【Kill Thread Part.1-8】双刃剑:多线程会导致的问题
【Kill Thread Part.1-8】双刃剑:多线程会导致的问题
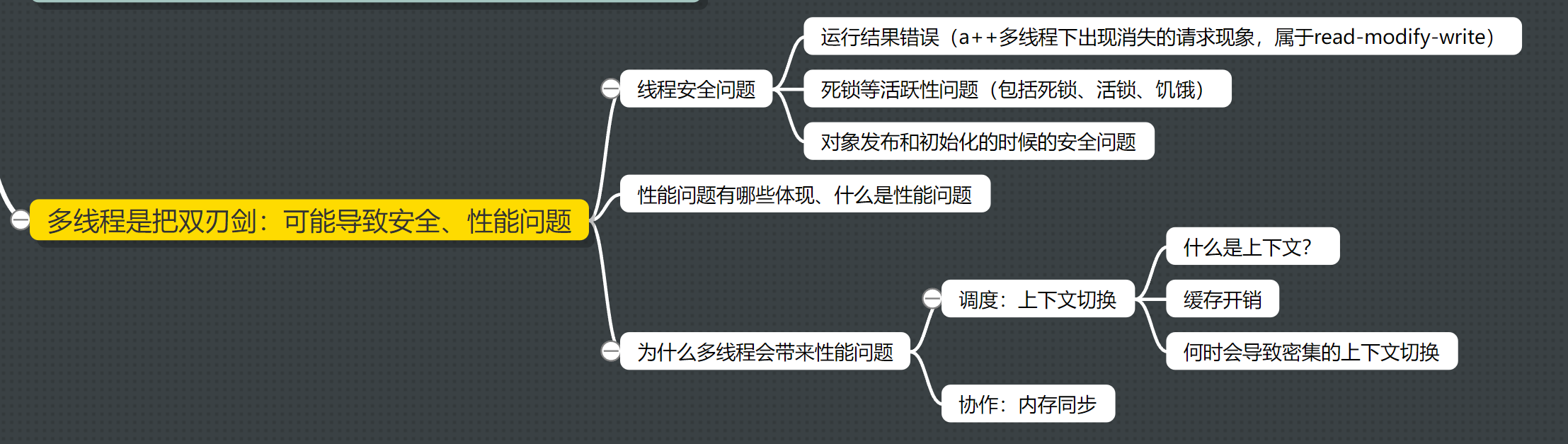
- 一共有哪几类线程安全问题?
- 哪些场景需要额外注意线程安全的问题?
- 什么事多线程带来的上下文切换?
一、线程安全问题
1、什么是线程安全

通俗的讲:

2、运行结果错误:a++多线程下出现消失的请求现象
①出错代码
/**
* 描述: 第一种:运行结果出错
* 演示:计数不准确(减少),找出具体出错的位置
*/
public class MultiThreadsError implements Runnable{
static MultiThreadsError instance = new MultiThreadsError();
int index = 0;
@Override
public void run() {
//while (index < 10000) {
// index++;
//}
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
index++;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(instance);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(instance);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
System.out.println(instance.index);
}
}
运行之后,index的值每次都不一样。
②原理分析
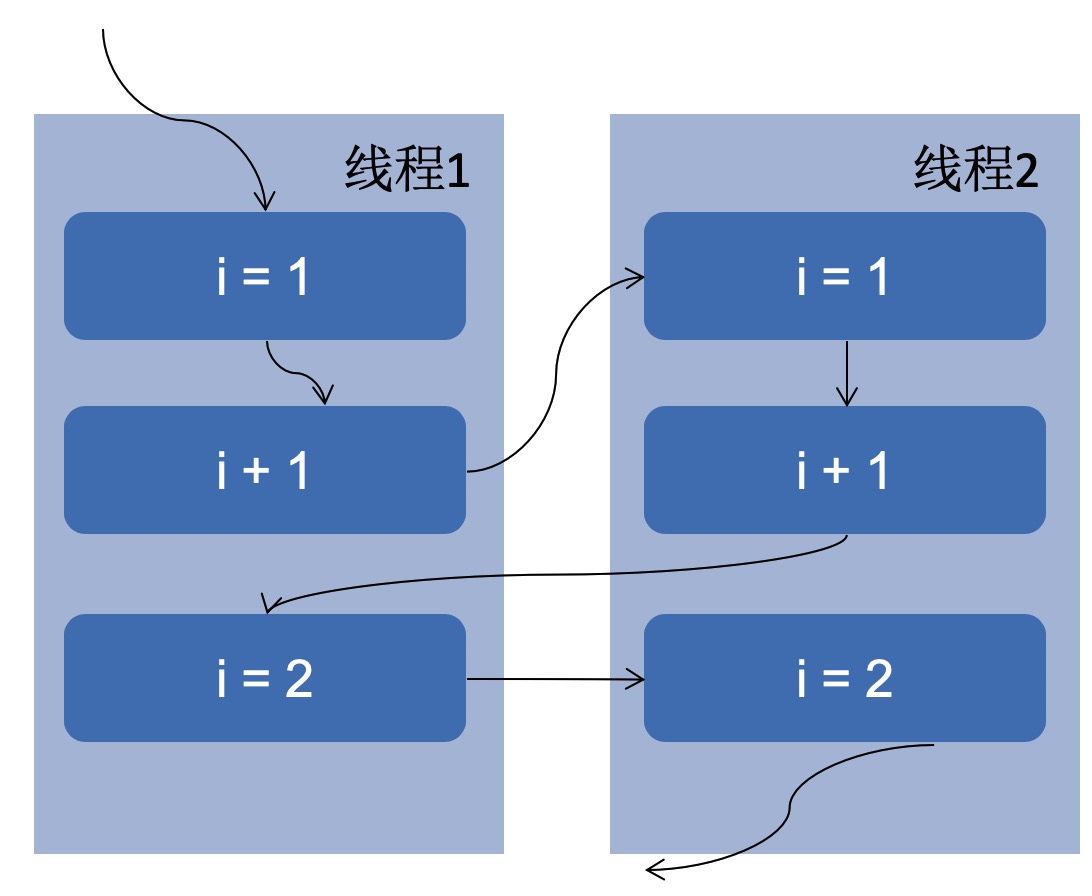
线程1执行了i+1的操作,还没有写回去,此时线程2访问i,i还是1,加一操作还是2,最后两个线程写入i,i还是2,发生了两次操作,只有一次生效的结果。
③代码升级
/**
* 描述: 第一种:运行结果出错。 演示计数不准确(减少),找出具体出错的位置。
*/
public class MultiThreadsError implements Runnable {
static MultiThreadsError instance = new MultiThreadsError();
int index = 0;
static AtomicInteger realIndex = new AtomicInteger();
static AtomicInteger wrongCount = new AtomicInteger();
//让线程可以在某一个地方等待,直到等待的人员都就绪了,一起出发
static volatile CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier1 = new CyclicBarrier(2);
static volatile CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier2 = new CyclicBarrier(2);
final boolean[] marked = new boolean[10000000];
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(instance);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(instance);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
System.out.println("表面上结果是" + instance.index);
System.out.println("真正运行的次数" + realIndex.get());
System.out.println("错误次数" + wrongCount.get());
}
@Override
public void run() {
marked[0] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
try {
cyclicBarrier2.reset();
cyclicBarrier1.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
index++;
try {
cyclicBarrier1.reset();
cyclicBarrier2.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
realIndex.incrementAndGet();
synchronized (instance) {
if (marked[index] && marked[index - 1]) {
System.out.println("发生错误" + index);
wrongCount.incrementAndGet();
}
marked[index] = true;
}
}
}
}

3、活跃性问题:死锁、活锁、饥饿
①死锁
/**
* 描述: 第二章线程安全问题,演示死锁。
*/
public class MultiThreadError implements Runnable {
int flag = 1;
//类锁
static Object o1 = new Object();
static Object o2 = new Object();
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("flag = " + flag);
if (flag == 1) {
synchronized (o1) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (o2) {
System.out.println("1");
}
}
}
if (flag == 0) {
synchronized (o2) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (o1) {
System.out.println("0");
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MultiThreadError r1 = new MultiThreadError();
MultiThreadError r2 = new MultiThreadError();
r1.flag = 1;
r2.flag = 0;
new Thread(r1).start();
new Thread(r2).start();
}
}
两个线程一直等待对方释放锁
4、对象发布和初始化的时候的安全问题
①什么是对象发布
让一个对象可以在超过这个类的范围之外去其他类使用,比如:
- 一个对象被声明为public
- 一个方法的return是一个对象
- 一个类的对象作为参数,传递到某一个方法中
②什么是逸出

③private逸出
测试代码
/**
* 描述: 发布逸出
*/
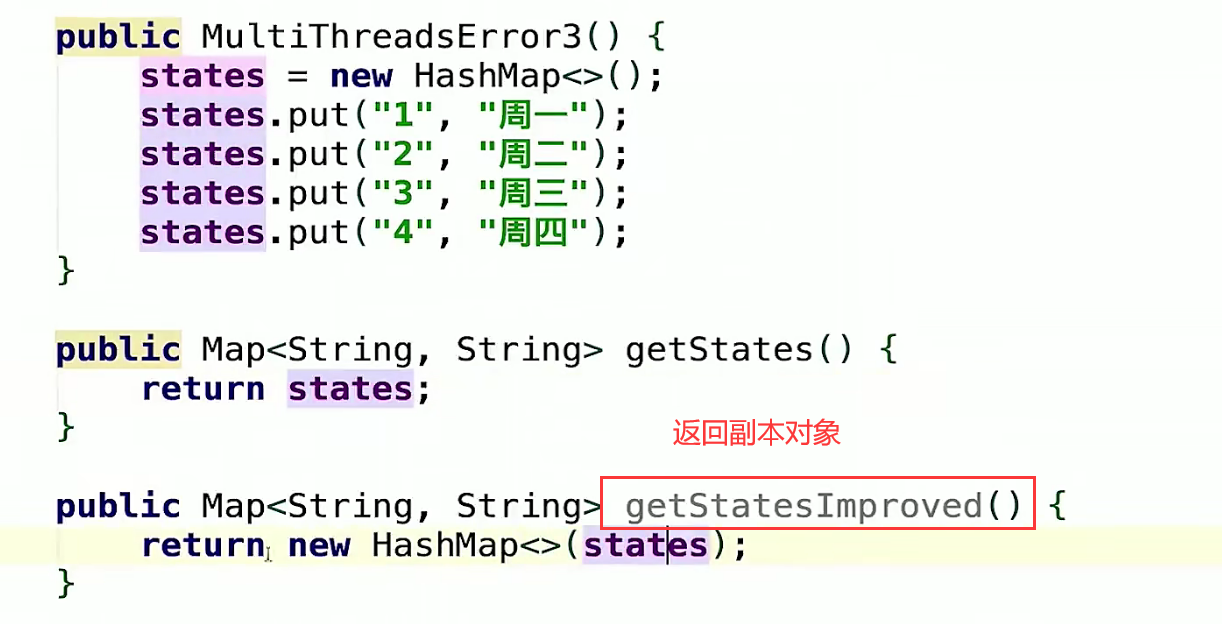
public class MultiThreadsError3 {
private Map<String, String> states;
public MultiThreadsError3() {
states = new HashMap<>();
states.put("1","周一");
states.put("2","周二");
states.put("3","周三");
states.put("4","周四");
}
//把私有的变量给发布出去了
public Map<String, String> getStates() {
return states;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MultiThreadsError3 multiThreadsError3 = new MultiThreadsError3();
Map<String, String> states = multiThreadsError3.getStates();
System.out.println(states.get("1"));
states.remove("1");
System.out.println(states.get("1"));
}
}
运行结果:

我们本意是,不允许线程修改states,但是在多线程的情况下,如果有一个线程把这个逸出的states给修改了,其他线程都会收到影响,危害很大。
④在构造函数中未初始化完毕就this赋值
/**
* 描述: 初始化未完毕,就this赋值
*/
public class MultiThreadsError4 {
static Point point;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new PointMaker().start();
//Thread.sleep(10); //结果为1,0
Thread.sleep(1000); //结果为1,1
if (point != null) {
System.out.println(point);
}
}
}
class Point{
private final int x, y;
public Point(int x, int y) throws InterruptedException {
this.x = x;
MultiThreadsError4.point = this;
Thread.sleep(100);
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return x + "," + y;
}
}
class PointMaker extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
try {
new Point(1, 1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
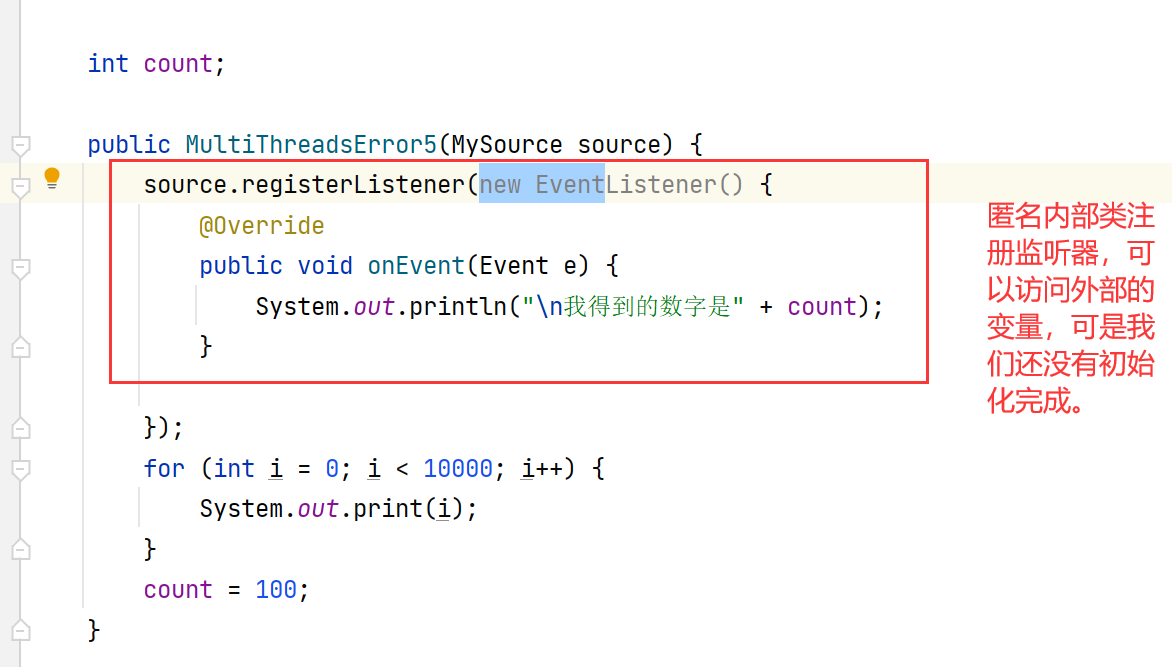
⑤观察者模式,匿名内部类注册监听器
/**
* 描述: 观察者模式
*/
public class MultiThreadsError5 {
int count;
public MultiThreadsError5(MySource source) {
source.registerListener(new EventListener() {
@Override
public void onEvent(Event e) {
System.out.println("\n我得到的数字是" + count);
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
System.out.print(i);
}
count = 100;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MySource mySource = new MySource();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
mySource.eventCome(new Event() {
});
}
}).start();
MultiThreadsError5 multiThreadsError5 = new MultiThreadsError5(mySource);
}
static class MySource {
private EventListener listener;
void registerListener(EventListener eventListener) {
this.listener = eventListener;
}
void eventCome(Event e) {
if (listener != null) {
listener.onEvent(e);
} else {
System.out.println("还未初始化完毕");
}
}
}
interface EventListener {
void onEvent(Event e);
}
interface Event {
}
}
分析:
⑥构造函数中新建线程
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 描述: 构造函数中新建线程
*/
public class MultiThreadsError6 {
private Map<String, String> states;
public MultiThreadsError6() {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
states = new HashMap<>();
states.put("1", "周一");
states.put("2", "周二");
states.put("3", "周三");
states.put("4", "周四");
}
}).start();
}
public Map<String, String> getStates() {
return states;
}
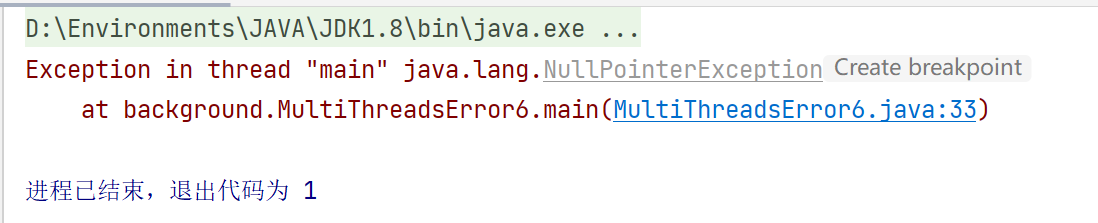
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MultiThreadsError6 multiThreadsError6 = new MultiThreadsError6();
//Thread.sleep(1000);时间不同,稳定性不同
System.out.println(multiThreadsError6.getStates().get("1"));
}
}
在初始化过程中新建线程,如果初始化没有完毕,去取值的话,会报空指针异常。
如果给主线程加个休眠的话,初始化完毕,就可以避免异常,这就造成了程序的稳定性很差。
二、解决多线程逸出问题
1、返回副本
- 解决private的问题
2、工厂模式使得初始化完毕
/**
* 描述: 用工厂模式修复刚才的初始化问题
*/
public class MultiThreadsError7 {
int count;
private EventListener listener;
private MultiThreadsError7(MySource source) {
listener = new EventListener() {
@Override
public void onEvent(MultiThreadsError5.Event e) {
System.out.println("\n我得到的数字是" + count);
}
};
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
System.out.print(i);
}
count = 100;
}
public static MultiThreadsError7 getInstance(MySource source) {
//初始化工作
MultiThreadsError7 safeListener = new MultiThreadsError7(source);
//注册监听器
source.registerListener(safeListener.listener);
return safeListener;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MySource mySource = new MySource();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
mySource.eventCome(new MultiThreadsError5.Event() {
});
}
}).start();
MultiThreadsError7 multiThreadsError7 = new MultiThreadsError7(mySource);
}
static class MySource {
private EventListener listener;
void registerListener(EventListener eventListener) {
this.listener = eventListener;
}
void eventCome(MultiThreadsError5.Event e) {
if (listener != null) {
listener.onEvent(e);
} else {
System.out.println("还未初始化完毕");
}
}
}
interface EventListener {
void onEvent(MultiThreadsError5.Event e);
}
interface Event {
}
}
通过使用工厂方法模式将初始化工作和注册监听器工作封装在一起。
三、各种需要考虑线程安全的情况

四、多线程会导致的性能问题
1、为什么多线程会带来性能问题

2、调度:上下文切换

上下文:保存现场
上下文切换:
- 挂起一个线程,把这个线程的状态保存下来(这个状态就是上下文)
- 包括我这个线程执行到哪一个指令了?变量的值是什么状态?
缓存开销:缓存失效
- 上下文切换之后,CPU需要重新进行缓存,寄存器的状态
何时会导致密集的上下文切换:抢锁、IO
3、协作:Java内存模型(下个章节)
编译器或者JVM会对我们的代码优化,对某些锁进行优化,内存方面的优化,如果缓存失效问题发生,也会造成开销。
想要多线程写锁,把多个线程进行调度,使得频繁上下文切换
五、总结
面试问题
- 你知道哪些线程不安全的情况?
- 平时哪些情况下需要额外注意线程安全问题
- 什么是多线程的上下文切换


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号