esp-now笔记
ESP NOW简介
介绍
- 官网介绍
ESP-NOW 是由乐鑫开发的另一款协议,可以使多个设备在没有或不使用 Wi-Fi 的情况下进行通信。这种协议类似常见于无线鼠标中的低功耗 2.4GHz 无线连接——设备在进行通信之前要进行配对。配对之后,设备之间的连接是持续的、点对点的,并且不需要握手协议。
- 启明云端:ESP-NOW的功能特性
一.简介
ESP-NOW是一种由乐鑫定义的无连接wi-fi通信,是由乐鑫开发的另一款协议,可以使多个设备在没有或不使用 Wi-Fi 的情况下进行通信。这种协议类似常见于无线鼠标中的低功耗 2.4GHz 无线连接——设备在进行通信之前要进行配对。配对之后,设备之间的连接是持续的、点对点的,并且不需要握手协议。
二.特点
1.无连接,设备配对简单,配对后可直接数据通信,距离授权,APP授权
2.协议精简O51上层5层协议精简为1层,降低延时,快速响应
3.加密安全
4.可以和wifi BLE共存
5.CPU,flash资源占用少
6.响应快,ms级
7.功耗低,协议精简,功耗降低
8.兼容性好,本地控制+远程控制,与路由器、热点共存
9.远距离快速稳定通信,可在视距500m稳定通信
10.支持单播、广播分组控制,同时支持上直设备
11.多形态控制 ,Button开关 ,Touch按键,LCD屏,语音,传感器控制等
- 来自于openAI的回复

相关学习页
获取本机mac地址
要通过 ESP-NOW 收发消息,需要知道接收板的 MAC 地址。每个开发板都有一个唯一的 MAC 地址,以下实例程序为打印mac地址。
示例程序01
#include <Arduino.h>
#ifdef ESP32
#include <WiFi.h>
#else
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#endif
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
WiFi.mode(WIFI_MODE_STA);
// 打印MAC地址
uint8_t mac[6];
WiFi.macAddress(mac);
Serial.println();
Serial.printf("const uint8_t mac_self[6] = {0x%02x, 0x%02x, 0x%02x, 0x%02x, 0x%02x, 0x%02x};", mac[0], mac[1], mac[2], mac[3], mac[4], mac[5]);
}
void loop()
{
delay(1000);
}
串口打印信息
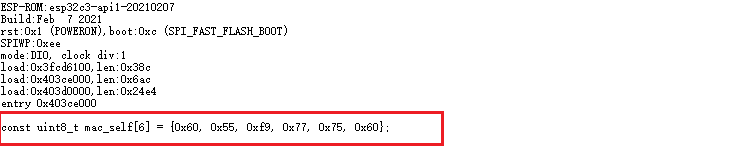
将打印的这一行信息复制到后续程序中
以下是我所使用的3块接收板mac地址速记信息
const uint8_t mac_self[6] = {0x60, 0x55, 0xf9, 0x77, 0x75, 0x60};//合宙esp32C3
const uint8_t mac_self[6] = {0x78, 0x21, 0x84, 0xc6, 0xd9, 0x8c};//esp32外置天线
const uint8_t mac_self[6] = {0x08, 0x3a, 0xf2, 0xb9, 0xa0, 0xe4};//esp32-旧CP2102
单向:一对多
使用 ESP-NOW(一对多)将数据从一个 ESP32 发送到多个 ESP32 或 ESP8266 开发板。
本示例均使用ESP32开发板,esp8266需对程序做适配修改。
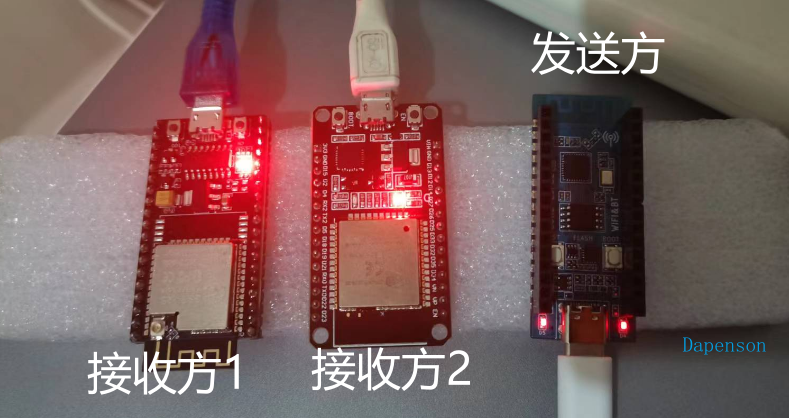
- 一台 ESP32 充当发送方;
- 多个 ESP32 或 ESP8266 板充当接收方。
- 如果消息成功下发,ESP32 发送方会收到一条确认消息。用以知道哪些板收到了消息,哪些板没有;
A接收方
将示例代码上传到接收方ESP32板中
示例程序02
#include <esp_now.h>
#include <WiFi.h>
//接收方用以接受数据的结构体 ***
//必须和发送方的结构体匹配 ***
typedef struct test_struct {
int x;
int y;
} test_struct;
//创建结构体 ***
test_struct myData;
//接收到数据时执行的回调函数 ***
void OnDataRecv(const uint8_t * mac, const uint8_t *incomingData, int len) {
memcpy(&myData, incomingData, sizeof(myData));
Serial.print("Bytes received: ");
Serial.println(len);
Serial.print("x: ");
Serial.println(myData.x);
Serial.print("y: ");
Serial.println(myData.y);
Serial.println();
}
void setup() {
//初始化串口
Serial.begin(115200);
//设置wifi模式为 Wi-Fi Station
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
//初始化 ESP-NOW,初始化失败则打印信息并退出
if (esp_now_init() != ESP_OK) {
Serial.println("Error initializing ESP-NOW");
return;
}
// 注册接受消息的回调函数
// 用以获取接收到的数据
esp_now_register_recv_cb(OnDataRecv);
}
void loop() {
delay(1000);
}
- 收到消息时打印的信息
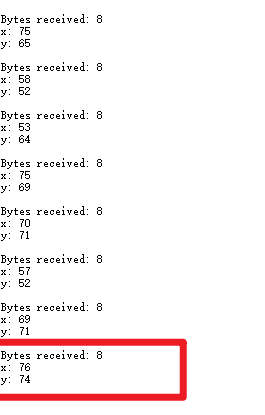
B发送方
以下代码通过 ESP-NOW 将不同的数据分别发送到指定的多个 ESP 板。或将相同数据一次性发送至所有接收方。
您应该使用接收方ESP板的 MAC 地址修改代码。还应该根据接收方ESP板的数量添加或删除代码行。
示例程序03
#include <esp_now.h>
#include <WiFi.h>
// 替换为esp接收方的MAC地址 ***
uint8_t mac_receive_1[] = {0x78, 0x21, 0x84, 0xc6, 0xd9, 0x8c}; // esp32外置天线
uint8_t mac_receive_2[] = {0x08, 0x3a, 0xf2, 0xb9, 0xa0, 0xe4}; // esp32-旧CP2102
// 发送方的结构体 ***
typedef struct test_struct
{
int x;
int y;
} test_struct;
// 创建结构体 ***
test_struct test_a;
test_struct test_b;
// 实例化espnow通讯的对等体
esp_now_peer_info_t peerInfo;
// 数据发送时的回调函数 ***
void OnDataSent(const uint8_t *mac_addr, esp_now_send_status_t status)
{
char macStr[18];
Serial.print("Packet to: ");
//把接收方mac地址复制为字符串
snprintf(macStr, sizeof(macStr), "%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x",
mac_addr[0], mac_addr[1], mac_addr[2], mac_addr[3], mac_addr[4], mac_addr[5]);
Serial.print(macStr);
Serial.print(" send status:\t");
Serial.println(status == ESP_NOW_SEND_SUCCESS ? "Delivery Success" : "Delivery Fail");
}
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
// 初始化espnow,如果失败则打印错误信息并退出
if (esp_now_init() != ESP_OK)
{
Serial.println("Error initializing ESP-NOW");
return;
}
// 注册消息发送的回调函数
esp_now_register_send_cb(OnDataSent);
// 配置对等体信息
// 通讯信道
peerInfo.channel = 0;
// 是否加密通讯信息
peerInfo.encrypt = false;
// 添加第1个对等体
memcpy(peerInfo.peer_addr, mac_receive_1, 6);
if (esp_now_add_peer(&peerInfo) != ESP_OK)
{
Serial.println("Failed to add peer");
return;
}
// 添加第2个对等体
memcpy(peerInfo.peer_addr, mac_receive_2, 6);
if (esp_now_add_peer(&peerInfo) != ESP_OK)
{
Serial.println("Failed to add peer");
return;
}
// 添加第3个对等体(如有更多则复制以下几行并修改mac地址)
/*
memcpy(peerInfo.peer_addr, mac_receive_3, 6);
if (esp_now_add_peer(&peerInfo) != ESP_OK)
{
Serial.println("Failed to add peer");
return;
}
*/
}
void loop()
{
test_a.x = random(0, 10);
test_a.y = random(0, 10);
test_b.x = random(50, 80);
test_b.y = random(50, 80);
// way 1: 发送数据给所有注册过的对等体
// peer_addr参数为0,则为发送数据给所有注册过的对等体
// esp_err_t result = esp_now_send(0, (uint8_t *)&test_a, sizeof(test_struct));
// way 2: 发送数据给指定的对等体
// peer_addr参数为指定的对等体的mac地址
esp_err_t result_1 = esp_now_send(mac_receive_1, (uint8_t *)&test_a, sizeof(test_struct));
esp_err_t result_2 = esp_now_send(mac_receive_2, (uint8_t *)&test_b, sizeof(test_struct));
if (result_1 == ESP_OK)
{
Serial.println("Sent with success: result_1");
}
else
{
Serial.println("Error sending the data: result_1");
}
if (result_2 == ESP_OK)
{
Serial.println("Sent with success: result_2");
}
else
{
Serial.println("Error sending the data: result_2");
}
delay(2000);
}
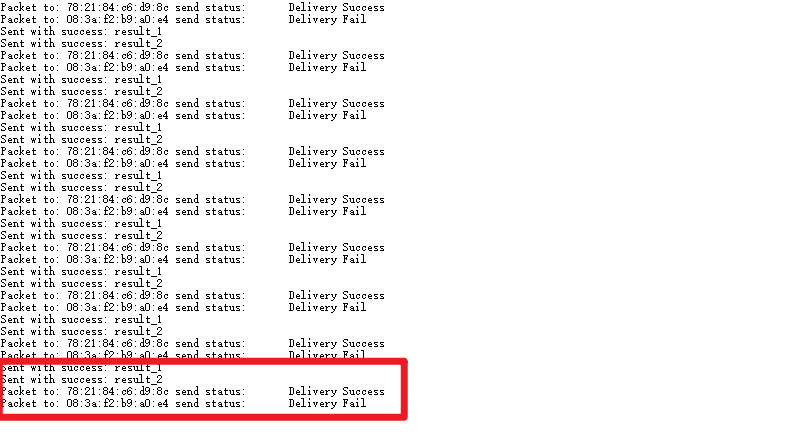
- 当2个接收方里一个正常,另外一个断电时
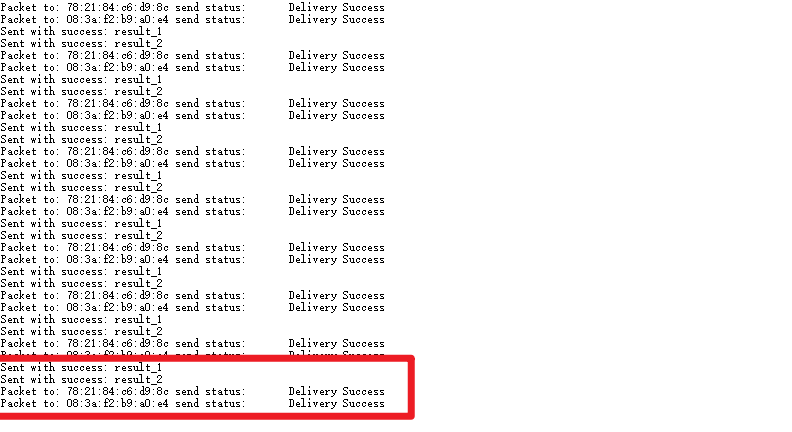
- 将2个接收方正常供电时
单向:多对一
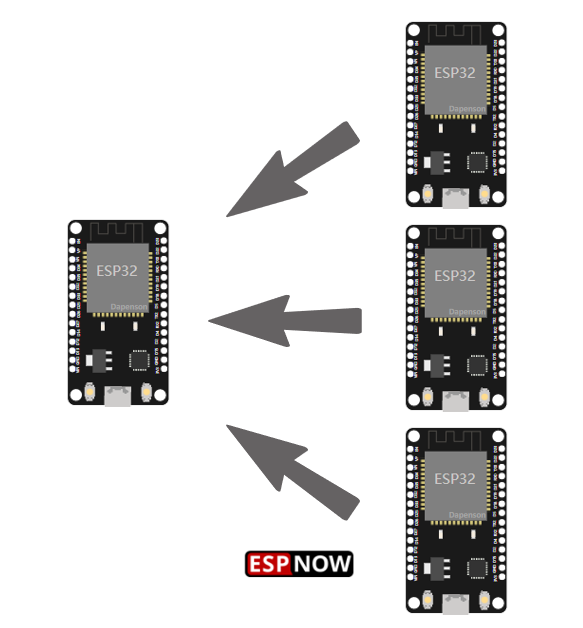
通过 ESP-NOW 通信协议(多对一)接收来自多个 ESP32 开发板的数据
- 发送方板收到一条确认消息,指示消息是否已成功传递;
- ESP32 接收方接收来自所有发送方的消息,并识别发送消息的板卡;
A发送方
对于接收方来说,接收方可以通过其唯一的 MAC 地址来识别每个发送方。
但是,在接收端处理不同的MAC地址以识别哪个板发送了哪个消息可能会让人难以区分。
因此,为了方便起见,示例将使用唯一的编号(id) 从 1 开始。该 ID 将与其他变量一起发送到接收方。
示例程序04
需根据多个开发板序号改变结构体中的id
#include <esp_now.h>
#include <WiFi.h>
// 替换为esp接收方的MAC地址 ***
const uint8_t mac_receive[6] = {0x60, 0x55, 0xf9, 0x77, 0x75, 0x60};//合宙esp32C3
// 发送方的结构体 ***
// 必须与接收方结构体匹配
typedef struct struct_message {
int id; // 每个发送方id必须是唯一的
int x;
int y;
} struct_message;
// 创建结构体 ***
struct_message myData;
// 实例化espnow通讯的对等体
esp_now_peer_info_t peerInfo;
// 数据发送时的回调函数 ***
void OnDataSent(const uint8_t *mac_addr, esp_now_send_status_t status) {
Serial.print("\r\nLast Packet Send Status:\t");
Serial.println(status == ESP_NOW_SEND_SUCCESS ? "Delivery Success" : "Delivery Fail");
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
// 初始化espnow,如果失败则打印错误信息并退出
if (esp_now_init() != ESP_OK) {
Serial.println("Error initializing ESP-NOW");
return;
}
// 注册消息发送的回调函数
esp_now_register_send_cb(OnDataSent);
// 配置对等体信息
// 通讯信道
peerInfo.channel = 0;
// 是否加密通讯信息
peerInfo.encrypt = false;
// 添加第1个对等体
memcpy(peerInfo.peer_addr, mac_receive, 6);
if (esp_now_add_peer(&peerInfo) != ESP_OK){
Serial.println("Failed to add peer");
return;
}
}
void loop() {
// 赋值要发送的结构体数据
myData.id = 1;
myData.x = random(0,50);
myData.y = random(0,50);
// 通过 ESP-NOW 发送数据
esp_err_t result = esp_now_send(mac_receive, (uint8_t *) &myData, sizeof(myData));
if (result == ESP_OK) {
Serial.println("Sent with success");
}
else {
Serial.println("Error sending the data");
}
delay(10000);
}
- 发送方串口信息
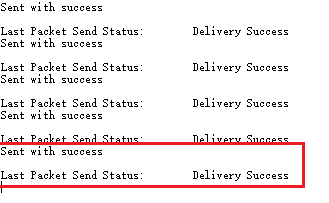
B接收方
示例程序从多个esp板接收数据,并通过mac或数据中的id来区分
示例程序05
#include <esp_now.h>
#include <WiFi.h>
//接收方用以接受数据的结构体 ***
//必须和发送方的结构体匹配 ***
typedef struct struct_message
{
int id;
int x;
int y;
} struct_message;
//创建结构体 ***
struct_message myData;
//创建不同的结构对象来分别保存每个板上的读数
struct_message board1;
struct_message board2;
struct_message board3;
// 创建一个包含所有结构的数组
struct_message boardsStruct[3] = {board1, board2, board3};
//接收到数据时执行的回调函数 ***
void OnDataRecv(const uint8_t *mac_addr, const uint8_t *incomingData, int len)
{
char macStr[18];
Serial.print("Packet received from: ");
snprintf(macStr, sizeof(macStr), "%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x",
mac_addr[0], mac_addr[1], mac_addr[2], mac_addr[3], mac_addr[4], mac_addr[5]);
Serial.println(macStr);
memcpy(&myData, incomingData, sizeof(myData));
Serial.printf("Board ID %u: %u bytes\n", myData.id, len);
// 用传入的数据更新各自对应的结构体
boardsStruct[myData.id - 1].x = myData.x;
boardsStruct[myData.id - 1].y = myData.y;
Serial.printf("x value: %d \n", boardsStruct[myData.id - 1].x);
Serial.printf("y value: %d \n", boardsStruct[myData.id - 1].y);
Serial.println();
}
void setup()
{
//初始化串口
Serial.begin(115200);
//设置wifi模式为 Wi-Fi Station
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
//初始化 ESP-NOW,初始化失败则打印信息并退出
if (esp_now_init() != ESP_OK)
{
Serial.println("Error initializing ESP-NOW");
return;
}
// 注册接受消息的回调函数
// 用以获取接收到的数据
esp_now_register_recv_cb(OnDataRecv);
}
void loop()
{
// 访问每个板对应的结构体变量
// for (size_t i = 0; i < 3; i++)
// {
// Serial.printf("Board %u: x = %d, y = %d \n", i + 1, boardsStruct[i].x, boardsStruct[i].y);
// }
delay(10000);
}
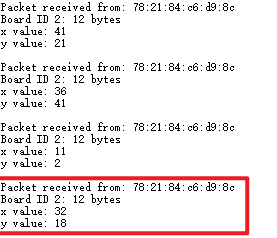
- 当有2块发送方时

- 当只有1块发送方时
双向:一对一 *
将以下代码修改mac地址后分别上传到2块ESP开发板中。
其实esp-now通讯主要有4个点:
- 数据发送回调函数 (用以判断对方是否成功收到消息或打印当前发送的目标地址等)
- 数据接收回调函数 (用以对接收的数据做解析等)
- 对等体配置 (用以配置通讯信道或内容是否加密等)
- 发送数据 (Dapenson : ) )
示例程序06
需要修改程序中接收方(对方)的mac地址
程序功能为获取传感器(随机数)数值,发送给指定的对方,接收对方发过来的传感器数值并串口打印
// espnow通讯主要有4个点:数据发送回调函数、数据接收回调函数、对等体配置、发送数据
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <esp_now.h>
#include <WiFi.h>
// 函数声明
void OnDataSent(const uint8_t *mac_addr, esp_now_send_status_t status);
void OnDataRecv(const uint8_t *mac, const uint8_t *incomingData, int len);
void getReadings();
void updateDisplay();
// 接收方(对方)的mac地址
// const uint8_t mac_target[6] = {0x78, 0x21, 0x84, 0xc6, 0xd9, 0x8c}; // esp32外置天线
const uint8_t mac_target[6] = {0x60, 0x55, 0xf9, 0x77, 0x75, 0x60};//合宙esp32C3
// 定义变量存储传感器读数
float temperature;
float humidity;
float pressure;
//定义变量存储接收到的传感器读数
float incomingTemp;
float incomingHum;
float incomingPres;
// 用于存储数据发送是否成功的变量
String success;
// 发送方或接收方的结构体 ***
// 必须与接收方结构体匹配,是消息传递的载体
typedef struct struct_message
{
float temp;
float hum;
float pres;
} struct_message;
// 创建一个struct_message类型的变量sensor_fake,用以存储传感器读数
// Create a struct_message called sensor_fake to hold sensor readings
struct_message sensor_fake;
// 创建一个struct_message类型的变量incomingReadings,用以存储接收到的传感器读数
// Create a struct_message to hold incoming sensor readings
struct_message incomingReadings;
// 实例化espnow通讯的对等体
esp_now_peer_info_t peerInfo;
// 数据发送时的回调函数 ***
void OnDataSent(const uint8_t *mac_addr, esp_now_send_status_t status)
{
Serial.print("\r\nLast Packet Send Status:\t");
Serial.println(status == ESP_NOW_SEND_SUCCESS ? "Delivery Success" : "Delivery Fail");
if (status == 0)
{
success = "Delivery Success";
}
else
{
success = "Delivery Fail";
}
}
// 数据接收时的回调函数 ***
// Callback when data is received
void OnDataRecv(const uint8_t *mac, const uint8_t *incomingData, int len)
{
memcpy(&incomingReadings, incomingData, sizeof(incomingReadings));
Serial.print("Bytes received: ");
Serial.println(len);
incomingTemp = incomingReadings.temp;
incomingHum = incomingReadings.hum;
incomingPres = incomingReadings.pres;
}
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
// 初始化espnow,如果失败则打印错误信息并退出
if (esp_now_init() != ESP_OK)
{
Serial.println("Error initializing ESP-NOW");
return;
}
// 注册消息发送的回调函数
esp_now_register_send_cb(OnDataSent);
// 配置对等体信息
peerInfo.channel = 0;
peerInfo.encrypt = false;
// 添加消息对等点
memcpy(peerInfo.peer_addr, mac_target, 6);
if (esp_now_add_peer(&peerInfo) != ESP_OK)
{
Serial.println("Failed to add peer");
return;
}
// 注册接受消息的回调函数
// 用以获取接收到的数据
esp_now_register_recv_cb(OnDataRecv);
}
void loop()
{
getReadings();
// 赋值要发送的结构体数据
sensor_fake.temp = temperature;
sensor_fake.hum = humidity;
sensor_fake.pres = pressure;
// 通过 ESP-NOW 发送数据
esp_err_t result = esp_now_send(mac_target, (uint8_t *)&sensor_fake, sizeof(sensor_fake));
if (result == ESP_OK)
{
Serial.println("Sent with success");
}
else
{
Serial.println("Error sending the data");
}
updateDisplay();
delay(10000);
}
// 从传感器获取数据
void getReadings()
{
temperature = random(20, 30);
humidity = random(50, 60);
pressure = random(1000, 1100);
}
void updateDisplay()
{
// 将数据更新显示在串口
Serial.println("INCOMING READINGS");
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(incomingReadings.temp);
Serial.println(" ºC");
Serial.print("Humidity: ");
Serial.print(incomingReadings.hum);
Serial.println(" %");
Serial.print("Pressure: ");
Serial.print(incomingReadings.pres);
Serial.println(" hPa");
Serial.println();
}
- 效果演示
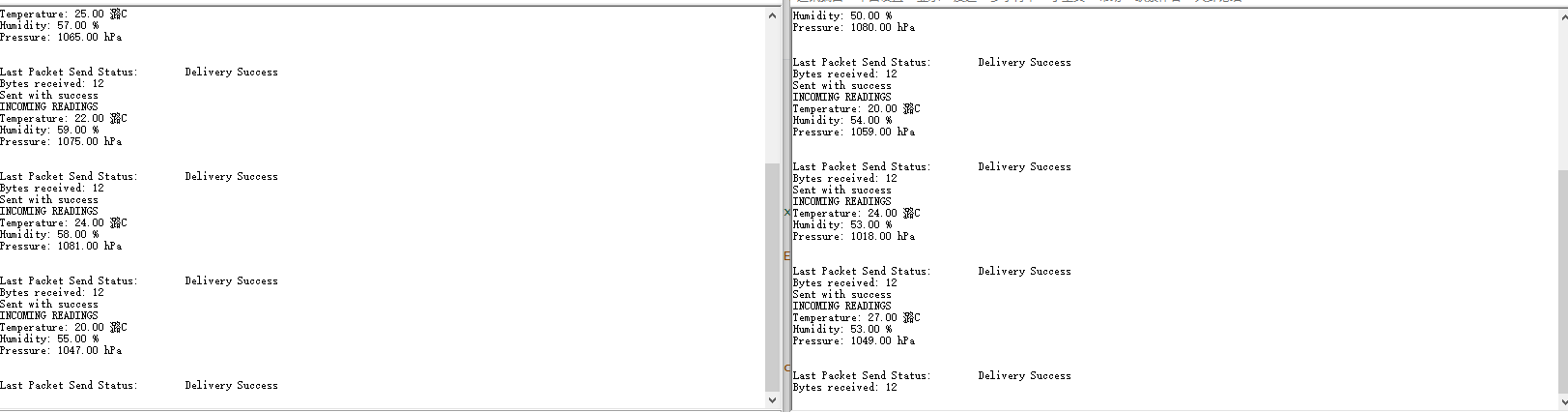
左右分别为2块开发板串口的打印信息,分别将对方的传感器数值显示出来
双向:多对多
理解了以上的,便可以在双向一对一的基础上写出多对多的程序,通过指定对方mac地址,定向的发送双方都通用的结构体数据,
在接收回调函数中写入结构体解析类的函数。
多块开发板之间可以通过mac地址,或在自定义的通用结构体中定义身份区分的唯一id值,即自定义数据通讯协议。
广播模式 *
由于使用广播模式,因此我们不需要知道对方其他ESP板的MAC地址,因此每个板都可以运行相同的代码。
程序功能:通过按下板载按钮,改变板载LED灯,同时将该状态相互广播出去,实现任一开发板按键控制所有开发板的LED
示例程序07
- 前面的示例程序都使用结构体来作为数据通讯的载体,因此本示例使用msg的方式直接发送数据
- 广播函数
void broadcast(const String &message)通过发送特殊的 MAC 地址FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF创建广播消息。每个对等方都会回复它的 MAC 地址,这些地址可用于发送数据。
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <esp_now.h>
// 函数声明
void formatMacAddress(const uint8_t *macAddr, char *buffer, int maxLength);
void receiveCallback(const uint8_t *macAddr, const uint8_t *data, int dataLen);
void sentCallback(const uint8_t *macAddr, esp_now_send_status_t status);
void sentCallback(const uint8_t *macAddr, esp_now_send_status_t status);
void broadcast(const String &message);
// 定义LED和按键状态布尔值
bool buttonDown = false;
bool ledOn = false;
// 宏定义LED和按键引脚,根据自己的开发板原理图修改
#ifdef ESP32C3
// 适配合宙esp32C3
#define STATUS_LED 12
#define STATUS_BUTTON 9
#elif ESP32
// 适配esp32
#define STATUS_LED 2
#define STATUS_BUTTON 0
#endif
// 格式化MAC地址
// Formats MAC Address
void formatMacAddress(const uint8_t *macAddr, char *buffer, int maxLength)
{
snprintf(buffer, maxLength, "%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x", macAddr[0], macAddr[1], macAddr[2], macAddr[3], macAddr[4], macAddr[5]);
}
// 接收到数据时的回调函数
// Called when data is received
void receiveCallback(const uint8_t *macAddr, const uint8_t *data, int dataLen)
{
// 消息最长250个字符,加上一个空字符
// Only allow a maximum of 250 characters in the message + a null terminating byte
char buffer[ESP_NOW_MAX_DATA_LEN + 1];
int msgLen = min(ESP_NOW_MAX_DATA_LEN, dataLen);
strncpy(buffer, (const char *)data, msgLen);
//确保以空字符结尾
// Make sure we are null terminated
buffer[msgLen] = 0;
// 格式化MAC地址
// Format the MAC address
char macStr[18];
formatMacAddress(macAddr, macStr, 18);
// 发送调试日志消息到串口
// Send Debug log message to the serial port
Serial.printf("Received message from: %s - %s\n", macStr, buffer);
// Dapenson 以下便可添加数据处理或逻辑处理代码
// 比较2个字符串是否相等,相等则返回0
// 如果消息是“on”,则打开LED
if (strcmp("on", buffer) == 0)
{
ledOn = true;
}
else
{
ledOn = false;
}
digitalWrite(STATUS_LED, ledOn);
}
// 消息发送后的回调函数,用以判断对方是否成功收到消息等
// Called when data is sent
void sentCallback(const uint8_t *macAddr, esp_now_send_status_t status)
{
char macStr[18];
formatMacAddress(macAddr, macStr, 18);
Serial.print("Last Packet Sent to: ");
Serial.println(macStr);
Serial.print("Last Packet Send Status: ");
Serial.println(status == ESP_NOW_SEND_SUCCESS ? "Delivery Success" : "Delivery Fail");
}
// 广播消息 ***
// Emulates a broadcast
void broadcast(const String &message)
{
// 将消息广播到每个在范围内的设备
// Broadcast a message to every device in range
uint8_t broadcastAddress[] = {0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF};
esp_now_peer_info_t peerInfo = {};
// 把broadcastAddress添加为消息对等体
memcpy(&peerInfo.peer_addr, broadcastAddress, 6);
if (!esp_now_is_peer_exist(broadcastAddress))
{
esp_now_add_peer(&peerInfo);
}
// 发送消息给所有范围内的设备
esp_err_t result = esp_now_send(broadcastAddress, (const uint8_t *)message.c_str(), message.length());
// 将发送结果打印到串口
// Print results to serial monitor
Serial.printf(esp_err_to_name(result));
Serial.println();
}
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(1000);
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
Serial.println("ESP-NOW Broadcast Demo");
// 初始化espnow,如果失败则打印错误信息并退出重启
if (esp_now_init() == ESP_OK)
{
Serial.println("ESP-NOW Init Success");
// 注册接受消息的回调函数
esp_now_register_recv_cb(receiveCallback);
// 注册消息发送的回调函数
esp_now_register_send_cb(sentCallback);
}
else
{
Serial.println("ESP-NOW Init Failed");
delay(3000);
// 重启esp设备
ESP.restart();
}
pinMode(STATUS_LED, OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
if (digitalRead(STATUS_BUTTON))
{
// 检测从低到高的转换
// Detect the transition from low to high
if (!buttonDown)
{
buttonDown = true;
// 翻转LED状态
// Toggle the LED state
ledOn = !ledOn;
digitalWrite(STATUS_LED, ledOn);
// 发送消息给所有范围内的设备,用以同步LED状态
// Send a message to all devices
if (ledOn)
{
broadcast("on");
}
else
{
broadcast("off");
}
}
// 延时以避免抖动
// Delay to avoid bouncing
delay(500);
}
else
{
// 重置按钮状态
// Reset the button state
buttonDown = false;
}
}
- 效果演示

- 实际按键效果视频


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号