(原)MobileNetV1
转载请注明出处:
https://www.cnblogs.com/darkknightzh/p/9410540.html
论文:
MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications
网址:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861?context=cs
非官方的pytorch代码:
https://github.com/marvis/pytorch-mobilenet
1. 深度可分离卷积
mobilenetV1使用的是深度可分离卷积(Depthwise Separable Convolution,DSC),DSC包含两部分:depthwise convolution(DWC)+ pointwise convolution(PWC)。DWC对输入的通道进行滤波,其不增加通道的数量,PWC用于将PWC不同的通道进行连接,其可以增加通道的数量。通过这种分解的方式,可以明显的减少计算量。
如下图所示,传统的卷积(a),卷积核参数为${{D}_{K}}\centerdot {{D}_{K}}\centerdot M\centerdot N$,其中${{D}_{K}}$为卷积核大小,M为输入的通道数,N为输出的通道数。DWC(b)中卷积核参数为${{D}_{K}}\centerdot {{D}_{K}}\centerdot 1\centerdot M$,其中M个${{D}_{K}}\centerdot {{D}_{K}}$的核和输入特征的对应通道进行卷积,如下式所示。PWC(c)中卷积核参数为$1\centerdot 1\centerdot M\centerdot N$,每个卷积核在特征维度上分别对输入的M个特征进行加权,最终得到N个特征(M≠N时,完成了升维或者降维)。
${{\mathbf{\hat{G}}}_{k,l,m}}=\sum\limits_{i,j}{{{{\mathbf{\hat{K}}}}_{k,l,m}}\centerdot {{\mathbf{F}}_{k+i-1,l+j-1,m}}}$
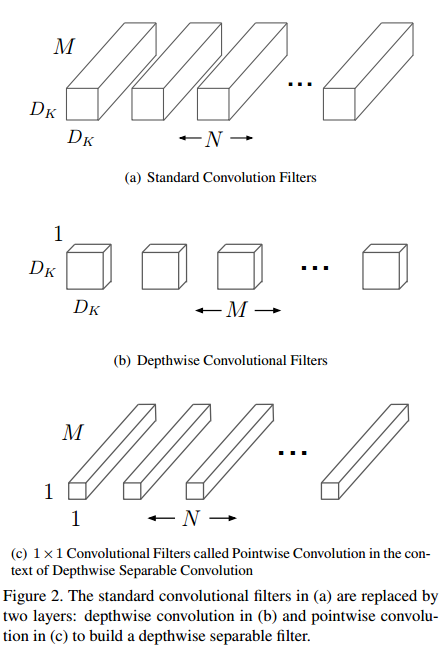
传统卷积的计算量为:
${{D}_{K}}\centerdot {{D}_{K}}\centerdot M\centerdot N\centerdot {{D}_{F}}\centerdot {{D}_{F}}$
DSC总共的计算量为:
${{D}_{K}}\centerdot {{D}_{K}}\centerdot M\centerdot {{D}_{F}}\centerdot {{D}_{F}}+M\centerdot N\centerdot {{D}_{F}}\centerdot {{D}_{F}}$
当使用3*3的卷积核时,DSC可将计算量降低为原来的1/8到1/9。
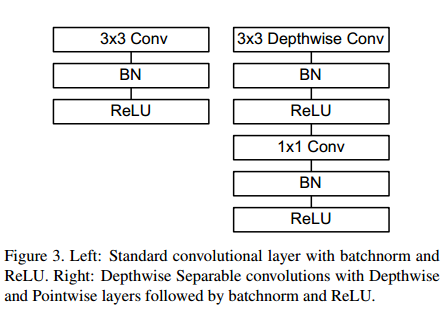
需要说明的是,DWC,PWC后面均有BN和ReLU。如下图所示,传统的卷积层为3*3conv+BN+ReLU,Depthwise Separable convolutions为3*3DWC+BN+ReLU+1*1conv+BN+ReLU。
2. 网络结构
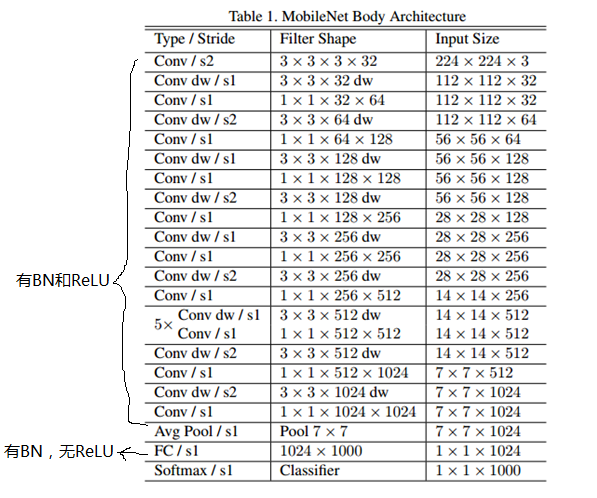
mobileNetV1的网络结构如下图所示。其中第一个卷积层为传统的卷积;前面的卷积层均有bn和relu,最后一个全连接层只有BN,无ReLU。
mobileNetV1使用RMSprop训练;由于参数很少,DWC使用比较小的或者不使用weight decay(l2 regularization)。
3. 宽度缩放因子(width multiplier)
文中引入了$\alpha $作为宽度缩放因子,其作用是在整体上对网络的每一层维度(特征数量)进行瘦身。$\alpha $影响模型的参数数量及前向计算时的乘加次数。此时网络每一层的输入为$\alpha M$维,输出为$\alpha N$维。此时DSC的计算量变为:
${{D}_{K}}\centerdot {{D}_{K}}\centerdot \alpha M\centerdot {{D}_{F}}\centerdot {{D}_{F}}+\alpha M\centerdot \alpha N\centerdot {{D}_{F}}\centerdot {{D}_{F}}$
$\alpha \in (0,1]$,典型值为1,0.75,0.5,0.25。
4. 分辨率缩放因子(resolution multiplier)
该因子即为$\rho $,用于降低输入图像的分辨率(如将224*224降低到192*192,160*160,128*128)。
此时DSC的计算量变为:
${{D}_{K}}\centerdot {{D}_{K}}\centerdot \alpha M\centerdot \rho {{D}_{F}}\centerdot \rho {{D}_{F}}+\alpha M\centerdot \alpha N\centerdot \rho {{D}_{F}}\centerdot \rho {{D}_{F}}$
5. pytorch代码
pytorch代码见参考网址中benchmark.py
1 class MobileNet(nn.Module): 2 def __init__(self): 3 super(MobileNet, self).__init__() 4 5 def conv_bn(inp, oup, stride): # 第一层传统的卷积:conv3*3+BN+ReLU 6 return nn.Sequential( 7 nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 3, stride, 1, bias=False), 8 nn.BatchNorm2d(oup), 9 nn.ReLU(inplace=True) 10 ) 11 12 def conv_dw(inp, oup, stride): # 其它层的depthwise convolution:conv3*3+BN+ReLU+conv1*1+BN+ReLU 13 return nn.Sequential( 14 nn.Conv2d(inp, inp, 3, stride, 1, groups=inp, bias=False), 15 nn.BatchNorm2d(inp), 16 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 17 18 nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False), 19 nn.BatchNorm2d(oup), 20 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 21 ) 22 23 self.model = nn.Sequential( 24 conv_bn( 3, 32, 2), # 第一层传统的卷积 25 conv_dw( 32, 64, 1), # 其它层depthwise convolution 26 conv_dw( 64, 128, 2), 27 conv_dw(128, 128, 1), 28 conv_dw(128, 256, 2), 29 conv_dw(256, 256, 1), 30 conv_dw(256, 512, 2), 31 conv_dw(512, 512, 1), 32 conv_dw(512, 512, 1), 33 conv_dw(512, 512, 1), 34 conv_dw(512, 512, 1), 35 conv_dw(512, 512, 1), 36 conv_dw(512, 1024, 2), 37 conv_dw(1024, 1024, 1), 38 nn.AvgPool2d(7), 39 ) 40 self.fc = nn.Linear(1024, 1000) # 全连接层 41 42 def forward(self, x): 43 x = self.model(x) 44 x = x.view(-1, 1024) 45 x = self.fc(x) 46 return x
posted on 2018-08-02 22:12 darkknightzh 阅读(11608) 评论(2) 编辑 收藏 举报



