机械制造作业考研题目答案分享——加工精度和误差2
Homework 14
版权声明
本内容由狂小虎原创整合,请不要售卖,为了防止爬虫以及保持免费性,设置为仅粉丝可见。另外,题目以及解释可能不完全正确,仅供参考,同时也欢迎各位在讨论区指点出内容的错误之处。
文章目录
- 版权声明
- 1 对比铣削、刨削、拉削加工方法的特点?其主要应用范围和限制?
- 2非回转表面加工中所用机床夹具由哪些部分组成?各组成部分有何功用?
- 3 加工非回转表面主要有哪些定位方式、常用哪些定位元件?
- 为什么机床部件的加载和卸载过程的静刚度曲线既不重合,又不封闭,且机床部件的刚度值远比其按实体估计的要小?
- 何谓误差复映规律?误差复映系数的含义是什么?它与哪些因素有关?减小误差复映有哪些工艺措施?
- 工艺系统受哪些热源作用?在各种热源的作用下,工艺系统各主要组成部分会产生何种热变形?有何规律性?对加工精度有何影响?采取何种措施可减小他们的影响?
- 分析工件产生残余应力的主要原因及经常出现的场合。
- 加工误差按其性质可分为哪几类?它们各有何特点或规律?各采用何种方法分析与计算?试举例说明。
- 6.7 在内圆磨床上磨削盲孔时(图6.43),试分析只考虑内圆磨头受力变形的条件下,工件内孔将产生什么样的加工误差?
- 6.8 在卧式镗床上采用浮动镗刀精镗孔时,是否会出现误差复映现象?为什么?
- 6.9 在车床上加工一批光轴的外圆,加工后经度量若整批工件发现有如图所示几何形状误差,试分别说明可能产生上述误差的各种因素?
- 6.10 一批圆柱销外圆的设计尺寸为 ,加工后测量发现外圆尺寸按正态规律分布,其均方根偏差为0.003mm,曲线顶峰位置偏离公差带中心,向右偏移0.005mm,试绘出分布曲线图,并求出合格品率和废品率,并分析废品能否修复及产生的原因。
第五章作业补充
1 对比铣削、刨削、拉削加工方法的特点?其主要应用范围和限制?
Characteristics
Milling: Milling operation involves using multi-point rotary cutters to remove material from workpiece. The machining efficiency is high and heat dissipation of cutters is great, but the cutting process is not stable.
Planning and shaping: Cutters can make a horizontal and relatively linear reciprocating motion on the workpiece. Main sport is a relatively linear reciprocation motion without cutting in return stroke and with single point cutter. As a result of it, cutting speed is limited, efficiency is low and there are impact and shake during cutting. However, the workpiece and cutting can be thoroughly cooled without lubricant.
Broaching: Cutters can make a vertical and relatively linear reciprocating motion on the workpiece. Broaching is the machining process that cutter make a low speed linear motion on the workpiece. Its efficiency is third to eighth as milling’s. IT8~IT7 can be attained. Broaching machine is structure-simple, and easy to be utilized. The cutting speed is slow so that tool life is long. However, the structure of cutter is complex and expensive.
Applications
Milling: Slab or plain milling, side milling, slotting, slitting or parting, end milling, face milling; forming, gear (teeth) milling, splining shaft, tool forming, T-slotting, thread-milling
Planning and shaping: Shaper is usually utilized in maintenance and assemble industry. With low speed and large width cutter, planner can be used to produced product with high machining precision and comparatively low surface roughness.
Broaching: Machining hole, plain, forming surface. Usually used in large production and product with specific shape and strict precision requirement.
Limits
Milling: The process of cutting is not stable so that the workpiece is easy to vibrate when cutters move in and out. Thus, cutters are easy to be worn.
Planning and shaping: Main sport is a relatively linear reciprocation motion without cutting in return stroke and with single point cutter. As a result of it, cutting speed is limited, efficiency is low and there are impact and shake during cutting.
Broaching: For machining hole, through hole must be pre-machined so that the cutter can be moved in. Moreover, it cannot be applied in machining blind hole, deep hole, step hole or other hole with block in profile.
2非回转表面加工中所用机床夹具由哪些部分组成?各组成部分有何功用?
Components of Fixtures of Non-rotational surface:
Clamping body: it can connect clamping elements and devices, and then we can easily set them in a whole part up on the machine tool.
Locating elements or device: to ensure the location of the workpiece on the fixture.
Feeler block: to guide the cutter and adjust the location of the cutter to the fixture.
Clamping device: to clamp the workpiece.
Locating pins: to ensure the location of fixture on the machine tool, and connect them tightly.
Connecting bolts: to connect the fixture with the machine tool.
Other elements and devices: to measure the degree, to reduce error, to prevent operators and so on.
3 加工非回转表面主要有哪些定位方式、常用哪些定位元件?
Method for locating:
Plain locating method
“One face two hole” locating method
Combination of plain and hole locating method
Locating elements:
Plain locating: Cylindrical support, adjusting support, self support, assistant support
Hole locating (center locating): Locating pins, arbor, tapered hole, tapered arbor
第六章作业
为什么机床部件的加载和卸载过程的静刚度曲线既不重合,又不封闭,且机床部件的刚度值远比其按实体估计的要小?
The curve is not straight line indicating that the deformation of machine tool’s components is not exactly elastic deformation. Furthermore, the curve is not closed showing that the deformation consists of plastic deformation.
The processes of loading and unloading will consume work of friction. Thus, the curve of loading and unloading is not coincident. The area of the curves and axis is the consuming power by fictional work and plastic deformation.
The rigidities of machine tool’s components (e.g. fixture of cutter) are comparatively large referring to their size of shape. However, components consist of many parts. After loading, the clearances among parts should be eliminated. And then contact deformation will be generated in interface between parts. Finally, the part, with lowest rigidity, would has relatively large deformation. The three listed deformation will cause deformation of the component. Thus, the deformation of the component is relatively large, which is larger than our estimation.
何谓误差复映规律?误差复映系数的含义是什么?它与哪些因素有关?减小误差复映有哪些工艺措施?
Principle of error copying
When blank has shape or location error, there is same type of machining error after machining. However, the error would be gradually reduced by each cutting step.
Coefficient of error copying
It is equal to workpiece error divided by blank error. ε=C/(K_system+C)
The coefficient is influenced by operation system rigidity and radial cutting force coefficient. It is negative correlation between K_system and ε, but positive correlation between C and ε.
Measurement to eliminate error copying
Error grouping can eliminate error copying effectively. (Reduce machining allowance for each step)
Increase operation system rigidity.
Increase the numbers of cutting steps or operation steps.
工艺系统受哪些热源作用?在各种热源的作用下,工艺系统各主要组成部分会产生何种热变形?有何规律性?对加工精度有何影响?采取何种措施可减小他们的影响?
Heating source
Friction heat, cutting heat, ambient temperature, solar radiation and so on.
Types of thermal deformation on different components
Machine tool: influenced by inner and outer heat source.
Cutters: cutting heat. The cutters would be enlengthened due to increasing of temperature.
Workpiece: mainly is cutting heat, but for large workpiece or some high accuracy part, room temperature can also considerably influence them. The more heat is generated on the workpiece and the lighter the workpiece is, the thermal deformation would be caused.
The law of thermal deformation
In the first period of temperature increasing, temperatures of different machine tool’s components are changing with time, and temperature distribution is not a stable field.
After a considerable time (4~6h), operation system would be in thermal equilibrium stage. The thermal deformation would be relatively stable, causing regular machining error, and temperature distribution would be more even.
Influence for machining accuracy
Most of them would cause lower machining accuracy of workpiece.
For example, cylindrical degree error or end face plain error would be caused during machining due to thermal deformation of cutters.
Measurement to eliminate thermal deformation
To reduce heat release from heat source or isolate heat source.
Using thermal compensation to reduce thermal deformation
To apply proper components of machine tool
Preheat the proper location of machine tool to speed up to be in thermal equilibrium stage
Control room temperature such as avoid solar radiation
分析工件产生残余应力的主要原因及经常出现的场合。
Reasons:
Residual stresses are generated by uneven micro or macro structural change of workpiece’s dimension during hot machining or cold machining.
Different places of workpiece are heated unevenly or heated uniformly but the cooling speeds are different as well as the grain structure’s change.
Occasions:
The process of manufacturing blank, such as casting, forging, welding, heat treatment etc.
The method utilized to eliminate the bending of slender shaft also cause residual stresses.
加工误差按其性质可分为哪几类?它们各有何特点或规律?各采用何种方法分析与计算?试举例说明。
Machining error can be divided into system error and random error judging by its characteristics.
Characteristics:
System error: machining error is either direction and size of machining error is unchangeable basically (static system error), or machining error is changing according to the order of machining (variable system error).
Random error: size and direction of machining error are randomly changing when continuously machining a batch of workpiece.
Analysis and calculus:
Statistical analysis (e.g. distribution curve) can be applied in both of them.
Example:
When using normal distribution curve to analyse machining error, the average value α reflects the system error and the standard deviation σ reflects the random error.
6.7 在内圆磨床上磨削盲孔时(图6.43),试分析只考虑内圆磨头受力变形的条件下,工件内孔将产生什么样的加工误差?
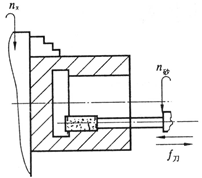
It would cause taper degree on the hole. Because the grinding cutter is cantilevered, which means the deflection of the left part is highest, the machined hole has big top surface and small bottom surface.
从而导致工件出现(一头大一头小)的形状误差。
6.8 在卧式镗床上采用浮动镗刀精镗孔时,是否会出现误差复映现象?为什么?
Yes, it would. Because floating boring cutters have low rigidity, the influence by changing of size of force is still large. Thus, the error copying still exists.
6.9 在车床上加工一批光轴的外圆,加工后经度量若整批工件发现有如图所示几何形状误差,试分别说明可能产生上述误差的各种因素?




6.10 一批圆柱销外圆的设计尺寸为 ,加工后测量发现外圆尺寸按正态规律分布,其均方根偏差为0.003mm,曲线顶峰位置偏离公差带中心,向右偏移0.005mm,试绘出分布曲线图,并求出合格品率和废品率,并分析废品能否修复及产生的原因。



The waste can be modified because their dimension normally larger than the desired product’s. Thus, grinding or turning them once more with lower machining allowance can fix it.
The reason for causing this error is that the tool may be worn, tool setting may be inappropriate, the fixture of workpiece or cutters may be not precise etc.
如果想以后消除这个误差,可以让车刀向刀具中心再进刀Δ_system/2




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)