Spring MVC例子
学习Spring MVC的一个例子,参考书籍《Servlet、JSP、Spring MVC学习指南》,简单总结一下。
代码下载:https://github.com/PeiranZhang/springmvc-demo
本文参考链接:
https://www.cnblogs.com/yhtboke/p/5780140.html
https://blog.csdn.net/liubin5620/article/details/79922692
项目目录
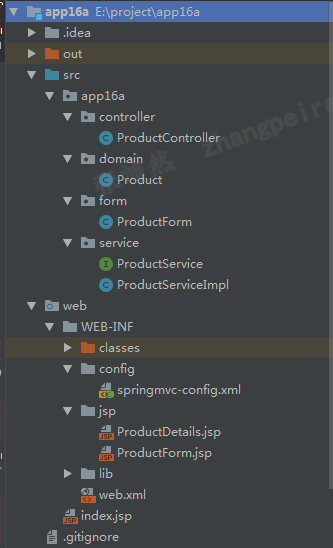
这里,没有采用maven来管理依赖,实际项目中可以使用maven方便管理项目,项目依赖的jar包如下所示

项目在IDEA中打包、部署到tomcat,可以参考博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/darange/p/10965700.html
web.xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0"> <!-- 配置前端控制器 --> <servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <!-- contextConfigLocation配置springmvc加载的配置文件适配器、处理映射器等--> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/config/springmvc-config.xml</param-value> </init-param> <!--值不为0表示,tomcat启动该应用时,加载servlet,而不是等到第一请求到来时再加载servlet--> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <!-- 所有访问都由DispatcherServlet进行解析--> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
springmvc-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 与spring注解配合使用,扫描指定包及其子包下面的带有Controller、Service注解下的类,生成bean--> <context:component-scan base-package="app16a.controller"></context:component-scan> <context:component-scan base-package="app16a.service"></context:component-scan> <!-- 如果在配置前端控制器时拦截了所有的请求,不做特殊处理就会导致部分静态资源无法使用。如果是这种情况就可以使用下面的配置来访问静态资源文件,所以使用resource配置--> <!-- 没有<annotation-driven/>,<resources/>元素会阻止任意控制器被调用--> <!-- 配置注解的处理器映射器和处理器适配器--> <mvc:annotation-driven/> <mvc:resources mapping="/*.html" location="/"/> <!-- 配置视图解析器,在Controller中设置视图名的时候会自动加上前缀和后缀 --> <bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"></property> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/> </bean> </beans>
Service
@Service注解可以指定名称,当一个接口有多个实现类时,在Controller里面注入时,可以指定实现类
//service加上名称,在一个接口多个实现类时,可以这样区分 @Service("productService") public class ProductServiceImpl implements ProductService { private Map<Long, Product> products = new HashMap<Long, Product>(); private AtomicLong generator = new AtomicLong(); @Override public Product add(Product product) { long newId = generator.incrementAndGet(); product.setId(newId); products.put(newId, product); System.out.println("Add" + product); return product; } @Override public Product get(long id) { return products.get(id); } }
Controller
Controller中使用@Qualifier指定具体的service
1.通过@RequestMapping,进行url与处理方法的映射,处理方法返回的是视图的名称,不需要写绝对路径和jsp后缀,这是因为web.xml中配置了视图解析器
2.处理方法里面参数可以自己定义,其中Model对象有spring生成,可以在model中添加对象,作为request对象,发送给jsp
3.注意转发与重定向的区别,代码编写方式可以参考代码。重定向返回的视图名字前加上"redirect:"
https://blog.csdn.net/liubin5620/article/details/79922692
1、转发使用的是getRequestDispatcher()方法;重定向使用的是sendRedirect();
2、转发:浏览器URL的地址栏不变。重定向:浏览器URL的地址栏改变;
3、转发是服务器行为,重定向是客户端行为;
4、转发是浏览器只做了一次访问请求。重定向是浏览器做了至少两次的访问请求;
5、转发2次跳转之间传输的信息不会丢失,重定向2次跳转之间传输的信息会丢失(request范围)。
转发是要比重定向快,因为重定向需要经过客户端,而转发没有。有时候,采用重定向会更好,若需要重定向到另外一个外部网站,则无法使用转发。另外,重定向还有一个应用场景:避免在用户重新加载页面时两次调用相同的动作。
例如,当提交产品表单的时候,执行保存的方法将会被调用,并执行相应的动作;这在一个真实的应用程序中,很有可能将表单中的所有产品信息加入到数据库中。但是如果在提交表单后,重新加载页面,执行保存的方法就很有可能再次被调用。同样的产品信息就将可能再次被添加,为了避免这种情况,提交表单后,你可以将用户重定向到一个不同的页面,这样的话,这个网页任意重新加载都没有副作用;
但是,使用重定向不太方便的地方是,使用它无法将值轻松地传递给目标页面。而采用转发,则可以简单地将属性添加到Model,使得目标视图可以轻松访问。由于重定向经过客户端,所以Model中的一切都会在重定向时丢失。但幸运的是,在Spring3.1版本以后,我们可以通过Flash属性,解决重定向时传值丢失的问题。
要使用Flash属性,必须在Spring MVC的配置文件中添加一个<annotation-driven/>。然后,还必须再方法上添加一个新的参数类型:org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.RedirectAttributes。
4.路径变量的使用,@PathVariable
5.获取请求参数,在处理方法中增加参数,并使用注解@RequestParam
Controller代码:
@Controller public class ProductController { @Autowired //按照名称,注入指定的接口实现类 @Qualifier("productService") ProductService productService; private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ProductController.class); @RequestMapping(value = "/product_input") public String inputProduct() { logger.info("inputProduct called"); return "ProductForm"; } //参数productForm中的字段与提交表当中的text文本框name一一对应 @RequestMapping(value = "/product_save") public String saveProduct(ProductForm productForm, Model model, RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes){ logger.info("saveProduct called"); Product product = new Product(); product.setName(productForm.getName()); product.setDescription(productForm.getDescription()); try { product.setPrice(Float.parseFloat( productForm.getPrice())); } catch (NumberFormatException e) { } productService.add(product); //转发 //model里面的内容作为request属性传递给jsp_servlet //model.addAttribute("product", product); //return "ProductDetails"; //重定向 // 客户端重新发送请求,Model无效 //通过addFlashAttribute,可以在jsp中引用对象 redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute(product); return "redirect:/product_details"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/product_details") public String productDetail(){ logger.info("productDetail called"); return "ProductDetails"; } //路径变量的使用 //http://localhost:8080/app16a/product/1 @RequestMapping(value = "/product/{id}") public String productGet(@PathVariable Long id,Model model){ Product product = productService.get(id); model.addAttribute(product); logger.info("productGet called"); return "ProductDetails"; } //获取请求参数 //http://localhost:8080/app16a/product?id=1 @RequestMapping(value = "/product") public String productGetWithParams(@RequestParam Long id,Model model){ Product product = productService.get(id); model.addAttribute(product); logger.info("productGetWithParams called"); return "ProductDetails"; } }
视图
PoductForm.jsp:form表单中各个文本输入控件的name作为request请求参数的键,发送给action指定的url
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>Add Product Form</title> </head> <body> <!--product_save与product_save.action效果一样--> <div id="global"> <form action="product_save.action" method="post"> <fieldset> <legend>Add a product</legend> <p> <label for="name">Product Name: </label> <input type="text" id="name" name="name" tabindex="1"> </p> <p> <label for="description1">Description: </label> <input type="text" id="description1" name="description" tabindex="2"> </p> <p> <label for="price">Price: </label> <input type="text" id="price" name="price" tabindex="3"> </p> <p id="buttons"> <input id="reset" type="reset" tabindex="4"> <input id="submit" type="submit" tabindex="5" value="Add Product"> </p> </fieldset> </form> </div> </body> </html>
ProductDetails.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>Save Product</title> </head> <body> <div id="global"> <h4>The product has been saved.</h4> <p> <h5>Details:</h5> <%-- Controller里面的Model中的product对象其实是作为request属性传递给jsp的,所以这里用requestScope来引用--%> Product Name: ${requestScope.product.name}<br/> Description: ${requestScope.product.description}<br/> Price: $${requestScope.product.price} </p> </div> </body> </html>
以上只是对Spring MVC的简单使用



