(原)Non-local Neural Networks
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
转载请注明出处:
https://www.cnblogs.com/darkknightzh/p/12592351.html
论文:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.07971
第三方pytorch代码:
https://github.com/AlexHex7/Non-local_pytorch
1. non local操作
该论文定义了通用了non local操作:
其中i为需要计算响应的输出位置的索引,j为所有的位置。x为输入信号(图像,序列,视频等,通常为这些信号的特征),y为个x相同尺寸的输出信号。f为pairwise的函数,f计算当前i和所有j之间的关系,并得到一个标量。一元函数g计算输入信号在位置j的表征。(这段翻译起来怪怪的)。C(x)为归一化系数,用于归一化f和g的结果。
2. non local和其他操作的区别
① non local考虑到了所有的位置j。卷积操作仅考虑了当前位置的一个邻域(如核为3的一维卷积仅考虑了i-1<=j<=i+1);循环操作通常只考虑当前和上一个时间,j=i或j=i-1.
② non local根据不同位置的关系计算响应,fc使用学习到的权重。换言之,fc中,和之间不是函数关系,而non local中则是函数关系。
③ non local支持输入不同尺寸,并且保持输出和输入相同的尺寸;fc则需要输入和输出均为固定的尺寸,并且丢失了位置关系。
④ non local可以用在网络的早期部分,fc通常用在网络最后。
3. f和g的形式
3.1 g的形式
为简单起见,只考虑g为线性形式,,为需要学习的权重向量,在空域可以使用1*1conv实现,在空间时间域(如时间序列的图像)可以通过1*1*1的卷积实现。
3.2 f为gaussian
其中为点乘,因为点乘在深度学习平台中更易实现(欧式距离也可以)。此时归一化系数
3.3 f为embedded Gaussian
其中,,此时
self attention模块和non local的关系:可以认为self attention为embedded Gaussian的特殊形式,如给定i,沿着j维度变成了计算softmax。此时,即为self attention的形式。
3.4 点乘
f可以定义为点乘的相似度(此处使用embedded的形式):
此时,归一化系数,N为x中所有位置的数量,而不是f的sum,这样可以简化梯度的计算。
点乘和embedded Gaussian的区别是是否使用了作为激活函数的softmax。
3.5 Concatenation
其中代表concatenation,即拼接。为权重向量,用于将拼接后的向量映射到一个标量。
4. Non local block
将之前公式的non local操作扩展成non local block,可以嵌入到目前的网络结构中,如下:
其中,代表残差连接。残差连接方便将non local block嵌入到之前与训练的模型中,避免打乱其初始行为(如将初始化为0)。
non local block如下图所示。3.2,3.3,3.4中的pairwise计算对应于下图中的矩阵乘法。在网络后面的特征图上,pairwise计算量比较小。
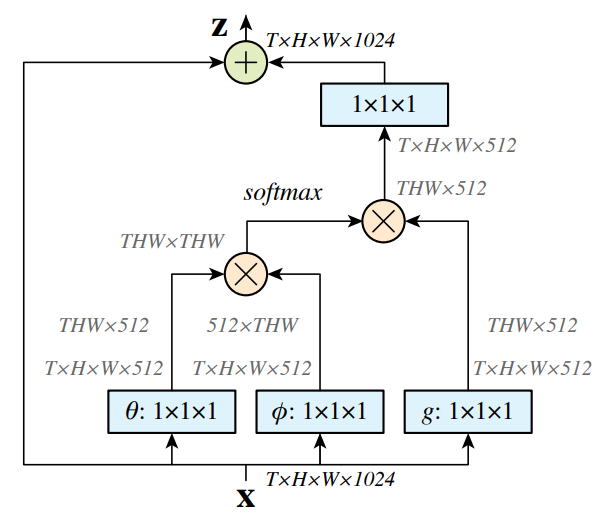
说明:
1. 若为图像,则使用1*1conv,且图中无T;若为视频,则使用1*1*1conv,且图中有T。
2. 图中softmax指对该矩阵每行计算softmax。
5. 降低计算量
5.1 降低x的通道数量
将,,降低为x的通道数量的一半,可以降低计算量。
5.2 对x下采样。
对x下采样,可以进一步降低计算量。
此时,1中的共识修改为,其中为对x进行下采样后的输入(如pooling)。这种方式可以降低pariwsie计算到原来的1/4,一方面不影响non local的行为,另一方面,使得计算更加稀疏。可以通过在上图中和后面加一个max pooling来实现。
6. 代码:
6.1 embedded_gaussian

1 class _NonLocalBlockND(nn.Module): 2 def __init__(self, in_channels, inter_channels=None, dimension=3, sub_sample=True, bn_layer=True): 3 """ 4 :param in_channels: 5 :param inter_channels: 6 :param dimension: 7 :param sub_sample: 8 :param bn_layer: 9 """ 10 11 super(_NonLocalBlockND, self).__init__() 12 13 assert dimension in [1, 2, 3] 14 15 self.dimension = dimension 16 self.sub_sample = sub_sample 17 18 self.in_channels = in_channels 19 self.inter_channels = inter_channels 20 21 if self.inter_channels is None: 22 self.inter_channels = in_channels // 2 23 if self.inter_channels == 0: 24 self.inter_channels = 1 25 26 if dimension == 3: 27 conv_nd = nn.Conv3d 28 max_pool_layer = nn.MaxPool3d(kernel_size=(1, 2, 2)) 29 bn = nn.BatchNorm3d 30 elif dimension == 2: 31 conv_nd = nn.Conv2d 32 max_pool_layer = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2)) 33 bn = nn.BatchNorm2d 34 else: 35 conv_nd = nn.Conv1d 36 max_pool_layer = nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=(2)) 37 bn = nn.BatchNorm1d 38 39 self.g = conv_nd(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.inter_channels, 40 kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0) # g函数,1*1conv,用于降维 41 42 if bn_layer: 43 self.W = nn.Sequential( # 1*1conv,用于图2中变换到原始维度 44 conv_nd(in_channels=self.inter_channels, out_channels=self.in_channels, 45 kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0), 46 bn(self.in_channels) 47 ) 48 nn.init.constant_(self.W[1].weight, 0) 49 nn.init.constant_(self.W[1].bias, 0) 50 else: 51 self.W = conv_nd(in_channels=self.inter_channels, out_channels=self.in_channels, 52 kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0) # 1*1conv,用于图2中变换到原始维度 53 nn.init.constant_(self.W.weight, 0) 54 nn.init.constant_(self.W.bias, 0) 55 56 self.theta = conv_nd(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.inter_channels, 57 kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0) # θ函数,1*1conv,用于降维 58 self.phi = conv_nd(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.inter_channels, 59 kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0) # φ函数,1*1conv,用于降维 60 61 if sub_sample: 62 self.g = nn.Sequential(self.g, max_pool_layer) 63 self.phi = nn.Sequential(self.phi, max_pool_layer) 64 65 def forward(self, x, return_nl_map=False): 66 """ 67 :param x: (b, c, t, h, w) 68 :param return_nl_map: if True return z, nl_map, else only return z. 69 :return: 70 """ 71 # 令x维度B*C*(K):一维时,x为B*C*(K1);二维时,x为B*C*(K1*K2);三维时,x为B*C*(K1*K2*K3) 72 batch_size = x.size(0) # batchsize 73 74 g_x = self.g(x).view(batch_size, self.inter_channels, -1) # 通过g函数,并reshape,得到B*inter_channels*(K)矩阵 75 g_x = g_x.permute(0, 2, 1) # 得到B*(K)*inter_channels矩阵,和图2中一致 76 77 theta_x = self.theta(x).view(batch_size, self.inter_channels, -1) # 通过θ函数,并reshape,得到B*inter_channels*(K)矩阵 78 theta_x = theta_x.permute(0, 2, 1) # 得到B*(K)*inter_channels矩阵,和图2中一致 79 phi_x = self.phi(x).view(batch_size, self.inter_channels, -1) # 通过φ函数,并reshape,得到B*inter_channels*(K)矩阵 80 f = torch.matmul(theta_x, phi_x) # 得到B*(K)*(K)矩阵,和图2中一致 81 f_div_C = F.softmax(f, dim=-1) # 通过softmax,对最后一维归一化,得到归一化的特征,即概率,B*(K)*(K) 82 83 y = torch.matmul(f_div_C, g_x) # 得到B*(K)*inter_channels矩阵,和图2中一致 84 y = y.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous() # 得到B*inter_channels*(K)矩阵,和图2中一致 85 y = y.view(batch_size, self.inter_channels, *x.size()[2:]) # 得到B*inter_channels*(K1或K1*K2或K1*K2*K3)矩阵,和图2中一致 86 W_y = self.W(y) # 得到B*C*(K)矩阵,和图2中一致 87 z = W_y + x # 特征图和non local的图相加,得到新的特征图,B*C*(K) 88 89 if return_nl_map: 90 return z, f_div_C # 返回结果及归一化的特征 91 return z 92 93 94 class NONLocalBlock1D(_NonLocalBlockND): 95 def __init__(self, in_channels, inter_channels=None, sub_sample=True, bn_layer=True): 96 super(NONLocalBlock1D, self).__init__(in_channels, 97 inter_channels=inter_channels, 98 dimension=1, sub_sample=sub_sample, 99 bn_layer=bn_layer) 100 101 102 class NONLocalBlock2D(_NonLocalBlockND): 103 def __init__(self, in_channels, inter_channels=None, sub_sample=True, bn_layer=True): 104 super(NONLocalBlock2D, self).__init__(in_channels, 105 inter_channels=inter_channels, 106 dimension=2, sub_sample=sub_sample, 107 bn_layer=bn_layer,) 108 109 110 class NONLocalBlock3D(_NonLocalBlockND): 111 def __init__(self, in_channels, inter_channels=None, sub_sample=True, bn_layer=True): 112 super(NONLocalBlock3D, self).__init__(in_channels, 113 inter_channels=inter_channels, 114 dimension=3, sub_sample=sub_sample, 115 bn_layer=bn_layer,) 116 117 118 if __name__ == '__main__': 119 import torch 120 121 for (sub_sample_, bn_layer_) in [(True, True), (False, False), (True, False), (False, True)]: 122 img = torch.zeros(2, 3, 20) 123 net = NONLocalBlock1D(3, sub_sample=sub_sample_, bn_layer=bn_layer_) 124 out = net(img) 125 print(out.size()) 126 127 img = torch.zeros(2, 3, 20, 20) 128 net = NONLocalBlock2D(3, sub_sample=sub_sample_, bn_layer=bn_layer_, store_last_batch_nl_map=True) 129 out = net(img) 130 print(out.size()) 131 132 img = torch.randn(2, 3, 8, 20, 20) 133 net = NONLocalBlock3D(3, sub_sample=sub_sample_, bn_layer=bn_layer_, store_last_batch_nl_map=True) 134 out = net(img) 135 print(out.size())
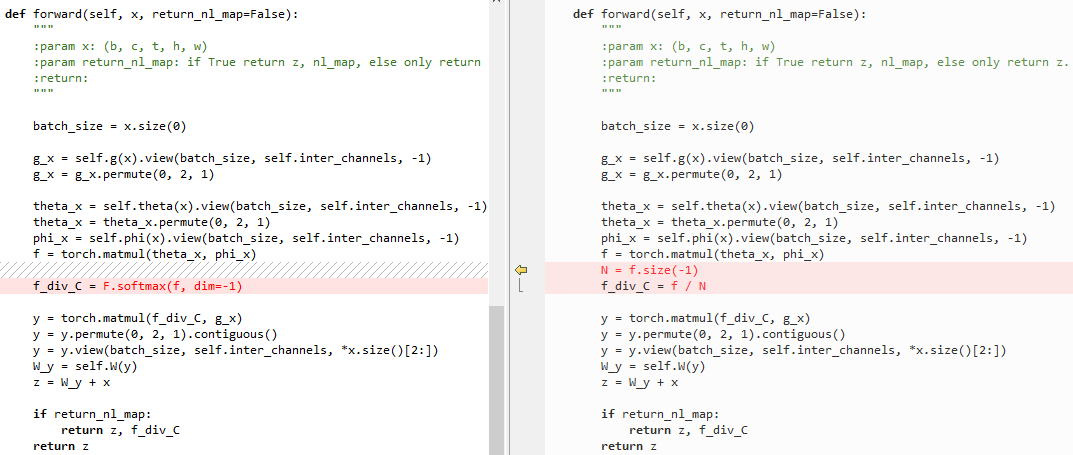
6.2 embedded Gaussian和点乘的区别
点乘代码:

1 class _NonLocalBlockND(nn.Module): 2 def __init__(self, in_channels, inter_channels=None, dimension=3, sub_sample=True, bn_layer=True): 3 super(_NonLocalBlockND, self).__init__() 4 5 assert dimension in [1, 2, 3] 6 7 self.dimension = dimension 8 self.sub_sample = sub_sample 9 10 self.in_channels = in_channels 11 self.inter_channels = inter_channels 12 13 if self.inter_channels is None: 14 self.inter_channels = in_channels // 2 15 if self.inter_channels == 0: 16 self.inter_channels = 1 17 18 if dimension == 3: 19 conv_nd = nn.Conv3d 20 max_pool_layer = nn.MaxPool3d(kernel_size=(1, 2, 2)) 21 bn = nn.BatchNorm3d 22 elif dimension == 2: 23 conv_nd = nn.Conv2d 24 max_pool_layer = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2)) 25 bn = nn.BatchNorm2d 26 else: 27 conv_nd = nn.Conv1d 28 max_pool_layer = nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=(2)) 29 bn = nn.BatchNorm1d 30 31 self.g = conv_nd(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.inter_channels, 32 kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0) 33 34 if bn_layer: 35 self.W = nn.Sequential( 36 conv_nd(in_channels=self.inter_channels, out_channels=self.in_channels, 37 kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0), 38 bn(self.in_channels) 39 ) 40 nn.init.constant_(self.W[1].weight, 0) 41 nn.init.constant_(self.W[1].bias, 0) 42 else: 43 self.W = conv_nd(in_channels=self.inter_channels, out_channels=self.in_channels, 44 kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0) 45 nn.init.constant_(self.W.weight, 0) 46 nn.init.constant_(self.W.bias, 0) 47 48 self.theta = conv_nd(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.inter_channels, 49 kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0) 50 51 self.phi = conv_nd(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.inter_channels, 52 kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0) 53 54 if sub_sample: 55 self.g = nn.Sequential(self.g, max_pool_layer) 56 self.phi = nn.Sequential(self.phi, max_pool_layer) 57 58 def forward(self, x, return_nl_map=False): 59 """ 60 :param x: (b, c, t, h, w) 61 :param return_nl_map: if True return z, nl_map, else only return z. 62 :return: 63 """ 64 # 令x维度B*C*(K):一维时,x为B*C*(K1);二维时,x为B*C*(K1*K2);三维时,x为B*C*(K1*K2*K3) 65 batch_size = x.size(0) 66 67 g_x = self.g(x).view(batch_size, self.inter_channels, -1) # 通过g函数,并reshape,得到B*inter_channels*(K)矩阵 68 g_x = g_x.permute(0, 2, 1) # 得到B*(K)*inter_channels矩阵,和图2中一致 69 70 theta_x = self.theta(x).view(batch_size, self.inter_channels, -1) # 通过θ函数,并reshape,得到B*inter_channels*(K)矩阵 71 theta_x = theta_x.permute(0, 2, 1) # 得到B*(K)*inter_channels矩阵,和图2中一致 72 phi_x = self.phi(x).view(batch_size, self.inter_channels, -1) # 通过φ函数,并reshape,得到B*inter_channels*(K)矩阵 73 f = torch.matmul(theta_x, phi_x) # 得到B*(K)*(K)矩阵,和图2中一致 74 N = f.size(-1) # 最后一维的维度 75 f_div_C = f / N # 对最后一维归一化 76 77 y = torch.matmul(f_div_C, g_x) # 得到B*(K)*inter_channels矩阵,和图2中一致 78 y = y.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous() # 得到B*inter_channels*(K)矩阵,和图2中一致 79 y = y.view(batch_size, self.inter_channels, *x.size()[2:]) # 得到B*inter_channels*(K1或K1*K2或K1*K2*K3)矩阵,和图2中一致 80 W_y = self.W(y) # 得到B*C*(K)矩阵,和图2中一致 81 z = W_y + x # 特征图和non local的图相加,得到新的特征图,B*C*(K) 82 83 if return_nl_map: 84 return z, f_div_C # 返回结果及归一化的特征 85 return z 86 87 88 class NONLocalBlock1D(_NonLocalBlockND): 89 def __init__(self, in_channels, inter_channels=None, sub_sample=True, bn_layer=True): 90 super(NONLocalBlock1D, self).__init__(in_channels, 91 inter_channels=inter_channels, 92 dimension=1, sub_sample=sub_sample, 93 bn_layer=bn_layer) 94 95 96 class NONLocalBlock2D(_NonLocalBlockND): 97 def __init__(self, in_channels, inter_channels=None, sub_sample=True, bn_layer=True): 98 super(NONLocalBlock2D, self).__init__(in_channels, 99 inter_channels=inter_channels, 100 dimension=2, sub_sample=sub_sample, 101 bn_layer=bn_layer) 102 103 104 class NONLocalBlock3D(_NonLocalBlockND): 105 def __init__(self, in_channels, inter_channels=None, sub_sample=True, bn_layer=True): 106 super(NONLocalBlock3D, self).__init__(in_channels, 107 inter_channels=inter_channels, 108 dimension=3, sub_sample=sub_sample, 109 bn_layer=bn_layer) 110 111 112 if __name__ == '__main__': 113 import torch 114 115 for (sub_sample_, bn_layer_) in [(True, True), (False, False), (True, False), (False, True)]: 116 img = torch.zeros(2, 3, 20) 117 net = NONLocalBlock1D(3, sub_sample=sub_sample_, bn_layer=bn_layer_) 118 out = net(img) 119 print(out.size()) 120 121 img = torch.zeros(2, 3, 20, 20) 122 net = NONLocalBlock2D(3, sub_sample=sub_sample_, bn_layer=bn_layer_) 123 out = net(img) 124 print(out.size()) 125 126 img = torch.randn(2, 3, 8, 20, 20) 127 net = NONLocalBlock3D(3, sub_sample=sub_sample_, bn_layer=bn_layer_) 128 out = net(img) 129 print(out.size())
左侧为embedded Gaussian,右侧为点乘
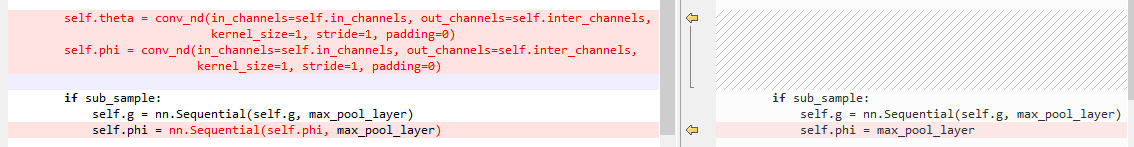
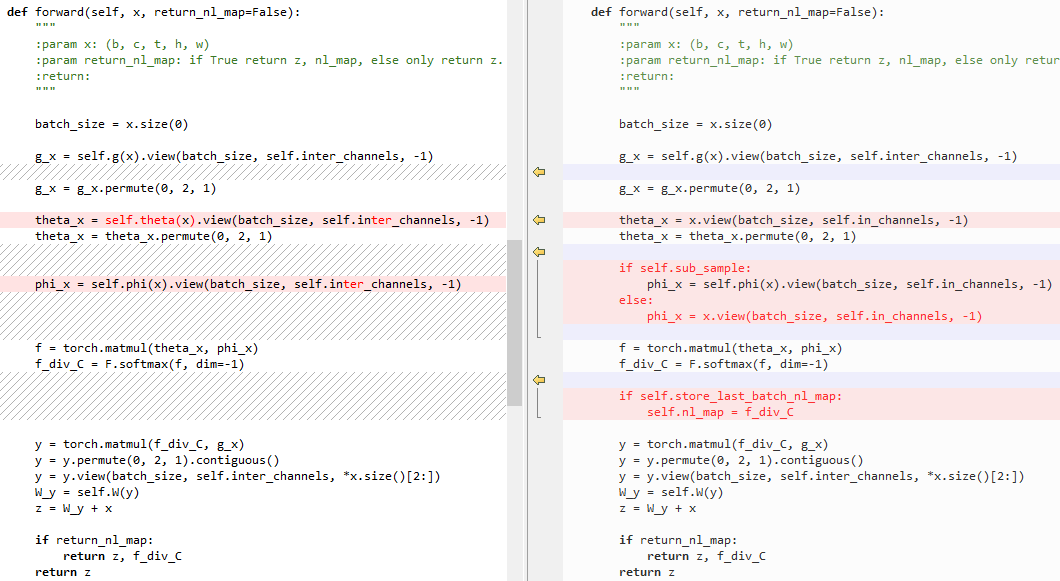
6.3 embedded Gaussian和Gaussian的区别
左侧为embedded Gaussian,右侧为Gaussian
初始化:
forward:
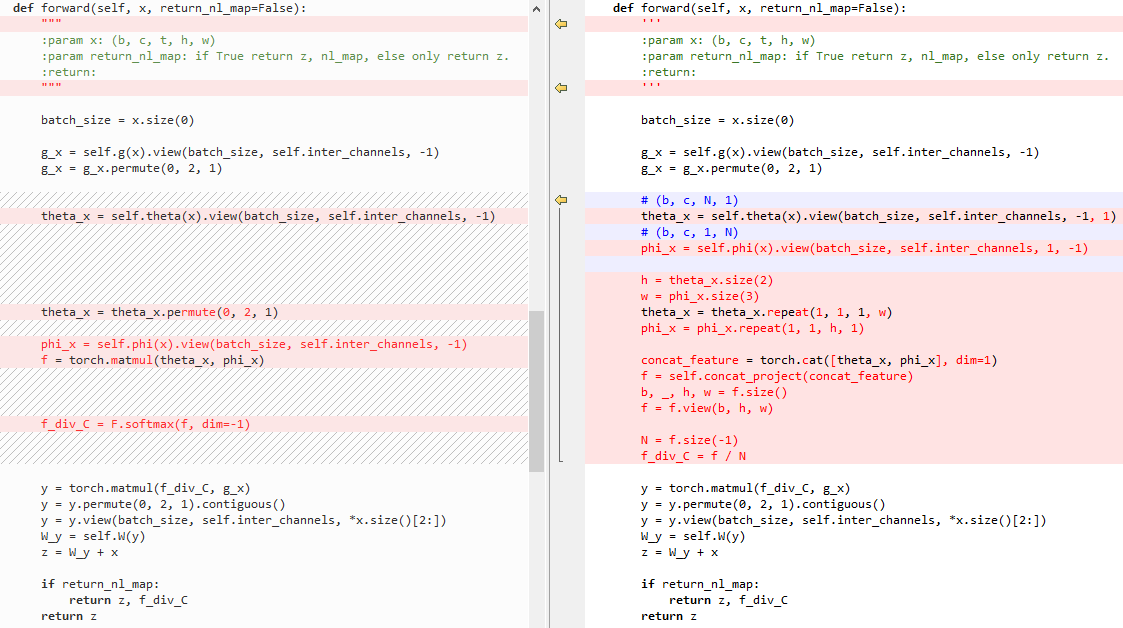
6.4 embedded Gaussian和Concatenation的区别
Concatenation代码:

1 class _NonLocalBlockND(nn.Module): 2 def __init__(self, in_channels, inter_channels=None, dimension=3, sub_sample=True, bn_layer=True): 3 super(_NonLocalBlockND, self).__init__() 4 5 assert dimension in [1, 2, 3] 6 7 self.dimension = dimension 8 self.sub_sample = sub_sample 9 10 self.in_channels = in_channels 11 self.inter_channels = inter_channels 12 13 if self.inter_channels is None: 14 self.inter_channels = in_channels // 2 15 if self.inter_channels == 0: 16 self.inter_channels = 1 17 18 if dimension == 3: 19 conv_nd = nn.Conv3d 20 max_pool_layer = nn.MaxPool3d(kernel_size=(1, 2, 2)) 21 bn = nn.BatchNorm3d 22 elif dimension == 2: 23 conv_nd = nn.Conv2d 24 max_pool_layer = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2)) 25 bn = nn.BatchNorm2d 26 else: 27 conv_nd = nn.Conv1d 28 max_pool_layer = nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=(2)) 29 bn = nn.BatchNorm1d 30 31 self.g = conv_nd(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.inter_channels, 32 kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0) 33 34 if bn_layer: 35 self.W = nn.Sequential( 36 conv_nd(in_channels=self.inter_channels, out_channels=self.in_channels, 37 kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0), 38 bn(self.in_channels) 39 ) 40 nn.init.constant_(self.W[1].weight, 0) 41 nn.init.constant_(self.W[1].bias, 0) 42 else: 43 self.W = conv_nd(in_channels=self.inter_channels, out_channels=self.in_channels, 44 kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0) 45 nn.init.constant_(self.W.weight, 0) 46 nn.init.constant_(self.W.bias, 0) 47 48 self.theta = conv_nd(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.inter_channels, 49 kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0) 50 51 self.phi = conv_nd(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.inter_channels, 52 kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0) 53 54 self.concat_project = nn.Sequential( # 将concat后的特征降维到1维的矩阵 55 nn.Conv2d(self.inter_channels * 2, 1, 1, 1, 0, bias=False), 56 nn.ReLU() 57 ) 58 59 if sub_sample: 60 self.g = nn.Sequential(self.g, max_pool_layer) 61 self.phi = nn.Sequential(self.phi, max_pool_layer) 62 63 def forward(self, x, return_nl_map=False): 64 ''' 65 :param x: (b, c, t, h, w) 66 :param return_nl_map: if True return z, nl_map, else only return z. 67 :return: 68 ''' 69 # 令x维度B*C*(K):一维时,x为B*C*(K1);二维时,x为B*C*(K1*K2);三维时,x为B*C*(K1*K2*K3) 70 batch_size = x.size(0) 71 72 g_x = self.g(x).view(batch_size, self.inter_channels, -1) # 通过g函数,并reshape,得到B*inter_channels*(K)矩阵 73 g_x = g_x.permute(0, 2, 1) # 得到B*(K)*inter_channels矩阵,和图2中一致 74 75 # (b, c, N, 1) 76 theta_x = self.theta(x).view(batch_size, self.inter_channels, -1, 1) # 通过θ函数,并reshape,得到B*inter_channels*(K)*1矩阵 77 # (b, c, 1, N) 78 phi_x = self.phi(x).view(batch_size, self.inter_channels, 1, -1) # 通过φ函数,并reshape,得到B*inter_channels*1*(K)矩阵 79 80 h = theta_x.size(2) # (K) 81 w = phi_x.size(3) # (K) 82 theta_x = theta_x.repeat(1, 1, 1, w) # B*inter_channels*(K)*(K) 83 phi_x = phi_x.repeat(1, 1, h, 1) # B*inter_channels*(K)*(K) 84 85 concat_feature = torch.cat([theta_x, phi_x], dim=1) # B*(2*inter_channels)*(K)*(K) 86 f = self.concat_project(concat_feature) # B*1*(K)*(K) 87 b, _, h, w = f.size() # B,_,(K),(K) 88 f = f.view(b, h, w) # B*(K)*(K) 89 90 N = f.size(-1) # (K) 91 f_div_C = f / N # 最后一维归一化,B*(K)*(K) 92 93 y = torch.matmul(f_div_C, g_x) # 得到B*(K)*inter_channels矩阵,和图2中一致 94 y = y.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous()# 得到B*inter_channels*(K)矩阵,和图2中一致 95 y = y.view(batch_size, self.inter_channels, *x.size()[2:]) # 得到B*inter_channels*(K1或K1*K2或K1*K2*K3)矩阵,和图2中一致 96 W_y = self.W(y) # 得到B*C*(K)矩阵,和图2中一致 97 z = W_y + x # 特征图和non local的图相加,得到新的特征图,B*C*(K) 98 99 if return_nl_map: 100 return z, f_div_C # 返回结果及归一化的特征 101 return z 102 103 104 class NONLocalBlock1D(_NonLocalBlockND): 105 def __init__(self, in_channels, inter_channels=None, sub_sample=True, bn_layer=True): 106 super(NONLocalBlock1D, self).__init__(in_channels, 107 inter_channels=inter_channels, 108 dimension=1, sub_sample=sub_sample, 109 bn_layer=bn_layer) 110 111 112 class NONLocalBlock2D(_NonLocalBlockND): 113 def __init__(self, in_channels, inter_channels=None, sub_sample=True, bn_layer=True): 114 super(NONLocalBlock2D, self).__init__(in_channels, 115 inter_channels=inter_channels, 116 dimension=2, sub_sample=sub_sample, 117 bn_layer=bn_layer) 118 119 120 class NONLocalBlock3D(_NonLocalBlockND): 121 def __init__(self, in_channels, inter_channels=None, sub_sample=True, bn_layer=True,): 122 super(NONLocalBlock3D, self).__init__(in_channels, 123 inter_channels=inter_channels, 124 dimension=3, sub_sample=sub_sample, 125 bn_layer=bn_layer) 126 127 128 if __name__ == '__main__': 129 import torch 130 131 for (sub_sample_, bn_layer_) in [(True, True), (False, False), (True, False), (False, True)]: 132 img = torch.zeros(2, 3, 20) 133 net = NONLocalBlock1D(3, sub_sample=sub_sample_, bn_layer=bn_layer_) 134 out = net(img) 135 print(out.size()) 136 137 img = torch.zeros(2, 3, 20, 20) 138 net = NONLocalBlock2D(3, sub_sample=sub_sample_, bn_layer=bn_layer_) 139 out = net(img) 140 print(out.size()) 141 142 img = torch.randn(2, 3, 8, 20, 20) 143 net = NONLocalBlock3D(3, sub_sample=sub_sample_, bn_layer=bn_layer_) 144 out = net(img) 145 print(out.size())
左侧为embedded Gaussian,右侧为Concatenation
初始化:

forward:
posted on 2020-03-29 15:02 darkknightzh 阅读(1489) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报








【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架