机械制造作业考研题目答案分享——金属切削课题研讨ppt展示
PRESENTATION TOPIC: PROBLEMS IN HIGH SPEED CUTTING AND MICRO-CUTTING。这是一次课题研讨的ppt制造的素材稿,里面介绍了高速切削和微纳切削的一些前沿研究。
版权声明
本内容由狂小虎原创整合,请不要售卖,为了防止爬虫以及保持免费性,设置为仅粉丝可见。另外,题目以及解释可能不完全正确,仅供参考,同时也欢迎各位在讨论区指点出内容的错误之处。
文章目录
What is high speed cutting
The speed of high speed cutting is 5~10 times of the normal cutting speed.
Characteristics
Higher productivity and throughput
Higher surface finish and machining accuracy.
Speed depends on properties of materia.

Z. Wang and M. Rahman, “High-Speed Machining,” Compr. Mater. Process., vol. 11, pp. 221–253, 2014.

H. Weule, V. Hüntrup, and H. Tritschle, “Micro-cutting of steel to meet new requirements in miniaturization,” CIRP Ann. - Manuf. Technol., vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 61–64, 2001.
refine grain structure for higher hardness
Problem
Machining various materials.
Low thermal diffusivity
Cutting temperature increase with an increase in cutting speed due to soften material
Cost per volume

Z. Wang and M. Rahman, “High-Speed Machining,” Compr. Mater. Process., vol. 11, pp. 221–253, 2014.
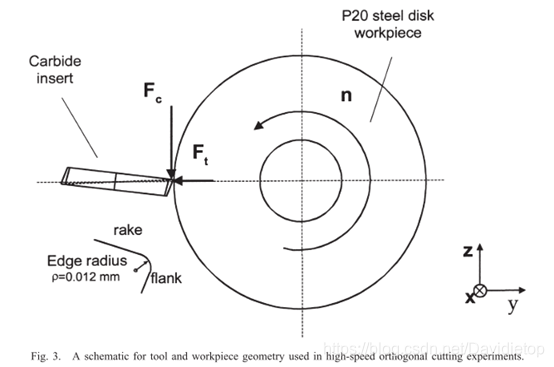
Possible Solution
Faster metal removal through high speed machining and laser assisted machining
What is micro cutting
Mechanical micromachining using geometrically defined and cutter edges carried out on conventional precision machines or micro machines.
[1] C. L. Yen, M. C. Lu, and J. L. Chen, “Applying the self-organization feature map (SOM) algorithm to AE-based tool wear monitoring in micro-cutting,” Mech. Syst. Signal Process., vol. 34, no. 1–2, pp. 353–366, 2013.
Characteristics
Smaller machine tool -micro lathe

Tiny cutting point instead of cutting edge.

Diamond single point tool for high hardness.
Small cutting chip
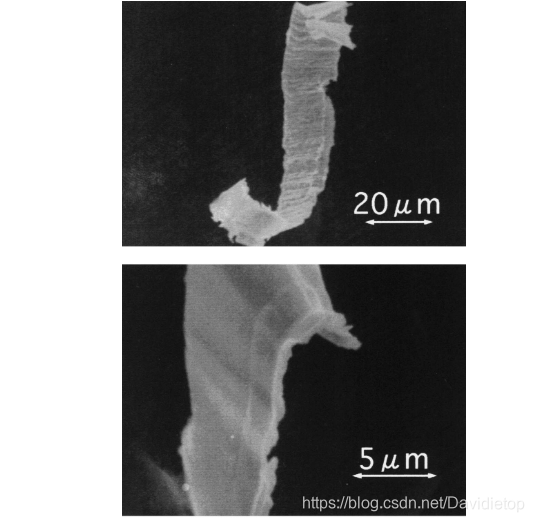
Z. Lu and T. Yoneyama, “Micro cutting in the micro lathe turning system,” Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf., vol. 39, no. 7, pp. 1171–1183, 1999.
High accuracy
Problem
Diamond has a very high affinity to iron, micro-cutting is mostly limited to non-ferrous (brass, aluminum, copper, electroless nickel)
Simple scaling cannot be used to model the phenomena of micro-cutting operations
Difficult to handle problems due to small scale (tool wear)
Plastic recovery, affecting surface finish

J. Chae, S. S. Park, and T. Freiheit, “Investigation of micro-cutting operations,” Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf., vol. 46, no. 3–4, pp. 313–332, 2006.
Possible Solution
Minimize the effect of affinity of diamond to iron
Saturated atmosphere
Cooling in the cutting process
Overlapping the tool thickness with ultrasonic vibration
Tool wear monitoring using AE (acoustic emission)
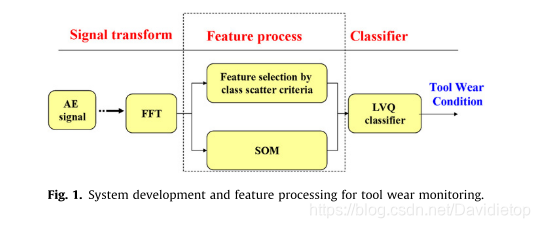
This figure shows the spectral signal for different tool wear. No1 is obtained on the first passing with a new cutting tool. No2, 3, 4 is the second, third, fourth passing with the same tool. 50kHZ, 90 kHz, 140 kHz, 190 kHz, 240 kHz. Tool wear or plastic deformation of the material on shear plane.

C. L. Yen, M. C. Lu, and J. L. Chen, “Applying the self-organization feature map (SOM) algorithm to AE-based tool wear monitoring in micro-cutting,” Mech. Syst. Signal Process., vol. 34, no. 1–2, pp. 353–366, 2013.
Nano-scratch





