数据结构—无序树
基本术语:
节点的度:书中某一节点拥有的子节点数量。
数的度:该树中所有节点的度的最大值。
叶节点(终端节点):度为零的节点。
分支节点(非终端节点):度不为零的节点。
根节点(开始节点):树中的第一个节点。
内部节点:树中除了根节点之外的节点。
节点的层数:若根节点层数为1,根节点的第n代子节点的层数为n。
树的高度:书中的节点的最大层数。
有序树和无序树:若树中某一节点的子节点无序,则该树为无序树,否则为有序树。
森林:去掉一棵树的根节点后得到的n棵树。
树的特点:
1.树是一种很基础很重要的非线性结构。
2.除表头(树根)和表尾(叶节点)外,任何一个节点只有一个直接前驱,但有多个直接后继。
3.树是数据的有限集,树分为空树和非空树。
非空树:有且只有一个根节点。若根节点的子节点大于1,可以理解为这棵非空树有m棵相互独立的非空树组成。
4.树的递归特性(★★★):一颗非空树有若干子树组成,每一棵子树又由更小的子组成。
C++实现:
[MyTree.h]:无序树类模板头文件
#pragma once
template<class T>
class MyTree
{
private:
struct TreeNode //定义私有,不让用户使用
{
T data; //数据域,可以多个数据
//指针域
TreeNode *parent; //节点的父指针
TreeNode *child; //子指针
TreeNode *brother; //兄弟指针 兄弟之间逐级管理
};
TreeNode *pRoot; //根节点
public:
MyTree();
~MyTree();
void clear();
void insertNode(const T& parentData, const T& insertData, bool insertChild = true); //默认插入为子节点
//bool isFind(const T& findData);
void preOrderPrint(TreeNode *root /*= pRoot*/); //前序(前根)遍历
void posOrderPrint(TreeNode *root /*= pRoot*/); //前序(后根)遍历
void inOrderPrint(TreeNode *root /*= pRoot*/); //中序(中根)遍历
TreeNode* getTreeRoot();
private:
void _clear(TreeNode *root); //用于clear()函数的实现,不提供接口
TreeNode* _find(TreeNode *root, const T& findData);
};
template<class T>
typename MyTree<T>::TreeNode* MyTree<T>::getTreeRoot()
{
return pRoot;
}
template<class T>
void MyTree<T>::inOrderPrint(TreeNode *root /*= pRoot*/)
{
if (!root)
return;
inOrderPrint(root->child);
std::cout << root->data << " ";
inOrderPrint(root->brother);
}
template<class T>
void MyTree<T>::posOrderPrint(TreeNode *root /*= pRoot*/)
{
if (!root)
return;
posOrderPrint(root->child);
posOrderPrint(root->brother);
std::cout << root->data << " ";
}
template<class T>
void MyTree<T>::preOrderPrint(TreeNode *root /*= pRoot*/)
{
if (!root)
return;
std::cout << root->data << " ";
preOrderPrint(root->child);
preOrderPrint(root->brother);
}
template<class T>
void MyTree<T>::insertNode(const T& parentData, const T& insertData, bool insertChild /*= true*/)
{
TreeNode *tempInsertNode = new TreeNode; //生成一个待插入的节点
tempInsertNode->data = insertData;
tempInsertNode->parent = NULL;
tempInsertNode->child = NULL;
tempInsertNode->brother = NULL;
if (pRoot) //判断树是否为空
{
TreeNode *findNode = _find(pRoot, parentData); //找到插入位置
if (findNode)
{//找到了插入位置
if (insertChild)
{//在子节点插入
TreeNode *temp = findNode->child;
if (temp)
{
while (temp->brother)
temp = temp->brother;
temp->brother = tempInsertNode;
tempInsertNode->parent = findNode;
}
else
{
findNode->child = tempInsertNode;
tempInsertNode->parent = findNode;
}
}
else
{//在兄弟节点插入
if (findNode->brother)
{
TreeNode *tempNode = findNode->brother;
while (tempNode->brother)
tempNode = tempNode->brother;
tempNode->brother = tempInsertNode;
tempInsertNode->parent = tempNode->parent;
}
else
{
//没有兄弟节点
findNode->brother = tempInsertNode;
tempInsertNode->parent = findNode->parent;
}
}
}
else
{//如果没有找到插入位置 设计为插入在末尾
std::cout << "can not find the parent,insert the data in the end" << std::endl;
TreeNode *temp = pRoot;
while (temp->child)
temp = temp->child;
temp->child = tempInsertNode;
tempInsertNode->parent = temp;
}
}
else
{//树为空的情况
// TreeNode *temp = new TreeNode;
// temp->data = insertData;
// temp->parent = NULL;
// inNode->child = inNode->brother = NULL;
pRoot = tempInsertNode;
}
}
template<class T>
typename MyTree<T>::TreeNode * MyTree<T>::_find(TreeNode *root, const T& findData)
{
if (root) /*递归结束条件 传入的的指针为空 例如判断叶节点是 将叶子节点的子节点传入递归函数,
不满足条件直接返回空*/
{
//先判断本节点 在判断子节点 最后判断兄弟节点 找到直接返回 不继续找
if (root->data == findData) //判断当前节点是否为 需要找的节点
return root;
TreeNode * temp = _find(root->child, findData);
if (temp)
return temp;
if (temp = _find(root->brother, findData))
return temp;
}
return NULL; //若没有找到 返回为空
}
template<class T>
void MyTree<T>::_clear(TreeNode *root)
{
//用递归删除所有节点 树的递归特性
if (root)
{
_clear(root->child);
_clear(root->brother); //先删除兄弟和先删除儿子一样
delete[]root; //必须先删除兄弟和儿子后才能删除自己
root = nullptr; //所有内存被释放后 指针置空
}
}
template<class T>
void MyTree<T>::clear()
{
_clear(pRoot); //不需要再进行判空 ,_clear()中会判断
}
template<class T>
MyTree<T>::~MyTree()
{
clear();
}
template<class T>
MyTree<T>::MyTree()
{
pRoot = nullptr;
}
代码测试:
// 无序树.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "MyTree.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
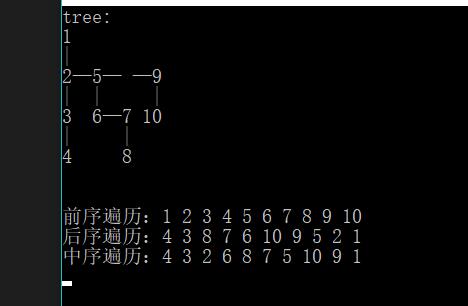
MyTree<int> tree;
std::cout << "tree:" << endl;;
tree.insertNode(1, 1);
cout << 1 << '\n' << '|' << endl;;
tree.insertNode(1, 2, 1);
tree.insertNode(2, 5, 0);
tree.insertNode(2, 9, 0);
cout << 2 << "—" << 5<<"— —"<<9<<endl;
cout << '|' << " " << "|" <<" "<<"|"<< endl;
tree.insertNode(2, 3, 1);
tree.insertNode(5, 6, 1);
tree.insertNode(6, 7, 0);
tree.insertNode(9, 10, 1);
cout << 3 << " " << 6 << "—" << 7 <<" "<< 10 << endl;
cout << "|" << " " << "|" << endl;
tree.insertNode(3, 4, 1);
tree.insertNode(7, 8, 1);
cout << 4 << " " << 8 << "\n\n"<<endl;
std::cout << "前序遍历:";
tree.preOrderPrint(tree.getTreeRoot());
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "后序遍历:";
tree.posOrderPrint(tree.getTreeRoot());
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "中序遍历:";
tree.inOrderPrint(tree.getTreeRoot());
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cin.get();
return 0;
}
测试结果:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号