序列。在该序列中可以包含三种不同类型的消息通知:正常的包含元素的消息、序列结束的消息和序列出错的消息。当消息通知产生时,订阅者中对应的方法 onNext(), onComplete()和 onError()会被调用。Mono 表示的是包含 0 或者 1 个元素的异步序列。该序列中同样可以包含与 Flux 相同的三种类型的消息通知。Flux 和 Mono 之间可以进行转换。对一个 Flux 序列进行计数操作,得到的结果是一个 Mono<Long>对象。把两个 Mono 序列合并在一起,得到的是一个 Flux 对象。
简单说Mono返回单个元素,Flux返回多个元素
3. spring webflux处理请求流程
核心控制器DispatcherHandler,等同于阻塞方式的DispatcherServlet
/** * Central dispatcher for HTTP request handlers/controllers. Dispatches to * registered handlers for processing a request, providing convenient mapping * facilities. * * <p>{@code DispatcherHandler} discovers the delegate components it needs from * Spring configuration. It detects the following in the application context: * <ul> * <li>{@link HandlerMapping} -- map requests to handler objects * <li>{@link HandlerAdapter} -- for using any handler interface * <li>{@link HandlerResultHandler} -- process handler return values * </ul> * * <p>{@code DispatcherHandler} is also designed to be a Spring bean itself and * implements {@link ApplicationContextAware} for access to the context it runs * in. If {@code DispatcherHandler} is declared with the bean name "webHandler" * it is discovered by {@link WebHttpHandlerBuilder#applicationContext} which * creates a processing chain together with {@code WebFilter}, * {@code WebExceptionHandler} and others. * * <p>A {@code DispatcherHandler} bean declaration is included in * {@link org.springframework.web.reactive.config.EnableWebFlux @EnableWebFlux} * configuration. * * @author Rossen Stoyanchev * @author Sebastien Deleuze * @author Juergen Hoeller * @since 5.0 * @see WebHttpHandlerBuilder#applicationContext(ApplicationContext) */
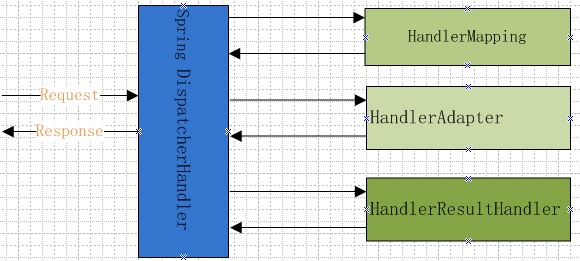
3.1 初始化
获取HandlerMapping,HandlerAdapter,HandlerResultHandler的所有实例
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { Map<String, HandlerMapping> mappingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors( context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false); //1 ArrayList<HandlerMapping> mappings = new ArrayList<>(mappingBeans.values()); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(mappings); this.handlerMappings = Collections.unmodifiableList(mappings); Map<String, HandlerAdapter> adapterBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors( context, HandlerAdapter.class, true, false); //2 this.handlerAdapters = new ArrayList<>(adapterBeans.values()); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerAdapters); Map<String, HandlerResultHandler> beans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors( context, HandlerResultHandler.class, true, false); //3 this.resultHandlers = new ArrayList<>(beans.values()); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.resultHandlers); }
其中,1.获取所有HandlerMapping实例
2.获取所有HandlerAdapter实例
3.获取所有HandlerResultHandler实例
3.2 流式处理请求
public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) { if (this.handlerMappings == null) { return createNotFoundError(); } return Flux.fromIterable(this.handlerMappings) .concatMap(mapping -> mapping.getHandler(exchange))//1 .next() .switchIfEmpty(createNotFoundError())//2 .flatMap(handler -> invokeHandler(exchange, handler))//3 .flatMap(result -> handleResult(exchange, result));//4 }
其中,第一步,从handlerMapping这个map中获取HandlerMapping
第二步,触发HandlerApter的handle方法
private Mono<HandlerResult> invokeHandler(ServerWebExchange exchange, Object handler) { if (this.handlerAdapters != null) { for (HandlerAdapter handlerAdapter : this.handlerAdapters) { if (handlerAdapter.supports(handler)) { return handlerAdapter.handle(exchange, handler); } } } return Mono.error(new IllegalStateException("No HandlerAdapter: " + handler)); }
第三步,触发HandlerResultHandler 的handleResult方法
private Mono<Void> handleResult(ServerWebExchange exchange, HandlerResult result) { return getResultHandler(result).handleResult(exchange, result) .onErrorResume(ex -> result.applyExceptionHandler(ex).flatMap(exceptionResult -> getResultHandler(exceptionResult).handleResult(exchange, exceptionResult))); } private HandlerResultHandler getResultHandler(HandlerResult handlerResult) { if (this.resultHandlers != null) { for (HandlerResultHandler resultHandler : this.resultHandlers) { if (resultHandler.supports(handlerResult)) { return resultHandler; } } } throw new IllegalStateException("No HandlerResultHandler for " + handlerResult.getReturnValue()); }
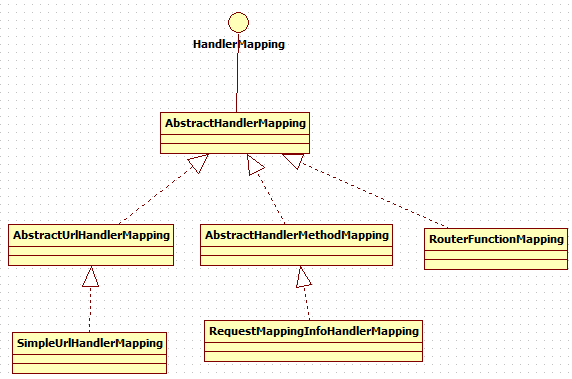
4.HandlerMapping实现
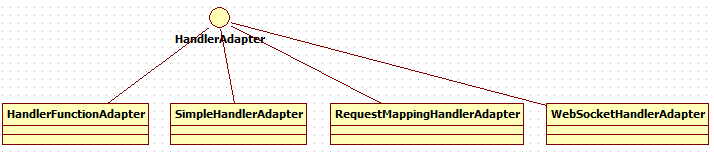
5.HanlderAdapter的实现
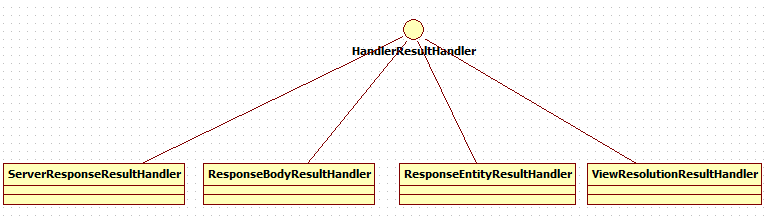
6.HandlerResultHandler的实现
7.不同容器的实现
7.1 Reactor实现ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter
执行apply方法
@Override public Mono<Void> apply(HttpServerRequest reactorRequest, HttpServerResponse reactorResponse) { NettyDataBufferFactory bufferFactory = new NettyDataBufferFactory(reactorResponse.alloc()); try { ReactorServerHttpRequest request = new ReactorServerHttpRequest(reactorRequest, bufferFactory); ServerHttpResponse response = new ReactorServerHttpResponse(reactorResponse, bufferFactory); if (request.getMethod() == HttpMethod.HEAD) { response = new HttpHeadResponseDecorator(response); } return this.httpHandler.handle(request, response) .doOnError(ex -> logger.trace(request.getLogPrefix() + "Failed to complete: " + ex.getMessage())) .doOnSuccess(aVoid -> logger.trace(request.getLogPrefix() + "Handling completed")); } catch (URISyntaxException ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Failed to get request URI: " + ex.getMessage()); } reactorResponse.status(HttpResponseStatus.BAD_REQUEST); return Mono.empty(); } }
其中,HttpHandler的定义
** * Lowest level contract for reactive HTTP request handling that serves as a * common denominator across different runtimes. * * <p>Higher-level, but still generic, building blocks for applications such as * {@code WebFilter}, {@code WebSession}, {@code ServerWebExchange}, and others * are available in the {@code org.springframework.web.server} package. * * <p>Application level programming models such as annotated controllers and * functional handlers are available in the {@code spring-webflux} module. * * <p>Typically an {@link HttpHandler} represents an entire application with * higher-level programming models bridged via * {@link org.springframework.web.server.adapter.WebHttpHandlerBuilder}. * Multiple applications at unique context paths can be plugged in with the * help of the {@link ContextPathCompositeHandler}. * * @author Arjen Poutsma * @author Rossen Stoyanchev * @since 5.0 * @see ContextPathCompositeHandler */
具体的实现类为:ContextPathCompositeHandler
/** * {@code HttpHandler} delegating requests to one of several {@code HttpHandler}'s * based on simple, prefix-based mappings. * * <p>This is intended as a coarse-grained mechanism for delegating requests to * one of several applications -- each represented by an {@code HttpHandler}, with * the application "context path" (the prefix-based mapping) exposed via * {@link ServerHttpRequest#getPath()}. * * @author Rossen Stoyanchev * @since 5.0 */ @Override public Mono<Void> handle(ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response) { // Remove underlying context path first (e.g. Servlet container) String path = request.getPath().pathWithinApplication().value(); return this.handlerMap.entrySet().stream() .filter(entry -> path.startsWith(entry.getKey())) .findFirst() .map(entry -> { String contextPath = request.getPath().contextPath().value() + entry.getKey(); ServerHttpRequest newRequest = request.mutate().contextPath(contextPath).build(); return entry.getValue().handle(newRequest, response); }) .orElseGet(() -> { response.setStatusCode(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND); return response.setComplete(); }); }
基于前缀的映射Handler
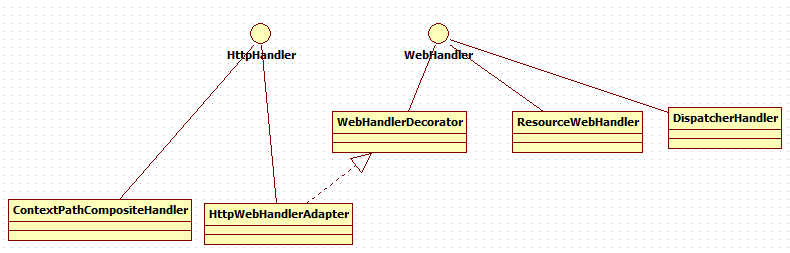
7.2 Jetty实现JettyHttpHandlerAdapter
继承自ServletHttpHandlerAdapter 实现了Servlet,执行service方法
@Override public void service(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // Check for existing error attribute first if (DispatcherType.ASYNC.equals(request.getDispatcherType())) { Throwable ex = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(WRITE_ERROR_ATTRIBUTE_NAME); throw new ServletException("Failed to create response content", ex); } // Start async before Read/WriteListener registration AsyncContext asyncContext = request.startAsync(); asyncContext.setTimeout(-1); ServletServerHttpRequest httpRequest; try { httpRequest = createRequest(((HttpServletRequest) request), asyncContext);//1 } catch (URISyntaxException ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Failed to get request URL: " + ex.getMessage()); } ((HttpServletResponse) response).setStatus(400); asyncContext.complete(); return; } ServerHttpResponse httpResponse = createResponse(((HttpServletResponse) response), asyncContext, httpRequest);//2 if (httpRequest.getMethod() == HttpMethod.HEAD) { httpResponse = new HttpHeadResponseDecorator(httpResponse); } AtomicBoolean isCompleted = new AtomicBoolean(); HandlerResultAsyncListener listener = new HandlerResultAsyncListener(isCompleted, httpRequest); asyncContext.addListener(listener); HandlerResultSubscriber subscriber = new HandlerResultSubscriber(asyncContext, isCompleted, httpRequest); this.httpHandler.handle(httpRequest, httpResponse).subscribe(subscriber);//3 }
其中,1.创建request
2.创建response
3.handler执行的结果进行subscribe
JettyHttpHandlerAdapter是ServletHttpHandlerAdapter 的扩展,重写了创建request 创建response方法
7.3 Tomcat实现TomcatHttpHandlerAdapter
TomcatHttpHandlerAdapter是ServletHttpHandlerAdapter 的扩展,重写了创建request 创建response方法
7.4 AbstractReactiveWebInitializer抽象类
继承自AbstractReactiveWebInitializer的类可以在servlet容器中安装一个Spring Reactive Web Application。
@Override public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException { String servletName = getServletName(); Assert.hasLength(servletName, "getServletName() must not return null or empty"); ApplicationContext applicationContext = createApplicationContext(); Assert.notNull(applicationContext, "createApplicationContext() must not return null"); refreshApplicationContext(applicationContext); registerCloseListener(servletContext, applicationContext); HttpHandler httpHandler = WebHttpHandlerBuilder.applicationContext(applicationContext).build(); ServletHttpHandlerAdapter servlet = new ServletHttpHandlerAdapter(httpHandler); ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletContext.addServlet(servletName, servlet); if (registration == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to register servlet with name '" + servletName + "'. " + "Check if there is another servlet registered under the same name."); } registration.setLoadOnStartup(1); registration.addMapping(getServletMapping()); registration.setAsyncSupported(true); }
它通过将ServletHttpHandlerAdapter实例作为一个servlet安装到servler容器中。
8.总结
DispatcherHandler的流程是
1.通过 HandlerMapping(和DispathcherServlet中的HandlerMapping不同)获取到HandlerAdapter放到ServerWebExchange的属性中
2.获取到HandlerAdapter后触发handle方法,得到HandlerResult
3.通过HandlerResult,触发handleResult,针对不同的返回类找到不同的HandlerResultHandler如
视图渲染ViewResolutionResultHandler,
ServerResponseResultHandler,
ResponseBodyResultHandler,
ResponseEntityResultHandler
不同容器有不同的实现,如Reactor,Jetty,Tomcat等。
参考文献:
【1】https://blog.csdn.net/qq_15144655/article/details/80708915
【2】https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-cn-with-reactor-response-encode/index.html

微信公众号: 架构师日常笔记 欢迎关注!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号