机械制造作业考研题目答案分享——加工方法、工序和夹紧
Homework 7
版权声明
本内容由狂小虎原创整合,请不要售卖,为了防止爬虫以及保持免费性,设置为仅粉丝可见。另外,题目以及解释可能不完全正确,仅供参考,同时也欢迎各位在讨论区指点出内容的错误之处。
加工方法、工序和夹紧
1.零件的加工表面的加工方法的选择应遵循哪些原则?
- 所选加工方法应考虑每种加工方法的加工经济精度范围要与加工表面的精度要求和表面粗糙度要求相适应;2) 所选加工方法能确保加工面的几何尺寸精度、形状精度和表面相互位置精度的要求。 3) 所选加工方法要与零件材料的可加工性相适应。例如:淬火钢、耐热钢等因硬度高则应采用磨削作为精加工;有色金属宜采用高速精细车或精细镗切削作为精加工。 4 )所选加工方法应与零件的结构形状、尺寸及工作情况相适应。例如:箱体上IT7的孔,一般不采用拉或磨,而选择镗(大孔时)或铰(小孔时);狭长平面不用铣削而更适宜刨削加工。 5) 加工方法要与生产类型相适应,大批量生产时,应采用高效的机床设备和先进的加工方法。在单件小批生产中,多采用通用机床和常规加工方法。 6) 所选加工方法要与企业现有设备条件和工人技术水平相适应。
2.在制订加工工艺规程中,为什么要划分加工阶段?
The process is usually divided into two phases for the parts which require high efficiency and low roughness. The reason for dividing the process into rough machining and finish machining are listed on the following content.
In rough machining, a large amount of metal is removed and the faults within the raw material such as slag, a crack or an air vent can be found as early as possible so that the part can be disposed of without wasting much machining time.
As metal removal is very rapid, the rough machining phase easily causes large deformation.
It can ensure that the machine tools are properly used.
It can also make it possible to inset necessary heat treatment operations.
3.切削加工顺序安排的原则是哪些?
Perform rough machining before finish machining
Perform datum surface machining before that of other surfaces
Perform main functional surface machining before less important surface machining
Perform plane surface machining before hole surface machining
4.在机械加工工艺规程中通常有哪些热处理工序?它们起什么作用?如何安排?
In order to improve the mechanical and cutting performance of the material, heat treatment is often arranged during machining. There are four kinds of widely used heat treatment in the operation processes.
Annealing and normalising can release the internal stress and improve the cutting performance of material. They are usually arranged before machining. Sometimes annealing is also arranged after rough machining. Thus, many medium carbon steels and alloys steels are often treated by this method.
A manual time-dependent stress release treatment is often arranged after rough machining for some large and complex casting to reduce the internal stress, however it is better to arrange a natural time-dependent treatment before rough machining.
Quenching or carbonising treatment can raise the surface hardness and wear resistance. Quenching is usually arranged before grinding, but it can be last operation when using high frequency quenching. Carbonising can be carried out before or after semi-finish machining.
Surface treatment (including electroplating and oxidising) can raise the corrosion resistance and wear resistance, and improve the appearance. It is usually carried out in the last operation.
5.什么叫工序集中?什么叫工序分散?什么情况下采用工序集中?什么情况下采用工序分散?
(1)Process concentration: assemble several sub-operations into one operation, for instance, a multi-spindle machine tool can machine 14 holes in sewing machine shell simultaneously.
Process dispersal (or operational dispersal) means a large number of operations and long process routes, but each operation includes few sub-operations.
(2) Using concentrated or dispersed operation depends on the production scale, the geometrical characteristics of the part, the technical requirement and the process equipment available.
有时,还要考虑各工序生产节拍的一致性。一般情况下,单件小批生产时,只能工序集中,在一台普通机床上加工出尽量多的表面;大批大量生产时,既可以采用多刀、多轴等高效、自动机床,将工序集中,也可以将工序分散后组织流水生产,以便提高生产率和保证加工质量。
6.什么叫加工余量?影响加工余量的因素有哪些?
Machining allowance (or metal removal) ( Z t ) (Z_t) (Zt) is the whole thickness of the removal metal, which is to ensure the accuracy and roughness of some surfaces and is removed from a rough casting. The metal removed in each operation is called operation allowance ( Z i ) (Z_i) (Zi).
Z t = Z 1 + Z 2 + ⋯ + Z n Z_t=Z_1+Z_2+⋯+Z_n Zt=Z1+Z2+⋯+Zn
Where n is the number of jobs or sub-jobs for the surface.
Factors affecting the rate of machining allowance.
- Surface qualities produced by the preceding operation – roughness R_a and tolerance T a T_a Ta.
- Tolerance δ a δ_a δa of the preceding operation includes various kinds of geometrical shape error. For instance, the degree of coning, ellipsing and surface flatness.
- Relative position error ρ a ρ_a ρa between preceding machined surfaces includes the degree of linearity, of parallelism between axes, of perpendicularity between axis and surface, coaxiality between inner and external surfaces, and flatness of surface.
- Current clamping error ( Δ ε b ) (Δ ε_b) (Δεb) includes both positioning and clamping error.
7. 如何设计夹紧力?对夹紧装置的基本要求有哪些?试比较斜楔夹紧和螺旋夹紧装置的优缺点。
- The clamping force vector consists of the force magnitude, clamping direction and clamping position.
The principle to design the clamping force.
The clamping direction.
When two or more than two surfaces are used as the location datum, if the workpiece is large, the clamping force should be directed towards each of the location datum so as to keep the correct position; if the workpiece is small, the clamping force is only needed to direct the main datum surface and the location to ensure there are enough contact area.
The clamping direction should be in favour of easy setup and reducing the magnitude of the clamping force.
The clamping direction should be in favour of reducing the clamping deformation of workpiece.
The clamping position.
The clamping position should secure the location instead of making the workpiece move or rotate.
The clamping position should be in the place where the workpiece has a larger stiffness, and the clamping number should be sufficient enough to minimize the clamping deformation.
The clamping position should be near the current machined surface as close as possible to reduce the cutting torque caused by the cutting force as well as the vibration.
The magnitude if clamping force.
Q=K∙Q’
Where K is safe coefficient within 1.3~3 to ensure the clamping security, Q’ is the desired clamping force and Q is real clamping force. - Clamping device’ basic requirements: 夹紧动作要准确迅速;操作方便省力;夹紧安全可靠;结构简单、易于制造。
- The superiorities and weakness of wedge clamping device and screw clamping device are shown in table 1.
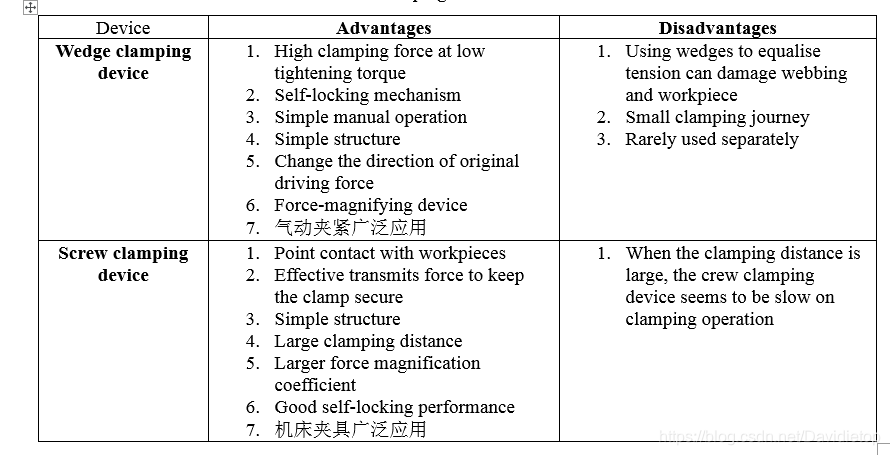
Table 1 The superiorities and weakness of wedge clamping device and screw clamping device
8.画简图表示用下列方法加工所需表面时,需要哪些运动,分别属于哪种获得形状精度的成形方法?
Answers:
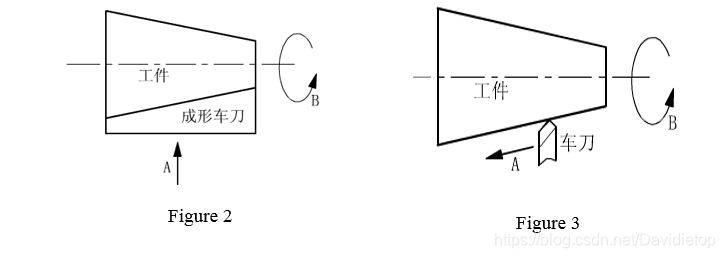
① 用成型车刀车削外圆锥面
Track marking. A is turning tool’s feed motion. B is the rotation of the workpiece. See figure 2.
② 用尖头车刀纵、横向同时运动车外圆锥面
Track marking. A is turning tool’s feed motion. B is the rotation of the workpiece. See figure 3.
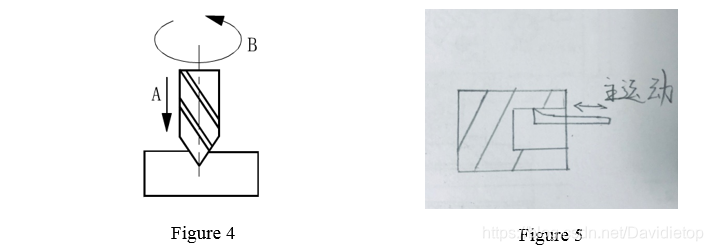
③ 用钻头钻孔
Tangential machining. A is drilling tool’s feed motion. B is the rotation of the drilling tool. See figure 4.
④ 用拉刀拉削圆柱孔
Form machining. See figure 5.
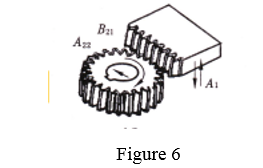
⑤ 插齿刀插削直齿圆柱齿轮
Generating process. See figure 6.
9.有哪几种获得工件尺寸(精度)和位置(精度)的方法?
- Methods of obtaining dimension of the workpiece.
Trial cutting method
Setting dimension method
Adjust method
Automatic control method
(a) Automatic inspection
(b) Numerical control - Methods of obtaining position of the workpiece.
When location accuracy should be guaranteed by multiple times of clamping, there are two methods to obtaining location accuracy.
Proper location methods
Positioning and clamping by direct location
Clamping according to pre-marked trail of the outline
Clamped with a fixture
By planning to machine relative surfaces during one clamping operation to improve relative location accuracy of machining surfaces.




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)