pytest学习
安装
pip install pytest
pytest --version
第一个test
test.py def func(x): return x + 1 def test_answer(): assert func(3) == 5
运行结果如图所示:
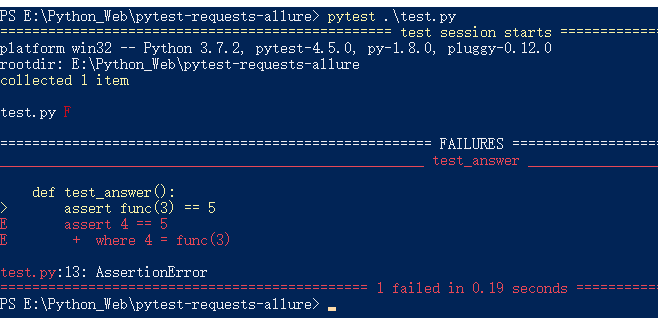
运行
默认会执行当前目录及子目录的所有test_*.py或*_test.py文件。用例执行成功为.,失败为F pytest 静默执行 pytest -q E:\Python_Web\pytest-requests-allure\test.py # 调试方式执行,可以打印print日志等详情信息 $ pytest E:\Python_Web\pytest-requests-allure\test.py -s -v # python模块方式执行 $ python -m pytest E:\Python_Web\pytest-requests-allure\test.py # 执行单个目录下的tests $ python E:\Python_Web\pytest-requests-allure\
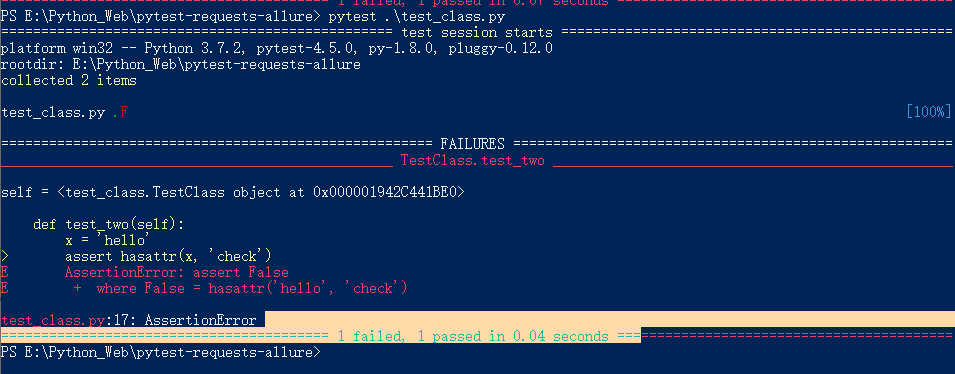
test类包含多个tests
# pytest默认会执行所有test_前缀的函数 class TestClass(object): def test_one(self): x = "this" assert 'h' in x def test_two(self): x = 'hello' assert hasattr(x, 'check')
执行结果:
pytest常见的exit codes
Exit code 0 所有tests全部通过
Exit code 1 部分tests失败了
Exit code 2 用户中止test执行
Exit code 3 执行test时,内部报错
Exit code 4 pytest命令使用姿势不对
Exit code 5 无tests可执行
pytest常见帮助选项
ytest --version # 显示版本信息
pytest fixtures(明确的、模块化的、可扩展的)
- fixtures由明确的命名,可以通过测试函数、模块、类或整个项目激活
- fixtures以模块化的方式实现,因为每个名称会触发一个fixtures函数,同时函数本身也可以使用其它fixtures
- fixtures管理从简单的单元到复杂的功能测试,允许参数化fixtures和根据配置和组件进行测试或通过函数、类、模块或整个test会话范围重用fixtures
Fixtures作为函数参数
测试函数可以接收fixture对象作为输入参数,使用@pytest.fixture
import pytest @pytest.fixture def smtp_connection(): import smtplib return smtplib.SMTP(host='smtp.qq.com', port=587, timeout=5) def test_ehlo(smtp_connection): response, msg = smtp_connection.ehlo() assert response == 250 assert 0
执行结果
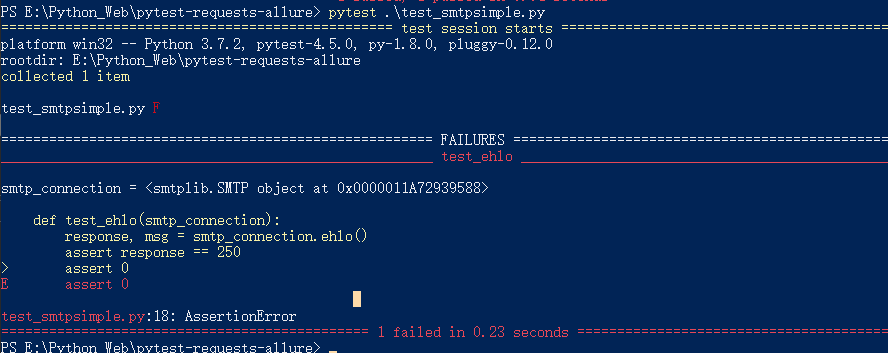
Fixtures 依赖注入
Fixtures 允许测试函数非常容易的接收和使用特定的预初始化程序对象,而无需特别去关注import/setup/cleanup等细节
config.py:共享fixture函数
如果多个测试文件需要用到一个fixture函数,则把它写到conftest.py文件当中。使用时无需导入这个fixture函数,因为pytest会自动获取
共享测试数据
- 如果在测试中,需要从文件加载测试数据到tests,可以使用fixture方式加载,pytest有自动缓存机制
- 另外一种方式是添加测试数据文件到tests目录,如使用pytest-datadir和pytest-datafiles插件
Scope:共享一个fixture实列(类、模块或会话)
Scope - module
conftest.py
import pytest import smtplib @pytest.fixture(scope='module') def smtp_connection(): return smtplib.SMTP(host='smtp.qq.com', port=587, timeout=5)
test_module.py def test_ehlo(smtp_connection): response, msg = smtp_connection.ehlo() assert response == 250 assert b'smtp.qq.com' in msg assert 0 def test_noop(smtp_connection): response, msg = smtp_connection.noop() assert response == 250 assert 0
执行结果:
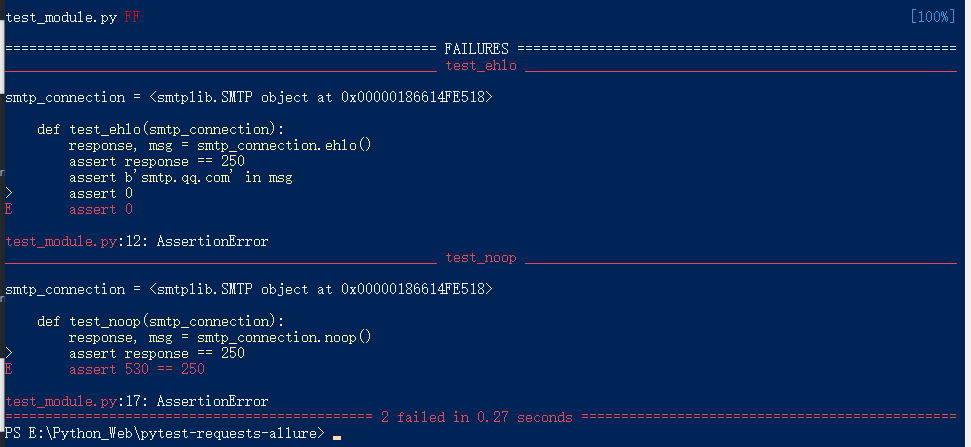
Scope - session
import pytest import smtplib # 所有tests能使用到它的,都是共享同一个fixture值 @pytest.fixture(scope='session') def smtp_connection(): return smtplib.SMTP(host='smtp.qq.com', port=587, timeout=5)
Scope - class
import pytest import smtplib # 每个test类,都是共享同一个fixture值 @pytest.fixture(scope='class') def smtp_connection(): return smtplib.SMTP(host='smtp.qq.com', port=587, timeout=5)
高级别的scope fixtures第一个实例化
@pytest.fixture(scope="session") def s1(): pass @pytest.fixture(scope="module") def m1(): pass @pytest.fixture def f1(tmpdir): pass @pytest.fixture def f2(): pass def test_foo(f1, m1, f2, s1): ......
- s1: 是最高级别的fxiture(session)
- m1: 是第二高级别的fixture(module)
- tmpdir: 是一个function的fixture,依赖f1
- f1:在test_foo列表参数当中,是第一个function的fixture
- f2:在test_foo列表参数当中,是最后一个function的fixture
Fixture结束或执行teardown代码
- 当fixture超过其scope范围,pytest支持执行fixture特定的结束代码
- 使用yield替换return,所有yield声明之后的代码都作为teardown代码处理
yield替换return
conftest.py import pytest import smtplib # print和smtp_connection.close()只会在module范围内最后一个test执行结束后执行,除非中间有异常 @pytest.fixture(scope='module') def smtp_connection(): smtp_connection = smtplib.SMTP(host='smtp.qq.com', port=587, timeout=5) yield smtp_connection print('teardown smtp') smtp_connection.close()
执行
pytest -s -q 01\test_module.py --tb=no FFteardown smtp 2 failed in 0.96 seconds
with替换yield
conftest.py import pytest import smtplib # 使用了with声明,smtp_connection等test执行完后,自动关闭 # 注意:yield之前的setup代码发生了异常,teardown代码将不会被调用 @pytest.fixture(scope='module') def smtp_connection(): with smtplib.SMTP(host='smtp.qq.com', port=587, timeout=5) as smtp_connection: yield smtp_connection
使用addfinalizer清理
yield和addfinalizer方法类似,但addfinalizer有两个不同的地方
可以注册多个finalizer函数
不论setup代码是否发生异常,均会关闭所有资源
@pytest.fixture def equipments(request): r = [] for port in ('C1', 'C3', 'C28'): equip = connect(port) request.addfinalizer(equip.disconnect) r.append(equip) return r # 假设C28抛出一次,C1和C2将正常被关闭。当然异常发生在finalize函数注册之前,它将不被执行
conftest.py import pytest import smtplib @pytest.fixture(scope='module') def smtp_connection(request): smtp_connection = smtplib.SMTP(host='smtp.qq.com', port=587, timeout=5) def fin(): print('teardown smtp_connection') smtp_connection.close() request.addfinalizer(fin) return smtp_connection
执行
pytest -s -q 01\test_module.py --tb=no FFteardown smtp_connection 2 failed in 0.99 seconds
Fixture可以使用request对象来管理 测试内容
Fixture函数可以接收一个request对象
conftest.py import pytest import smtplib # 所有使用fixture的test module,都可以读取一个可选的smtpserver地址 @pytest.fixture(scope='module') def smtp_connection(request): server = getattr(request.module, 'smtpserver', 'smtp.qq.com') smtp_connection = smtplib.SMTP(host=server, port=587, timeout=5) yield smtp_connection print('finalizing %s (%s)' % (smtp_connection, server)) smtp_connection.close()
执行1
pytest -s -q --tb=no .FFFfinalizing <smtplib.SMTP object at 0x00000266A3912470> (smtp.qq.com) FF 5 failed, 1 passed in 2.11 seconds test_anothersmtp.py smtpserver = 'mail.python.org' # 自动读取并替换fixture默认的值 def test_showhelo(smtp_connection): assert 0, smtp_connection.helo()
执行2
pytest -qq --tb=short 01\test_anothersmtp.py F [100%] ================================== FAILURES =================================== ________________________________ test_showhelo ________________________________ 01\test_anothersmtp.py:5: in test_showhelo assert 0, smtp_connection.helo() E AssertionError: (250, b'mail.python.org') E assert 0 -------------------------- Captured stdout teardown --------------------------- finalizing <smtplib.SMTP object at 0x000001C1F631DBE0> (mail.python.org)
Fixture工厂模式
在单个test中,fixture结果需要被多次使用
@pytest.fixture def make_customer_record(): def _make_customer_record(name): return { "name": name, "orders": [] } return _make_customer_record def test_customer_records(make_customer_record): customer_1 = make_customer_record("Lisa") customer_2 = make_customer_record("Mike") customer_3 = make_customer_record("Meredith") # 创建的数据需要工厂管理时,采用这种方式 @pytest.fixture def make_customer_record(): created_records = [] def _make_customer_record(name): record = models.Customer(name=name, orders=[]) created_records.append(record) return record yield _make_customer_record for record in created_records: record.destroy() def test_customer_records(make_customer_record): customer_1 = make_customer_record("Lisa") customer_2 = make_customer_record("Mike") customer_3 = make_customer_record("Meredith")
Fixture 参数
Fixture可以参数化,当需要执行多次时
conftest.py
import pytest
import smtplib
@pytest.fixture(scope='module',
params=['smtp.qq.com', 'mail.python.org'])
def smtp_connection(request):
smtp_connection = smtplib.SMTP(host=request.param, port=587, timeout=5)
yield smtp_connection
print('finalizing %s' % (smtp_connection))
smtp_connection.close()
执行
pytest -q 01\test_module.py FFFF [100%] ================================== FAILURES =================================== ___________________________ test_ehlo[smtp.qq.com] ____________________________ smtp_connection = <smtplib.SMTP object at 0x000002769B09A908> def test_ehlo(smtp_connection): response, msg = smtp_connection.ehlo() assert response == 250 assert b'smtp.qq.com' in msg > assert 0 E assert 0 01\test_module.py:7: AssertionError ___________________________ test_noop[smtp.qq.com] ____________________________ smtp_connection = <smtplib.SMTP object at 0x000002769B09A908> def test_noop(smtp_connection): response, msg = smtp_connection.noop() > assert response == 250 E assert 530 == 250 01\test_module.py:12: AssertionError _________________________ test_ehlo[mail.python.org] __________________________ smtp_connection = <smtplib.SMTP object at 0x000002769B09AA58> def test_ehlo(smtp_connection): response, msg = smtp_connection.ehlo() assert response == 250 > assert b'smtp.qq.com' in msg E AssertionError: assert b'smtp.qq.com' in b'mail.python.org\nPIPELINING\nSIZE 51200000\nETRN\nSTARTTLS\nAUTH DIGEST-MD5 NTLM CRAM-MD5\nENHANCEDST ATUSCODES\n8BITMIME\nDSN\nSMTPUTF8' 01\test_module.py:6: AssertionError ---------------------------- Captured stdout setup ---------------------------- finalizing <smtplib.SMTP object at 0x000002769B09A908> _________________________ test_noop[mail.python.org] __________________________ smtp_connection = <smtplib.SMTP object at 0x000002769B09AA58> def test_noop(smtp_connection): response, msg = smtp_connection.noop() assert response == 250 > assert 0 E assert 0 01\test_module.py:13: AssertionError -------------------------- Captured stdout teardown --------------------------- finalizing <smtplib.SMTP object at 0x000002769B09AA58> 4 failed in 4.29 seconds
标记fixture参数
test_fixture_marks.py import pytest @pytest.fixture(params=[0, 1, pytest.param(2, marks=pytest.mark.skip)]) def data_set(request): return request.param def test_data(data_set): pass
执行
$ pytest 01\test_fixture_marks.py -v ============================= test session starts ============================= platform win32 -- Python 3.6.4, pytest-3.7.4, py-1.6.0, pluggy-0.7.1 -- d:\projects\python\pytest_notes\.venv\scripts\python.exe cachedir: .pytest_cache rootdir: D:\projects\python\pytest_notes, inifile: collected 3 items 01/test_fixture_marks.py::test_data[0] PASSED [ 33%] 01/test_fixture_marks.py::test_data[1] PASSED [ 66%] 01/test_fixture_marks.py::test_data[2] SKIPPED [100%] ===================== 2 passed, 1 skipped in 0.14 seconds =====================
经典的xunit风格setup
Module级别的setup/teardown
如果有多个test函数或test类在一个模块内,可以选择的实现setup_module和teardown_module,一般模块内的所有函数都会调用一次
def setup_module(module):
pass
def teardown_module(module):
pass
Class级别的setup/teardown
在类内,所有的方法均会调用到
@classmethod
def setup_class(cls):
pass
@classmethod
def teardown_class(cls):
pass
Method和Function级别的setup/teardown
# 指定方法调用
def setup_method(self, method):
pass
def teardown_method(self, method):
pass
# 模块级别内可以直接使用function调用
def setup_function(function):
pass
def teardown_function(function):
pass
目前还在学习中,希望会对大家有所帮助,觉得不错,就点赞支持一下。
另外,转载时请附带链接。谢谢!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号