zuul 是netflix开源的一个API Gateway 服务器, 本质上是一个web servlet应用。
Zuul可以通过加载动态过滤机制,从而实现以下各项功能:
- 验证与安全保障: 识别面向各类资源的验证要求并拒绝那些与要求不符的请求。
- 审查与监控: 在边缘位置追踪有意义数据及统计结果,从而为我们带来准确的生产状态结论。
- 动态路由: 以动态方式根据需要将请求路由至不同后端集群处。
- 压力测试: 逐渐增加指向集群的负载流量,从而计算性能水平。
- 负载分配: 为每一种负载类型分配对应容量,并弃用超出限定值的请求。
- 静态响应处理: 在边缘位置直接建立部分响应,从而避免其流入内部集群。
- 多区域弹性: 跨越AWS区域进行请求路由,旨在实现ELB使用多样化并保证边缘位置与使用者尽可能接近。
网关zuul从1.0到2.0 经历了较大的变化,先从架构上看看吧
zuul 1.0的架构
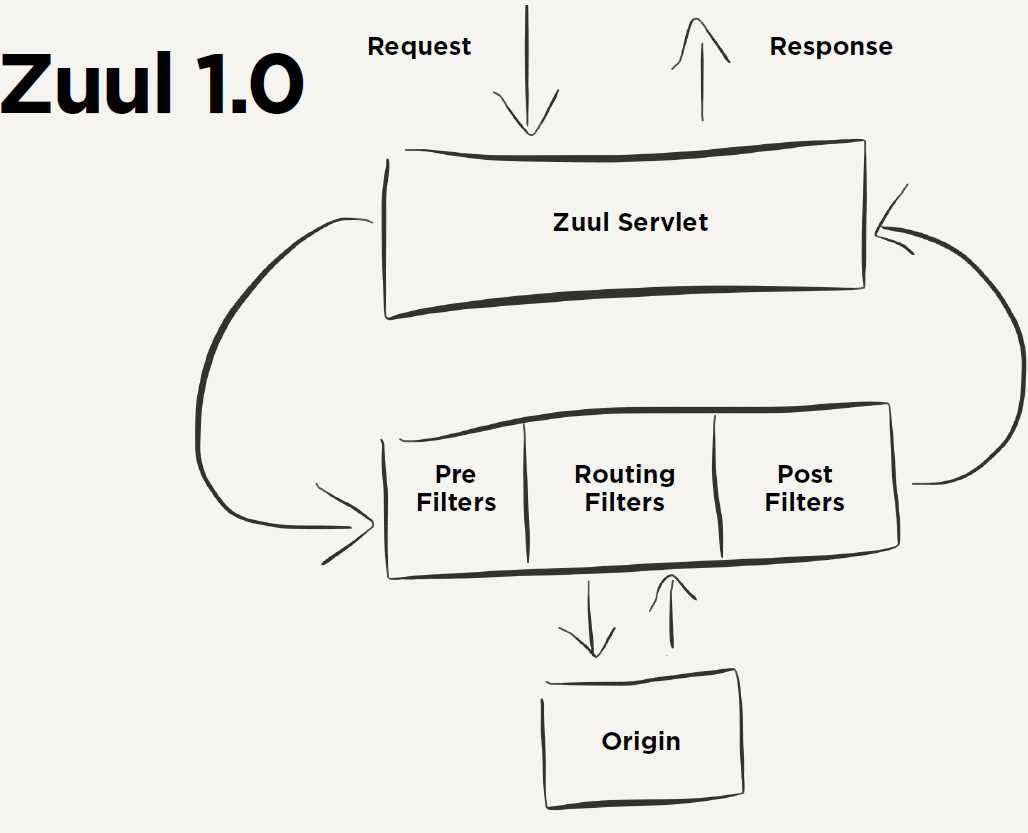
从上图看,
1.ZuulServlet负责接收请求,对filter进行处理
/** * Core Zuul servlet which intializes and orchestrates zuulFilter execution * * @author Mikey Cohen * Date: 12/23/11 * Time: 10:44 AM */ @Override public void service(javax.servlet.ServletRequest servletRequest, javax.servlet.ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException { try { init((HttpServletRequest) servletRequest, (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse); // Marks this request as having passed through the "Zuul engine", as opposed to servlets // explicitly bound in web.xml, for which requests will not have the same data attached RequestContext context = RequestContext.getCurrentContext(); context.setZuulEngineRan(); try { preRoute(); } catch (ZuulException e) { error(e); postRoute(); return; } try { route(); } catch (ZuulException e) { error(e); postRoute(); return; } try { postRoute(); } catch (ZuulException e) { error(e); return; } } catch (Throwable e) { error(new ZuulException(e, 500, "UNHANDLED_EXCEPTION_" + e.getClass().getName())); } finally { RequestContext.getCurrentContext().unset(); } }
其中
FilterProcessor处理核心类
前置filter
runFilters("pre"); //前置filter类型
跳转filter
runFilters("route");
后置filter
runFilters("post");
2. zuul的核心是一系列的filters, 其作用可以类比Servlet框架的Filter,或者AOP。工作原理如下图所示
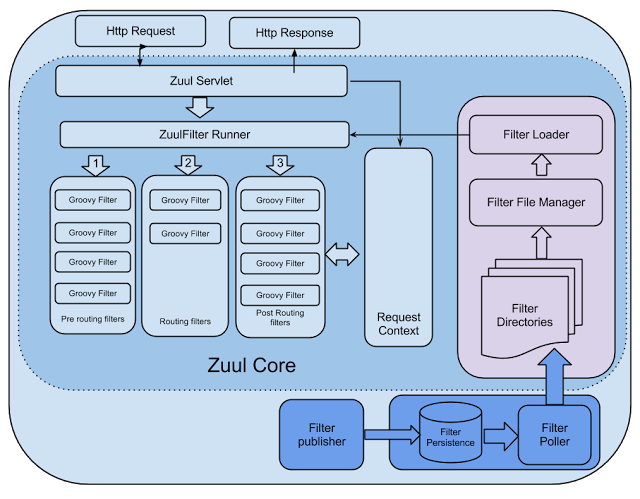
Zuul可以对Groovy过滤器进行动态的加载,编译,运行。FilterFileManager.java
/** * This class manages the directory polling for changes and new Groovy filters. * Polling interval and directories are specified in the initialization of the class, and a poller will check * for changes and additions. * * @author Mikey Cohen * Date: 12/7/11 * Time: 12:09 PM */ void processGroovyFiles(List<File> aFiles) throws Exception { List<Callable<Boolean>> tasks = new ArrayList<>(); for (File file : aFiles) { tasks.add(() -> { try { return filterLoader.putFilter(file); } catch(Exception e) { LOG.error("Error loading groovy filter from disk! file = " + String.valueOf(file), e); return false; } }); } processFilesService.invokeAll(tasks, FILE_PROCESSOR_TASKS_TIMEOUT_SECS.get(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); }
3.对groovy文件的动态操作管理类FilterScriptManagerServlet
/** * Servlet for uploading/downloading/managing scripts. * <p/> * <ul> * <li>Upload scripts to the registry for a given endpoint.</li> * <li>Download scripts from the registry</li> * <li>List all revisions of scripts for a given endpoint.</li> * <li>Mark a particular script revision as active for production.</li> * </ul> */ @Override protected void doPut(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { if (!adminEnabled.get()) { response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_FORBIDDEN, "Filter admin is disabled. See the zuul.filters.admin.enabled FastProperty."); return; } // retrieve arguments and validate String action = request.getParameter("action"); /* validate the action and method */ if (!isValidAction(request, response)) { return; } // perform action if ("UPLOAD".equals(action)) { handleUploadAction(request, response); } else if ("ACTIVATE".equals(action)) { handleActivateAction(request, response); } else if ("CANARY".equals(action)) { handleCanaryAction(request, response); } else if ("DEACTIVATE".equals(action)) { handledeActivateAction(request, response); } }
zuul 2.0架构
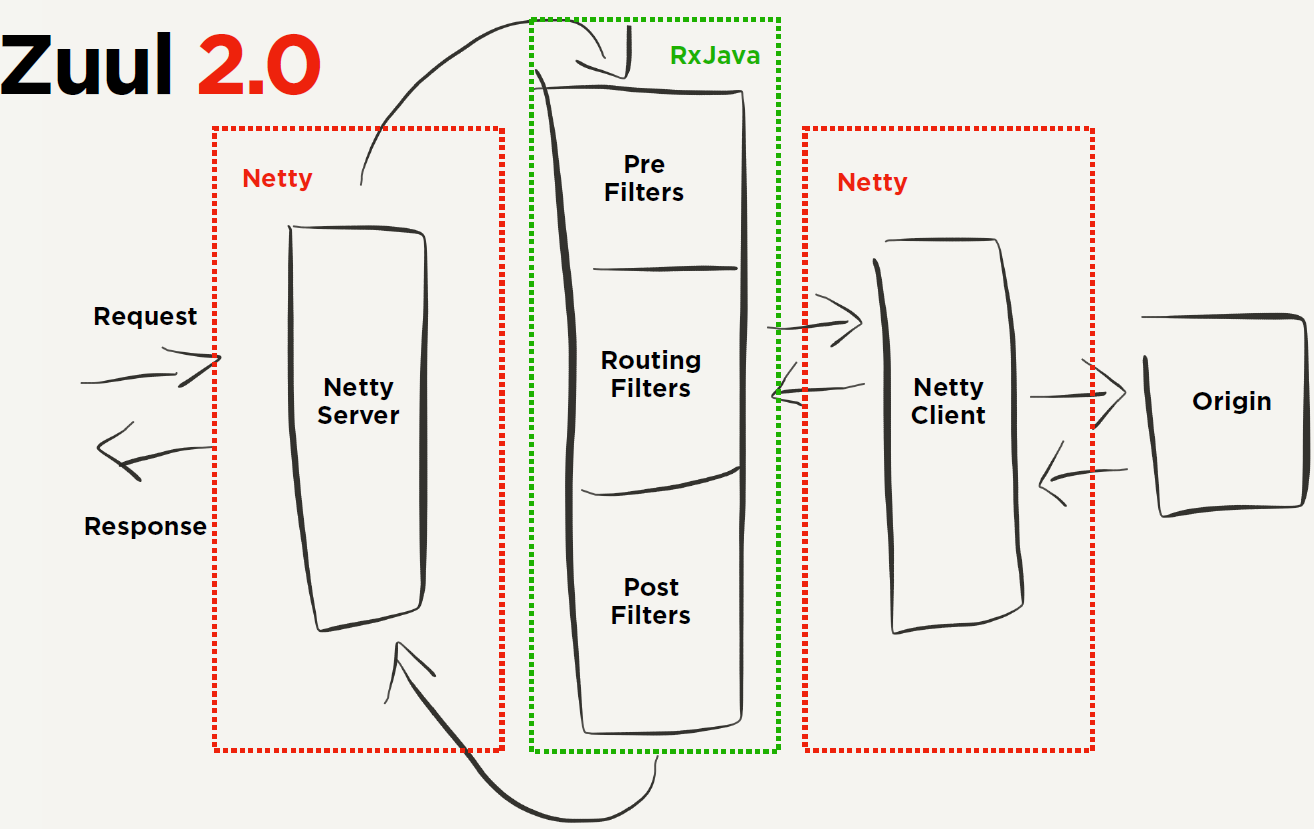
从上图可以看到:
1.Zuul引入了Netty和RxJava,正如之前的 ZuulFilter 分为了 Pre,Post,Route,Error,Zuul2的Filter分为三种类型
- Inbound Filters: 在路由之前执行
- Endpoint Filters: 路由操作
- Outbound Filters: 得到相应数据之后执行
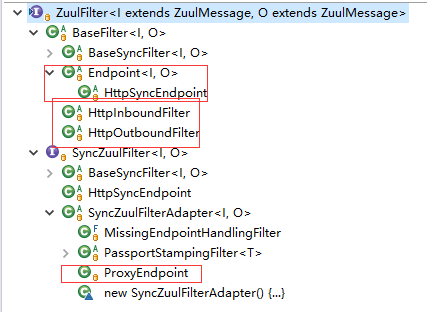
使用RxJava重写了Pre,Post,Route ZuulFilter的结构如下
ZuulServerChannelInitializer.java
@Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { // Configure our pipeline of ChannelHandlerS. ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); storeChannel(ch); addTimeoutHandlers(pipeline); addPassportHandler(pipeline); addTcpRelatedHandlers(pipeline); addHttp1Handlers(pipeline); addHttpRelatedHandlers(pipeline); addZuulHandlers(pipeline); }
其父类实现了addZuulHandlers方法
protected void addZuulHandlers(final ChannelPipeline pipeline) { pipeline.addLast("logger", nettyLogger); pipeline.addLast(new ClientRequestReceiver(sessionContextDecorator)); pipeline.addLast(passportLoggingHandler); addZuulFilterChainHandler(pipeline); pipeline.addLast(new ClientResponseWriter(requestCompleteHandler, registry)); } protected void addZuulFilterChainHandler(final ChannelPipeline pipeline) { final ZuulFilter<HttpResponseMessage, HttpResponseMessage>[] responseFilters = getFilters( //1 new OutboundPassportStampingFilter(FILTERS_OUTBOUND_START), new OutboundPassportStampingFilter(FILTERS_OUTBOUND_END)); // response filter chain final ZuulFilterChainRunner<HttpResponseMessage> responseFilterChain = getFilterChainRunner(responseFilters, filterUsageNotifier); // endpoint | response filter chain final FilterRunner<HttpRequestMessage, HttpResponseMessage> endPoint = getEndpointRunner(responseFilterChain, //2 filterUsageNotifier, filterLoader); final ZuulFilter<HttpRequestMessage, HttpRequestMessage>[] requestFilters = getFilters( //3 new InboundPassportStampingFilter(FILTERS_INBOUND_START), new InboundPassportStampingFilter(FILTERS_INBOUND_END)); // request filter chain | end point | response filter chain final ZuulFilterChainRunner<HttpRequestMessage> requestFilterChain = getFilterChainRunner(requestFilters, filterUsageNotifier, endPoint); pipeline.addLast(new ZuulFilterChainHandler(requestFilterChain, responseFilterChain)); }
调用Handler处理
@Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { if (msg instanceof HttpRequestMessage) { zuulRequest = (HttpRequestMessage)msg; //Replace NETTY_SERVER_CHANNEL_HANDLER_CONTEXT in SessionContext final SessionContext zuulCtx = zuulRequest.getContext(); zuulCtx.put(NETTY_SERVER_CHANNEL_HANDLER_CONTEXT, ctx); zuulCtx.put(ZUUL_FILTER_CHAIN, requestFilterChain); requestFilterChain.filter(zuulRequest); } else if ((msg instanceof HttpContent)&&(zuulRequest != null)) { requestFilterChain.filter(zuulRequest, (HttpContent) msg); } else { LOG.debug("Received unrecognized message type. " + msg.getClass().getName()); ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg); } }
调用ZuulFilterChainRunner的filter方法
@Override public void filter(T inMesg, HttpContent chunk) { String filterName = "-"; try { Preconditions.checkNotNull(inMesg, "input message"); final AtomicInteger runningFilterIdx = getRunningFilterIndex(inMesg); final int limit = runningFilterIdx.get(); for (int i = 0; i < limit; i++) { final ZuulFilter<T, T> filter = filters[i]; filterName = filter.filterName(); if ((! filter.isDisabled()) && (! shouldSkipFilter(inMesg, filter))) { final HttpContent newChunk = filter.processContentChunk(inMesg, chunk); if (newChunk == null) { //Filter wants to break the chain and stop propagating this chunk any further return; } //deallocate original chunk if necessary if ((newChunk != chunk) && (chunk.refCnt() > 0)) { chunk.release(chunk.refCnt()); } chunk = newChunk; } } if (limit >= filters.length) { //Filter chain has run to end, pass down the channel pipeline invokeNextStage(inMesg, chunk); } else { inMesg.bufferBodyContents(chunk); boolean isAwaitingBody = isFilterAwaitingBody(inMesg); // Record passport states for start and end of buffering bodies. if (isAwaitingBody) { CurrentPassport passport = CurrentPassport.fromSessionContext(inMesg.getContext()); if (inMesg.hasCompleteBody()) { if (inMesg instanceof HttpRequestMessage) { passport.addIfNotAlready(PassportState.FILTERS_INBOUND_BUF_END); } else if (inMesg instanceof HttpResponseMessage) { passport.addIfNotAlready(PassportState.FILTERS_OUTBOUND_BUF_END); } } else { if (inMesg instanceof HttpRequestMessage) { passport.addIfNotAlready(PassportState.FILTERS_INBOUND_BUF_START); } else if (inMesg instanceof HttpResponseMessage) { passport.addIfNotAlready(PassportState.FILTERS_OUTBOUND_BUF_START); } } } if (isAwaitingBody && inMesg.hasCompleteBody()) { //whole body has arrived, resume filter chain runFilters(inMesg, runningFilterIdx); } } } catch (Exception ex) { handleException(inMesg, filterName, ex); } }
2.NettyClient
if (filter.getSyncType() == FilterSyncType.SYNC) { final SyncZuulFilter<I, O> syncFilter = (SyncZuulFilter) filter; final O outMesg = syncFilter.apply(inMesg); recordFilterCompletion(SUCCESS, filter, startTime, inMesg, snapshot); return (outMesg != null) ? outMesg : filter.getDefaultOutput(inMesg); } // async filter filter.incrementConcurrency(); resumer = new FilterChainResumer(inMesg, filter, snapshot, startTime); filter.applyAsync(inMesg) .observeOn(Schedulers.from(getChannelHandlerContext(inMesg).executor())) .doOnUnsubscribe(resumer::decrementConcurrency) .subscribe(resumer);
ProxyEndpoint.java
@Override public HttpResponseMessage apply(final HttpRequestMessage input) { // If no Origin has been selected, then just return a 404 static response. // handle any exception here try { if (origin == null) { handleNoOriginSelected(); return null; } origin.getProxyTiming(zuulRequest).start(); // To act the same as Ribbon, we must do this before starting execution (as well as before each attempt). IClientConfig requestConfig = origin.getExecutionContext(zuulRequest).getRequestConfig(); originalReadTimeout = requestConfig.getProperty(ReadTimeout, null); setReadTimeoutOnContext(requestConfig, 1); origin.onRequestExecutionStart(zuulRequest); proxyRequestToOrigin(); //Doesn't return origin response to caller, calls invokeNext() internally in response filter chain return null; } catch (Exception ex) { handleError(ex); return null; } }
将请求转发至远端
private void proxyRequestToOrigin() { Promise<PooledConnection> promise = null; try { attemptNum += 1; requestStat = createRequestStat(); origin.preRequestChecks(zuulRequest); concurrentReqCount++; // update RPS trackers updateOriginRpsTrackers(origin, attemptNum); // We pass this AtomicReference<Server> here and the origin impl will assign the chosen server to it. promise = origin.connectToOrigin(zuulRequest, channelCtx.channel().eventLoop(), attemptNum, passport, chosenServer, chosenHostAddr); storeAndLogOriginRequestInfo(); currentRequestAttempt = origin.newRequestAttempt(chosenServer.get(), context, attemptNum); requestAttempts.add(currentRequestAttempt); passport.add(PassportState.ORIGIN_CONN_ACQUIRE_START); if (promise.isDone()) { operationComplete(promise); } else { promise.addListener(this); } } catch (Exception ex) { LOG.error("Error while connecting to origin, UUID {} " + context.getUUID(), ex); storeAndLogOriginRequestInfo(); if (promise != null && ! promise.isDone()) { promise.setFailure(ex); } else { errorFromOrigin(ex); } } }
调用BasicNettyOrigin
@Override public Promise<PooledConnection> connectToOrigin(HttpRequestMessage zuulReq, EventLoop eventLoop, int attemptNumber, CurrentPassport passport, AtomicReference<Server> chosenServer, AtomicReference<String> chosenHostAddr) { return clientChannelManager.acquire(eventLoop, null, zuulReq.getMethod().toUpperCase(), zuulReq.getPath(), attemptNumber, passport, chosenServer, chosenHostAddr); }
3.小结
>> zuul2通过启动BaseServerStartup的实现类,启动一个netty server
>> netty server将ZuulFilter (Inbound, Outbound, EndPoint)包裹成ChainRunner组合成netty的一个handler:ZuulFilterChainHandler
>> ZuulFilterChainHandler将请求包装成SyncZuulFilter封装成NettyClient
4.zuul1和zuul2的选择
性能对比
Zuul 1 (阻塞)的应用场景
cpu密集型任务
简单操作的需求
开发简单的需求
实时请求高的
zuul2(非阻塞)的应用场景
io密集的任务
大请求或者大文件
队列的流式数据
超大量的连接
参考文献
【1】https://www.cnblogs.com/lexiaofei/p/7080257.html
【2】https://blog.csdn.net/lengyue309/article/details/82192118
【】https://github.com/strangeloop/StrangeLoop2017/blob/master/slides/ArthurGonigberg-ZuulsJourneyToNonBlocking.pdf

微信公众号: 架构师日常笔记 欢迎关注!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号