SSD目标检测网络解读(含网络结构和内容解读)
SSD实现思路
SSD具有如下主要特点:
- 从YOLO中继承了将detection转化为regression的思路,一次完成目标定位与分类
- 基于Faster RCNN中的Anchor,提出了相似的Prior box;
- 加入基于特征金字塔(Pyramidal Feature Hierarchy)的检测方式,即在不同感受野的feature map上预测目标
一、预测部分
1、主干网络介绍
SSD采用的主干网络是VGG网络,这里的VGG网络相比普通的VGG网络有一定的修改,主要修改的地方就是:
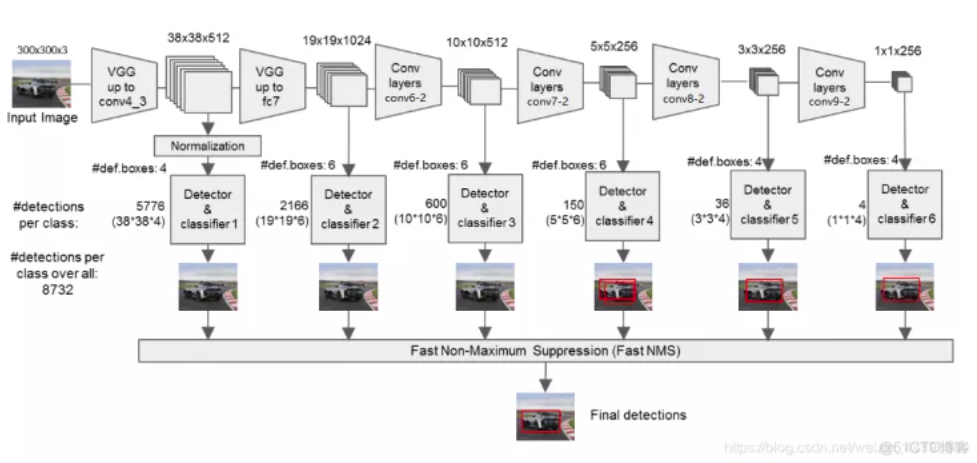
1、将VGG16的FC6和FC7层转化为卷积层。
2、去掉所有的Dropout层和FC8层;
3、新增了Conv6、Conv7、Conv8、Conv9。
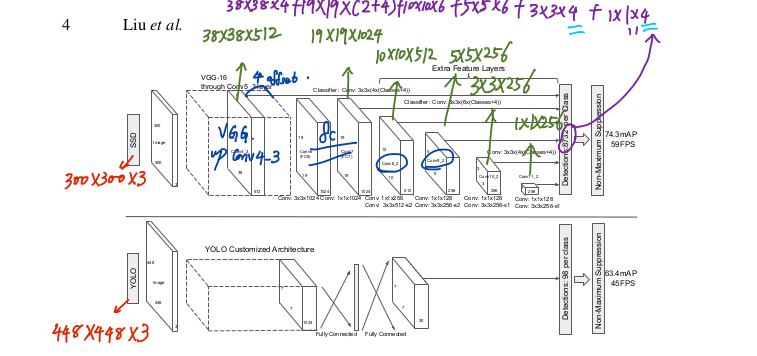
上图是原论文中的SSD300与YOLO网络结构图。为什么要把SSD与YOLO对比呢?因为截止到目前目标检测分为了2种主流框架:
- Two stages:以Faster RCNN为代表,即RPN网络先生成proposals目标定位,再对proposals进行classification+bounding box regression完成目标分类。
- Single shot:以YOLO/SSD为代表,一次性完成classification+bounding box regression。
同时,如图所示,输入的图片经过了改进的VGG网络(Conv1->fc7)和几个另加的卷积层(Conv6->Conv9),进行特征提取:
a、输入一张图片后,被resize到300x300的shape
b、conv1, 经过两次[3,3]卷积网络,输出的特征层为64,输出为(300,300,64),再2X2最大池化,输出net为(150,150,64)。
c、conv2, 经过两次[3,3]卷积网络,输出的特征层为128,输出net为(150,150,128),再2X2最大池化,输出net为(75,75,128)。
d、conv3, 经过三次[3,3]卷积网络,输出的特征层为256,输出net为(75,75,256),再2X2最大池化,输出net为(38,38,256)。
e、conv4, 经过三次[3,3]卷积网络,输出的特征层为512,输出net为(38,38,512),再2X2最大池化,输出net为(19,19,512)。
f、conv5,经过三次[3,3]卷积网络,输出的特征层为512,输出net为(19,19,512),再2X2最大池化,输出net为(19,19,512)。
g、利用卷积代替全连接层,进行了两次[3,3]卷积网络,输出的特征层为1024,因此输出的net为(19,19,1024)。(从这里往前都是VGG的结构)
h、conv6,经过一次[1,1]卷积网络,调整通道数,一次步长为2的[3,3]卷积网络,输出的特征层为512,因此输出的net为(10,10,512)。
i、conv7,经过一次[1,1]卷积网络,调整通道数,一次步长为2的[3,3]卷积网络,输出的特征层为256,因此输出的net为(5,5,256)。
j、conv8,经过一次[1,1]卷积网络,调整通道数,一次padding为valid的[3,3]卷积网络,输出的特征层为256,因此输出的net为(3,3,256)。
k、conv9,经过一次[1,1]卷积网络,调整通道数,一次padding为valid的[3,3]卷积网络,输出的特征层为256,因此输出的net为(1,1,256)。
代码实现(点击可展开)
base = [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'C', 512, 512, 512, 'M',
512, 512, 512]
def vgg(i):
layers = []
in_channels = i
for v in base:
if v == 'M':
layers += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)]
elif v == 'C':
layers += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)]
else:
conv2d = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, v, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
layers += [conv2d, nn.ReLU(inplace=True)]
in_channels = v
pool5 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
conv6 = nn.Conv2d(512, 1024, kernel_size=3, padding=6, dilation=6)
conv7 = nn.Conv2d(1024, 1024, kernel_size=1)
layers += [pool5, conv6,
nn.ReLU(inplace=True), conv7, nn.ReLU(inplace=True)]
return layers
def add_extras(i, batch_norm=False):
# Extra layers added to VGG for feature scaling
layers = []
in_channels = i
# Block 6
# 19,19,1024 -> 10,10,512
layers += [nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 256, kernel_size=1, stride=1)]
layers += [nn.Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)]
# Block 7
# 10,10,512 -> 5,5,256
layers += [nn.Conv2d(512, 128, kernel_size=1, stride=1)]
layers += [nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)]
# Block 8
# 5,5,256 -> 3,3,256
layers += [nn.Conv2d(256, 128, kernel_size=1, stride=1)]
layers += [nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1)]
# Block 9
# 3,3,256 -> 1,1,256
layers += [nn.Conv2d(256, 128, kernel_size=1, stride=1)]
layers += [nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1)]
return layers
2、从特征获取预测结果
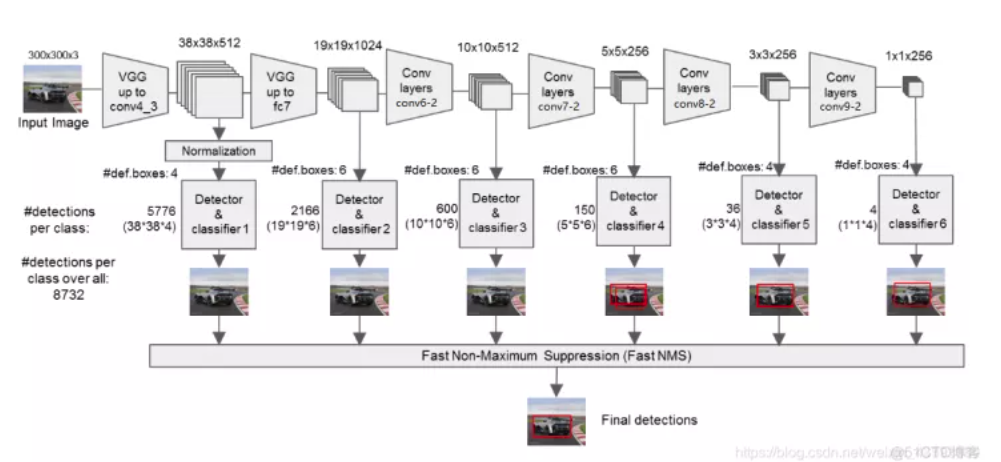
由上图我们可以知道,我们分别取conv4的第三次卷积的特征、fc7的特征、conv6的第二次卷积的特征、conv7的第二次卷积的特征、conv8的第二次卷积的特征、conv9的第二次卷积的特征,为了和普通特征层区分,我们称之为有效特征层,来获取预测结果。
对获取到的每一个有效特征层,我们分别对其进行一次num_priors x 4的卷积、一次num_priors x num_classes的卷积、并需要计算每一个有效特征层对应的先验框。而num_priors指的是该特征层所拥有的先验框数量。
其中:
num_priors x 4的卷积用于预测该特征层上每一个网格点上每一个先验框的变化情况。(为什么说是变化情况呢,这是因为ssd的预测结果需要结合先验框获得预测框,预测结果就是先验框的变化情况。)
num_priors x num_classes的卷积用于预测该特征层上每一个网格点上每一个预测框对应的种类。
每一个有效特征层对应的先验框对应着该特征层上每一个网格点上预先设定好的多个框。
所有的特征层对应的预测结果的shape如下:
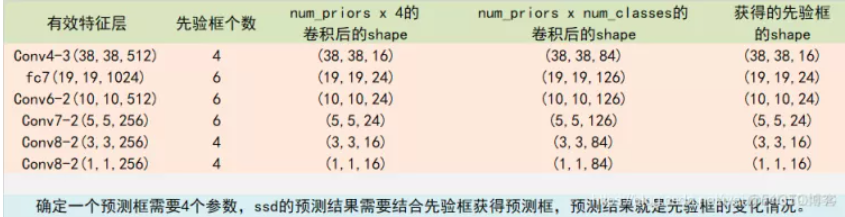
代码实现参考
class SSD(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, phase, base, extras, head, num_classes):
super(SSD, self).__init__()
self.phase = phase
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.cfg = Config
self.vgg = nn.ModuleList(base)
self.L2Norm = L2Norm(512, 20)
self.extras = nn.ModuleList(extras)
self.priorbox = PriorBox(self.cfg)
with torch.no_grad():
self.priors = Variable(self.priorbox.forward())
self.loc = nn.ModuleList(head[0])
self.conf = nn.ModuleList(head[1])
if phase == 'test':
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
self.detect = Detect(num_classes, 0, 200, 0.01, 0.45)
def forward(self, x):
sources = list()
loc = list()
conf = list()
# 获得conv4_3的内容
for k in range(23):
x = self.vgg[k](x)
s = self.L2Norm(x)
sources.append(s)
# 获得fc7的内容
for k in range(23, len(self.vgg)):
x = self.vgg[k](x)
sources.append(x)
# 获得后面的内容
for k, v in enumerate(self.extras):
x = F.relu(v(x), inplace=True)
if k % 2 == 1:
sources.append(x)
# 添加回归层和分类层
for (x, l, c) in zip(sources, self.loc, self.conf):
loc.append(l(x).permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous())
conf.append(c(x).permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous())
# 进行resize
loc = torch.cat([o.view(o.size(0), -1) for o in loc], 1)
conf = torch.cat([o.view(o.size(0), -1) for o in conf], 1)
if self.phase == "test":
# loc会resize到batch_size,num_anchors,4
# conf会resize到batch_size,num_anchors,
output = self.detect(
loc.view(loc.size(0), -1, 4), # loc preds
self.softmax(conf.view(conf.size(0), -1,
self.num_classes)), # conf preds
self.priors
)
else:
output = (
loc.view(loc.size(0), -1, 4),
conf.view(conf.size(0), -1, self.num_classes),
self.priors
)
return output
mbox = [4, 6, 6, 6, 4, 4]
def get_ssd(phase,num_classes):
vgg, extra_layers = add_vgg(3), add_extras(1024)
loc_layers = []
conf_layers = []
vgg_source = [21, -2]
for k, v in enumerate(vgg_source):
loc_layers += [nn.Conv2d(vgg[v].out_channels,
mbox[k] * 4, kernel_size=3, padding=1)]
conf_layers += [nn.Conv2d(vgg[v].out_channels,
mbox[k] * num_classes, kernel_size=3, padding=1)]
for k, v in enumerate(extra_layers[1::2], 2):
loc_layers += [nn.Conv2d(v.out_channels, mbox[k]
* 4, kernel_size=3, padding=1)]
conf_layers += [nn.Conv2d(v.out_channels, mbox[k]
* num_classes, kernel_size=3, padding=1)]
SSD_MODEL = SSD(phase, vgg, extra_layers, (loc_layers, conf_layers), num_classes)
return SSD_MODEL
3、预测结果的解码
我们通过对每一个特征层的处理,可以获得三个内容,分别是:
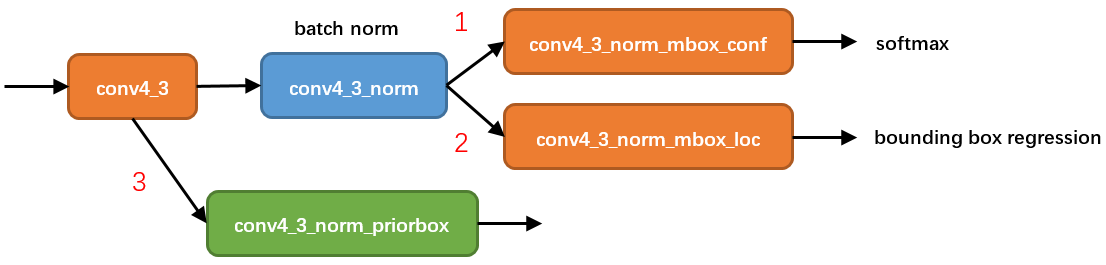
-
num_priors x 4的卷积用于预测该特征层上每一个网格点上每一个先验框的变化情况。
-
num_priors x num_classes的卷积用于预测该特征层上每一个网格点上每一个预测框对应的种类。
-
每一个有效特征层对应的先验框对应着该特征层上 每一个网格点上 预先设定好的多个框。
注意:此处num_priors在代码中是自己设定的(4,6,6,6,4,4)
其中默认框也就是default box / prior box 的选取和实现,可以参考论文中的这部分,
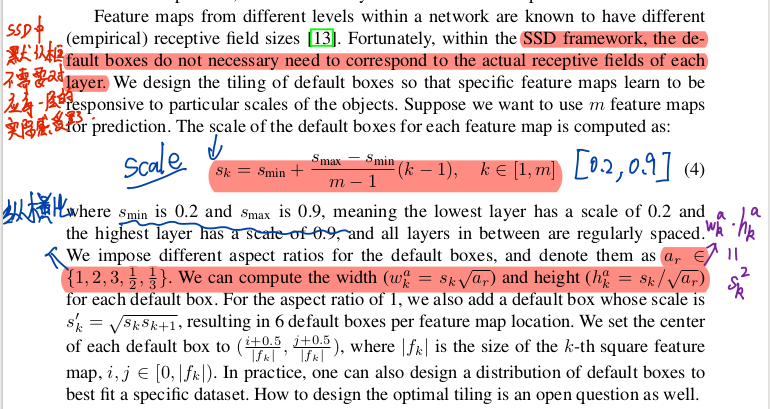
我们利用 num_priors x 4的卷积与每一个有效特征层对应的先验框获得框的真实位置。
每一个有效特征层对应的先验框就是,如图所示的作用:
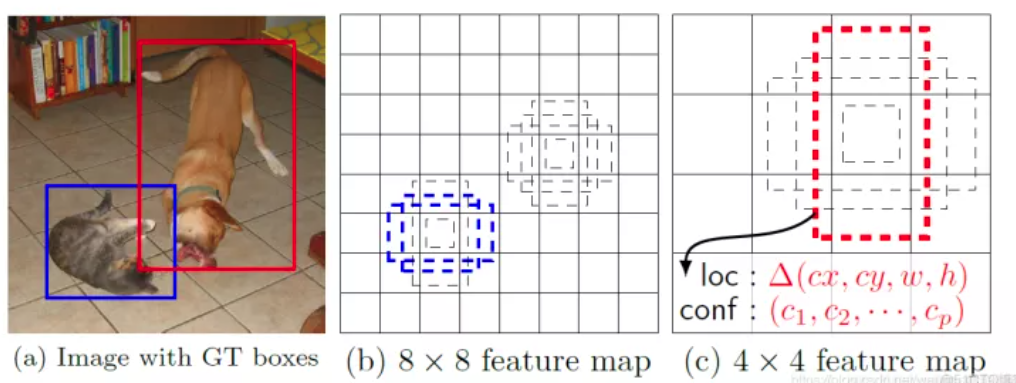
每一个有效特征层将整个图片分成与其长宽对应的网格,如conv4-3的特征层就是将整个图像分成38x38个网格;然后从每个网格中心建立多个先验框,如conv4-3的特征层就是建立了4个先验框;对于conv4-3的特征层来讲,整个图片被分成38x38个网格,每个网格中心对应4个先验框,一共包含了,38x38x4个,5776个先验框。
先验框虽然可以代表一定的框的位置信息与框的大小信息,但是其是有限的,无法表示任意情况,因此还需要调整,ssd利用num_priors x 4的卷积的结果对先验框进行调整。
num_priors x 4中的num_priors表示了这个网格点所包含的先验框数量,其中的4表示了x_offset、y_offset、h和w的调整情况。
x_offset与y_offset代表了真实框距离先验框中心的xy轴偏移情况。
h和w代表了真实框的宽与高相对于先验框的变化情况。
SSD解码过程就是将每个网格的中心点加上它对应的x_offset和y_offset,加完后的结果就是预测框的中心,然后再利用先验框和h、w结合计算出预测框的长和宽。这样就能得到整个预测框的位置了。
当然得到最终的预测结构后还要进行得分排序与非极大抑制筛选这一部分基本上是所有目标检测通用的部分。
1、取出每一类得分大于self.obj_threshold的框和得分。
2、利用框的位置和得分进行非极大抑制。
点击查看代码
# Adapted from https://github.com/Hakuyume/chainer-ssd
def decode(loc, priors, variances):
boxes = torch.cat((
priors[:, :2] + loc[:, :2] * variances[0] * priors[:, 2:],
priors[:, 2:] * torch.exp(loc[:, 2:] * variances[1])), 1)
boxes[:, :2] -= boxes[:, 2:] / 2
boxes[:, 2:] += boxes[:, :2]
return boxes
class Detect(Function):
def __init__(self, num_classes, bkg_label, top_k, conf_thresh, nms_thresh):
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.background_label = bkg_label
self.top_k = top_k
self.nms_thresh = nms_thresh
if nms_thresh <= 0:
raise ValueError('nms_threshold must be non negative.')
self.conf_thresh = conf_thresh
self.variance = Config['variance']
def forward(self, loc_data, conf_data, prior_data):
loc_data = loc_data.cpu()
conf_data = conf_data.cpu()
num = loc_data.size(0) # batch size
num_priors = prior_data.size(0)
output = torch.zeros(num, self.num_classes, self.top_k, 5)
conf_preds = conf_data.view(num, num_priors,
self.num_classes).transpose(2, 1)
# 对每一张图片进行处理
for i in range(num):
# 对先验框解码获得预测框
decoded_boxes = decode(loc_data[i], prior_data, self.variance)
conf_scores = conf_preds[i].clone()
for cl in range(1, self.num_classes):
# 对每一类进行非极大抑制
c_mask = conf_scores[cl].gt(self.conf_thresh)
scores = conf_scores[cl][c_mask]
if scores.size(0) == 0:
continue
l_mask = c_mask.unsqueeze(1).expand_as(decoded_boxes)
boxes = decoded_boxes[l_mask].view(-1, 4)
# 进行非极大抑制
ids, count = nms(boxes, scores, self.nms_thresh, self.top_k)
output[i, cl, :count] = \
torch.cat((scores[ids[:count]].unsqueeze(1),
boxes[ids[:count]]), 1)
flt = output.contiguous().view(num, -1, 5)
_, idx = flt[:, :, 0].sort(1, descending=True)
_, rank = idx.sort(1)
flt[(rank < self.top_k).unsqueeze(-1).expand_as(flt)].fill_(0)
return output
4、在原图上进行绘制
通过第三步,我们可以获得预测框在原图上的位置,而且这些预测框都是经过筛选的。这些筛选后的框可以直接绘制在图片上,就可以获得结果了。
二、训练部分
1、真实框的处理
从预测部分我们知道,每个特征层的预测结果,num_priors x 4的卷积用于预测该特征层上每一个网格点上每一个先验框的变化情况。
也就是说,我们直接利用ssd网络预测到的结果,并不是预测框在图片上的真实位置,需要解码才能得到真实位置。
而在训练的时候,我们需要计算loss函数,这个loss函数是相对于ssd网络的预测结果的。我们需要把图片输入到当前的ssd网络中,得到预测结果;同时还需要把真实框的信息,进行编码,这个编码是把真实框的位置信息格式转化为ssd预测结果的格式信息。
也就是,我们需要找到每一张用于训练的图片的每一个真实框对应的先验框,并求出如果想要得到这样一个真实框,我们的预测结果应该是怎么样的。
从预测结果获得真实框的过程被称作解码,而从真实框获得预测结果的过程就是编码的过程。
因此我们只需要将解码过程逆过来就是编码过程了。
点击查看代码
def encode(matched, priors, variances):
g_cxcy = (matched[:, :2] + matched[:, 2:])/2 - priors[:, :2]
g_cxcy /= (variances[0] * priors[:, 2:])
g_wh = (matched[:, 2:] - matched[:, :2]) / priors[:, 2:]
g_wh = torch.log(g_wh) / variances[1]
return torch.cat([g_cxcy, g_wh], 1)
在训练的时候我们只需要选择iou最大的先验框就行了,这个iou最大的先验框就是我们用来预测这个真实框所用的先验框。
因此我们还要经过一次筛选,将上述代码获得的真实框对应的所有的iou较大先验框的预测结果中,iou最大的那个筛选出来。
点击查看代码
def match(threshold, truths, priors, variances, labels, loc_t, conf_t, idx):
# 计算所有的先验框和真实框的重合程度
overlaps = jaccard(
truths,
point_form(priors)
)
# 所有真实框和先验框的最好重合程度
# [truth_box,1]
best_prior_overlap, best_prior_idx = overlaps.max(1, keepdim=True)
best_prior_idx.squeeze_(1)
best_prior_overlap.squeeze_(1)
# 所有先验框和真实框的最好重合程度
# [1,prior]
best_truth_overlap, best_truth_idx = overlaps.max(0, keepdim=True)
best_truth_idx.squeeze_(0)
best_truth_overlap.squeeze_(0)
# 找到与真实框重合程度最好的先验框,用于保证每个真实框都要有对应的一个先验框
best_truth_overlap.index_fill_(0, best_prior_idx, 2)
# 对best_truth_idx内容进行设置
for j in range(best_prior_idx.size(0)):
best_truth_idx[best_prior_idx[j]] = j
# 找到每个先验框重合程度最好的真实框
matches = truths[best_truth_idx] # Shape: [num_priors,4]
conf = labels[best_truth_idx] + 1 # Shape: [num_priors]
# 如果重合程度小于threhold则认为是背景
conf[best_truth_overlap < threshold] = 0 # label as background
loc = encode(matches, priors, variances)
loc_t[idx] = loc # [num_priors,4] encoded offsets to learn
conf_t[idx] = conf # [num_priors] top class label for each prior
2、利用处理完的真实框与对应图片的预测结果计算loss

loss的计算分为三个部分:
1、获取所有正标签的框的预测结果的回归loss。
2、获取所有正标签的种类的预测结果的交叉熵loss。
3、获取一定负标签的种类的预测结果的交叉熵loss。
由于在ssd的训练过程中,正负样本极其不平衡,即存在对应真实框的先验框可能只有十来个,但是不存在对应真实框的负样本却有几千个,这就会导致负样本的loss值极大,因此我们可以考虑减少负样本的选取,对于ssd的训练来讲,常见的情况是取三倍正样本数量的负样本用于训练(难例挖掘部分,详细见下图)。这个三倍呢,也可以修改,调整成自己喜欢的数字。

点击查看代码
class MultiBoxLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes, overlap_thresh, prior_for_matching,
bkg_label, neg_mining, neg_pos, neg_overlap, encode_target,
use_gpu=True):
super(MultiBoxLoss, self).__init__()
self.use_gpu = use_gpu
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.threshold = overlap_thresh
self.background_label = bkg_label
self.encode_target = encode_target
self.use_prior_for_matching = prior_for_matching
self.do_neg_mining = neg_mining
self.negpos_ratio = neg_pos
self.neg_overlap = neg_overlap
self.variance = Config['variance']
def forward(self, predictions, targets):
# 回归信息,置信度,先验框
loc_data, conf_data, priors = predictions
# 计算出batch_size
num = loc_data.size(0)
# 取出所有的先验框
priors = priors[:loc_data.size(1), :]
# 先验框的数量
num_priors = (priors.size(0))
num_classes = self.num_classes
# 创建一个tensor进行处理
loc_t = torch.Tensor(num, num_priors, 4)
conf_t = torch.LongTensor(num, num_priors)
for idx in range(num):
# 获得框
truths = targets[idx][:, :-1].data
# 获得标签
labels = targets[idx][:, -1].data
# 获得先验框
defaults = priors.data
# 找到标签对应的先验框
match(self.threshold, truths, defaults, self.variance, labels,
loc_t, conf_t, idx)
if self.use_gpu:
loc_t = loc_t.cuda()
conf_t = conf_t.cuda()
# 转化成Variable
loc_t = Variable(loc_t, requires_grad=False)
conf_t = Variable(conf_t, requires_grad=False)
# 所有conf_t>0的地方,代表内部包含物体
pos = conf_t > 0
# 求和得到每一个图片内部有多少正样本
num_pos = pos.sum(dim=1, keepdim=True)
# 计算回归loss
pos_idx = pos.unsqueeze(pos.dim()).expand_as(loc_data)
loc_p = loc_data[pos_idx].view(-1, 4)
loc_t = loc_t[pos_idx].view(-1, 4)
loss_l = F.smooth_l1_loss(loc_p, loc_t, size_average=False)
# 转化形式
batch_conf = conf_data.view(-1, self.num_classes)
# 你可以把softmax函数看成一种接受任何数字并转换为概率分布的非线性方法
# 获得每个框预测到真实框的类的概率
loss_c = log_sum_exp(batch_conf) - batch_conf.gather(1, conf_t.view(-1, 1))
loss_c = loss_c.view(num, -1)
loss_c[pos] = 0
# 获得每一张图新的softmax的结果
_, loss_idx = loss_c.sort(1, descending=True)
_, idx_rank = loss_idx.sort(1)
# 计算每一张图的正样本数量
num_pos = pos.long().sum(1, keepdim=True)
# 限制负样本数量
num_neg = torch.clamp(self.negpos_ratio*num_pos, max=pos.size(1)-1)
neg = idx_rank < num_neg.expand_as(idx_rank)
# 计算正样本的loss和负样本的loss
pos_idx = pos.unsqueeze(2).expand_as(conf_data)
neg_idx = neg.unsqueeze(2).expand_as(conf_data)
conf_p = conf_data[(pos_idx+neg_idx).gt(0)].view(-1, self.num_classes)
targets_weighted = conf_t[(pos+neg).gt(0)]
loss_c = F.cross_entropy(conf_p, targets_weighted, size_average=False)
# Sum of losses: L(x,c,l,g) = (Lconf(x, c) + αLloc(x,l,g)) / N
N = num_pos.data.sum()
loss_l /= N
loss_c /= N
return loss_l, loss_c
三、数据扩增
我认为这篇文章最终的一个部分也是数据扩增的一个过程,具体的部分,参考文章的这部分内容,
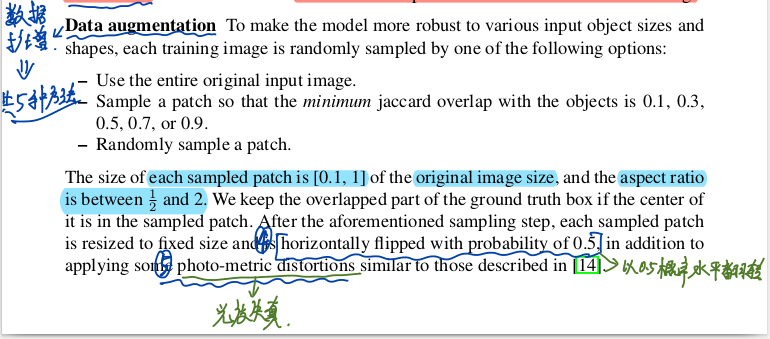
从下图的结果中,我们可以发现,数据扩增之后,MPA提高了8.8,因此他也是十分重要的。
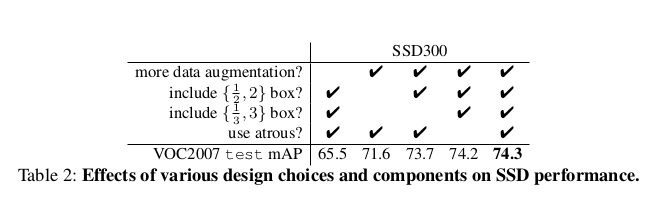
本文主要进行了一下几种变换,有的变换按照0.5概率执行,不是全部都会执行
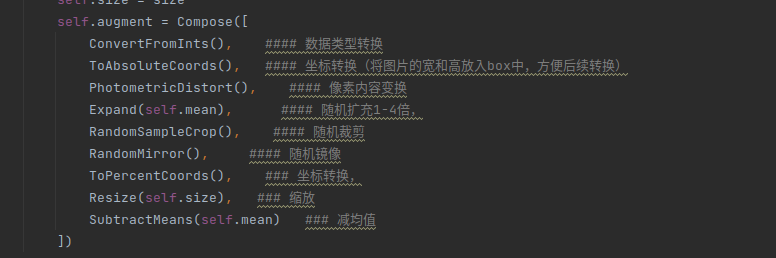
代码实现如下: 点击查看代码
class Compose(object):
"""Composes several augmentations together.
Args:
transforms (List[Transform]): list of transforms to compose.
Example:
>>> augmentations.Compose([
>>> transforms.CenterCrop(10),
>>> transforms.ToTensor(),
>>> ])
"""
def __init__(self, transforms):
self.transforms = transforms
def __call__(self, img, boxes=None, labels=None):
for t in self.transforms:
img, boxes, labels = t(img, boxes, labels)
return img, boxes, labels
class Lambda(object):
"""Applies a lambda as a transform."""
def __init__(self, lambd):
assert isinstance(lambd, types.LambdaType)
self.lambd = lambd
def __call__(self, img, boxes=None, labels=None):
return self.lambd(img, boxes, labels)
class ConvertFromInts(object):
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
return image.astype(np.float32), boxes, labels
class SubtractMeans(object):
def __init__(self, mean):
self.mean = np.array(mean, dtype=np.float32)
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
image = image.astype(np.float32)
image -= self.mean
return image.astype(np.float32), boxes, labels
class ToAbsoluteCoords(object):
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
height, width, channels = image.shape
boxes[:, 0] *= width
boxes[:, 2] *= width
boxes[:, 1] *= height
boxes[:, 3] *= height
return image, boxes, labels
class ToPercentCoords(object):
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
height, width, channels = image.shape
boxes[:, 0] /= width
boxes[:, 2] /= width
boxes[:, 1] /= height
boxes[:, 3] /= height
return image, boxes, labels
class Resize(object):
def __init__(self, size=300):
self.size = size
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
image = cv2.resize(image, (self.size,
self.size))
return image, boxes, labels
class RandomSaturation(object):
def __init__(self, lower=0.5, upper=1.5):
self.lower = lower
self.upper = upper
assert self.upper >= self.lower, "contrast upper must be >= lower."
assert self.lower >= 0, "contrast lower must be non-negative."
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
if random.randint(2):
image[:, :, 1] *= random.uniform(self.lower, self.upper)
return image, boxes, labels
class RandomHue(object):
def __init__(self, delta=18.0):
assert delta >= 0.0 and delta <= 360.0
self.delta = delta
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
if random.randint(2):
image[:, :, 0] += random.uniform(-self.delta, self.delta)
image[:, :, 0][image[:, :, 0] > 360.0] -= 360.0
image[:, :, 0][image[:, :, 0] < 0.0] += 360.0
return image, boxes, labels
class RandomLightingNoise(object):
def __init__(self):
self.perms = ((0, 1, 2), (0, 2, 1),
(1, 0, 2), (1, 2, 0),
(2, 0, 1), (2, 1, 0))
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
if random.randint(2):
swap = self.perms[random.randint(len(self.perms))]
shuffle = SwapChannels(swap) # shuffle channels
image = shuffle(image)
return image, boxes, labels
class ConvertColor(object):
def __init__(self, current='BGR', transform='HSV'):
self.transform = transform
self.current = current
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
if self.current == 'BGR' and self.transform == 'HSV':
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
elif self.current == 'HSV' and self.transform == 'BGR':
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR)
else:
raise NotImplementedError
return image, boxes, labels
class RandomContrast(object):
def __init__(self, lower=0.5, upper=1.5):
self.lower = lower
self.upper = upper
assert self.upper >= self.lower, "contrast upper must be >= lower."
assert self.lower >= 0, "contrast lower must be non-negative."
# expects float image
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
#### 生成(0-1),表示按照0.5的概率运行
if random.randint(2):
alpha = random.uniform(self.lower, self.upper) #### 随机扩大0.5-1.5倍
image *= alpha
return image, boxes, labels
class RandomBrightness(object):
def __init__(self, delta=32):
assert delta >= 0.0
assert delta <= 255.0
self.delta = delta
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
if random.randint(2):
delta = random.uniform(-self.delta, self.delta)
image += delta
return image, boxes, labels
class ToCV2Image(object):
def __call__(self, tensor, boxes=None, labels=None):
return tensor.cpu().numpy().astype(np.float32).transpose((1, 2, 0)), boxes, labels
class ToTensor(object):
def __call__(self, cvimage, boxes=None, labels=None):
return torch.from_numpy(cvimage.astype(np.float32)).permute(2, 0, 1), boxes, labels
class RandomSampleCrop(object):
"""Crop
Arguments:
img (Image): the image being input during training
boxes (Tensor): the original bounding boxes in pt form
labels (Tensor): the class labels for each bbox
mode (float tuple): the min and max jaccard overlaps
Return:
(img, boxes, classes)
img (Image): the cropped image
boxes (Tensor): the adjusted bounding boxes in pt form
labels (Tensor): the class labels for each bbox
"""
def __init__(self):
self.sample_options = (
# using entire original input image
None,
# sample a patch s.t. MIN jaccard w/ obj in .1,.3,.4,.7,.9
(0.1, None),
(0.3, None),
(0.7, None),
(0.9, None),
# randomly sample a patch
(None, None),
)
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
height, width, _ = image.shape
while True:
# randomly choose a mode
mode = random.choice(self.sample_options)
if mode is None:
return image, boxes, labels
min_iou, max_iou = mode
if min_iou is None:
min_iou = float('-inf')
if max_iou is None:
max_iou = float('inf')
# max trails (50)
for _ in range(50):
current_image = image
w = random.uniform(0.3 * width, width)
h = random.uniform(0.3 * height, height)
# aspect ratio constraint b/t .5 & 2
if h / w < 0.5 or h / w > 2:
continue
left = random.uniform(width - w)
top = random.uniform(height - h)
# convert to integer rect x1,y1,x2,y2
rect = np.array([int(left), int(top), int(left+w), int(top+h)])
# calculate IoU (jaccard overlap) b/t the cropped and gt boxes
overlap = jaccard_numpy(boxes, rect)
# is min and max overlap constraint satisfied? if not try again
if overlap.min() < min_iou and max_iou < overlap.max():
continue
# cut the crop from the image
current_image = current_image[rect[1]:rect[3], rect[0]:rect[2],
:]
# keep overlap with gt box IF center in sampled patch
centers = (boxes[:, :2] + boxes[:, 2:]) / 2.0
# mask in all gt boxes that above and to the left of centers
m1 = (rect[0] < centers[:, 0]) * (rect[1] < centers[:, 1])
# mask in all gt boxes that under and to the right of centers
m2 = (rect[2] > centers[:, 0]) * (rect[3] > centers[:, 1])
# mask in that both m1 and m2 are true
mask = m1 * m2
# have any valid boxes? try again if not
if not mask.any():
continue
# take only matching gt boxes
current_boxes = boxes[mask, :].copy()
# take only matching gt labels
current_labels = labels[mask]
# should we use the box left and top corner or the crop's
current_boxes[:, :2] = np.maximum(current_boxes[:, :2],
rect[:2])
# adjust to crop (by substracting crop's left,top)
current_boxes[:, :2] -= rect[:2]
current_boxes[:, 2:] = np.minimum(current_boxes[:, 2:],
rect[2:])
# adjust to crop (by substracting crop's left,top)
current_boxes[:, 2:] -= rect[:2]
return current_image, current_boxes, current_labels
class Expand(object):
def __init__(self, mean):
self.mean = mean
def __call__(self, image, boxes, labels):
if random.randint(2):
return image, boxes, labels
height, width, depth = image.shape
ratio = random.uniform(1, 4)
#### 根据随机的1-4倍数随机生成一个left,top值,病用均值进行填充,
left = random.uniform(0, width*ratio - width)
top = random.uniform(0, height*ratio - height)
expand_image = np.zeros(
(int(height*ratio), int(width*ratio), depth),
dtype=image.dtype)
expand_image[:, :, :] = self.mean
expand_image[int(top):int(top + height),
int(left):int(left + width)] = image
image = expand_image
### 最后将扩充后的图片写入GTbox 中
boxes = boxes.copy()
boxes[:, :2] += (int(left), int(top))
boxes[:, 2:] += (int(left), int(top))
return image, boxes, labels
class RandomMirror(object):
def __call__(self, image, boxes, classes):
_, width, _ = image.shape
if random.randint(2):
image = image[:, ::-1]
boxes = boxes.copy()
boxes[:, 0::2] = width - boxes[:, 2::-2]
return image, boxes, classes
class SwapChannels(object):
"""Transforms a tensorized image by swapping the channels in the order
specified in the swap tuple.
Args:
swaps (int triple): final order of channels
eg: (2, 1, 0)
"""
def __init__(self, swaps):
self.swaps = swaps
def __call__(self, image):
"""
Args:
image (Tensor): image tensor to be transformed
Return:
a tensor with channels swapped according to swap
"""
# if torch.is_tensor(image):
# image = image.data.cpu().numpy()
# else:
# image = np.array(image)
image = image[:, :, self.swaps]
return image
class PhotometricDistort(object):
def __init__(self):
self.pd = [
RandomContrast(), #### 随机扩大(0.5-1.5)倍的像素,增加或减少了对比度
ConvertColor(transform='HSV'), ### 图片从BGR改为HSV类型
RandomSaturation(), #### S通道,通过乘以(0.5-1.5)来改变饱和度
RandomHue(), #### 增加或减少H通道的(-18-18)来改变色度
ConvertColor(current='HSV', transform='BGR'),
RandomContrast()
]
self.rand_brightness = RandomBrightness() ### 随机增加(-32,32)之间的像素值
self.rand_light_noise = RandomLightingNoise() #### 随机改变通道位置来修改颜色通道
def __call__(self, image, boxes, labels):
im = image.copy()
im, boxes, labels = self.rand_brightness(im, boxes, labels)
### 以0.5概率从执行对比度和色度等的转换
if random.randint(2):
distort = Compose(self.pd[:-1])
else:
distort = Compose(self.pd[1:])
im, boxes, labels = distort(im, boxes, labels)
return self.rand_light_noise(im, boxes, labels)
class SSDAugmentation(object):
def __init__(self, size=300, mean=(104, 117, 123)):
self.mean = mean
self.size = size
self.augment = Compose([
ConvertFromInts(), #### 数据类型转换
ToAbsoluteCoords(), #### 坐标转换(将图片的宽和高放入box中,方便后续转换)
PhotometricDistort(), #### 像素内容变换
Expand(self.mean), #### 随机扩充1-4倍,
RandomSampleCrop(), #### 随机裁剪
RandomMirror(), #### 随机镜像
ToPercentCoords(), ### 坐标转换,
Resize(self.size), ### 缩放
SubtractMeans(self.mean) ### 减均值
])
def __call__(self, img, boxes, labels):
return self.augment(img, boxes, labels)
文章引用参考了https://blog.51cto.com/u_15274944/4896277#0__2
本文来自博客园,作者:高冷的程序员大大,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/danieldaren/p/16720766.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号