TensorFlow从入门到理解(五):你的第一个循环神经网络RNN(回归例子)
运行代码:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
BATCH_START = 0
TIME_STEPS = 20
BATCH_SIZE = 50
INPUT_SIZE = 1
OUTPUT_SIZE = 1
CELL_SIZE = 10
LR = 0.006
def get_batch():
global BATCH_START, TIME_STEPS
# xs shape (50batch, 20steps)
xs = np.arange(BATCH_START, BATCH_START+TIME_STEPS*BATCH_SIZE).reshape((BATCH_SIZE, TIME_STEPS)) / (10*np.pi)
seq = np.sin(xs)
res = np.cos(xs)
BATCH_START += TIME_STEPS
# plt.plot(xs[0, :], res[0, :], 'r', xs[0, :], seq[0, :], 'b--')
# plt.show()
# returned seq, res and xs: shape (batch, step, input)
return [seq[:, :, np.newaxis], res[:, :, np.newaxis], xs]
class LSTMRNN(object):
def __init__(self, n_steps, input_size, output_size, cell_size, batch_size):
self.n_steps = n_steps
self.input_size = input_size
self.output_size = output_size
self.cell_size = cell_size
self.batch_size = batch_size
with tf.name_scope('inputs'):
self.xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_steps, input_size], name='xs')
self.ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_steps, output_size], name='ys')
with tf.variable_scope('in_hidden'):
self.add_input_layer()
with tf.variable_scope('LSTM_cell'):
self.add_cell()
with tf.variable_scope('out_hidden'):
self.add_output_layer()
with tf.name_scope('cost'):
self.compute_cost()
with tf.name_scope('train'):
self.train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(LR).minimize(self.cost)
def add_input_layer(self,):
l_in_x = tf.reshape(self.xs, [-1, self.input_size], name='2_2D') # (batch*n_step, in_size)
# Ws (in_size, cell_size)
Ws_in = self._weight_variable([self.input_size, self.cell_size])
# bs (cell_size, )
bs_in = self._bias_variable([self.cell_size,])
# l_in_y = (batch * n_steps, cell_size)
with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'):
l_in_y = tf.matmul(l_in_x, Ws_in) + bs_in
# reshape l_in_y ==> (batch, n_steps, cell_size)
self.l_in_y = tf.reshape(l_in_y, [-1, self.n_steps, self.cell_size], name='2_3D')
def add_cell(self):
lstm_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell(self.cell_size, forget_bias=1.0, state_is_tuple=True)
with tf.name_scope('initial_state'):
self.cell_init_state = lstm_cell.zero_state(self.batch_size, dtype=tf.float32)
self.cell_outputs, self.cell_final_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(
lstm_cell, self.l_in_y, initial_state=self.cell_init_state, time_major=False)
def add_output_layer(self):
# shape = (batch * steps, cell_size)
l_out_x = tf.reshape(self.cell_outputs, [-1, self.cell_size], name='2_2D')
Ws_out = self._weight_variable([self.cell_size, self.output_size])
bs_out = self._bias_variable([self.output_size, ])
# shape = (batch * steps, output_size)
with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'):
self.pred = tf.matmul(l_out_x, Ws_out) + bs_out
def compute_cost(self):
losses = tf.contrib.legacy_seq2seq.sequence_loss_by_example(
[tf.reshape(self.pred, [-1], name='reshape_pred')],
[tf.reshape(self.ys, [-1], name='reshape_target')],
[tf.ones([self.batch_size * self.n_steps], dtype=tf.float32)],
average_across_timesteps=True,
softmax_loss_function=self.ms_error,
name='losses'
)
with tf.name_scope('average_cost'):
self.cost = tf.div(
tf.reduce_sum(losses, name='losses_sum'),
self.batch_size,
name='average_cost')
tf.summary.scalar('cost', self.cost)
@staticmethod
def ms_error(labels, logits):
return tf.square(tf.subtract(labels, logits))
def _weight_variable(self, shape, name='weights'):
initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(mean=0., stddev=1.,)
return tf.get_variable(shape=shape, initializer=initializer, name=name)
def _bias_variable(self, shape, name='biases'):
initializer = tf.constant_initializer(0.1)
return tf.get_variable(name=name, shape=shape, initializer=initializer)
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = LSTMRNN(TIME_STEPS, INPUT_SIZE, OUTPUT_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, BATCH_SIZE)
sess = tf.Session()
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("logs", sess.graph)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
# relocate to the local dir and run this line to view it on Chrome (http://0.0.0.0:6006/):
# $ tensorboard --logdir='logs'
plt.ion()
plt.show()
for i in range(200):
seq, res, xs = get_batch()
if i == 0:
feed_dict = {
model.xs: seq,
model.ys: res,
# create initial state
}
else:
feed_dict = {
model.xs: seq,
model.ys: res,
model.cell_init_state: state # use last state as the initial state for this run
}
_, cost, state, pred = sess.run(
[model.train_op, model.cost, model.cell_final_state, model.pred],
feed_dict=feed_dict)
# plotting
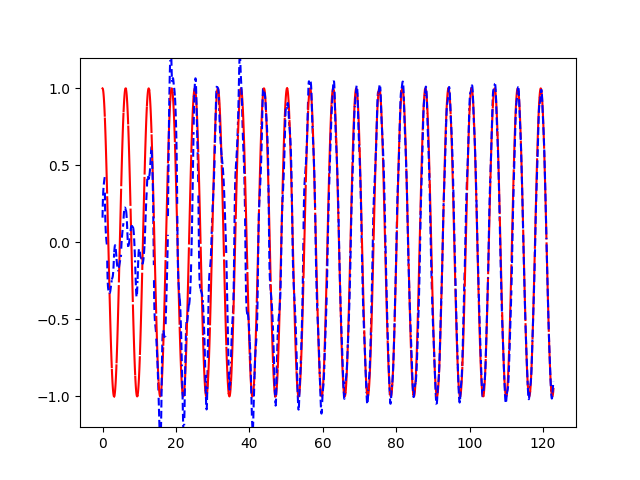
plt.plot(xs[0, :], res[0].flatten(), 'r', xs[0, :], pred.flatten()[:TIME_STEPS], 'b--')
plt.ylim((-1.2, 1.2))
plt.draw()
plt.pause(0.3)
if i % 20 == 0:
print('cost: ', round(cost, 4))
result = sess.run(merged, feed_dict)
writer.add_summary(result, i)
运行结果:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号