JS之style对象
一、style属性的获取和修改
在DOM当中,如果想设置样式,有两种形式:
- className(针对内嵌样式)
- style(针对行内样式)
这里我们就来讲一下style。
需要注意的是:style是一个对象,只能获取**行内样式**,不能获取内嵌的样式和外链的样式。例如:
```html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
div {
border: 6px solid red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1" style="width: 200px;height: 100px;background-color: pink;"></div>
<script>
var box1 = document.getElementsByTagName("div")[0];
console.log(box1.style.backgroundColor);
console.log(box1.style.border); //没有打印结果,因为这个属性不是行内样式
console.log(typeof box1.style); //因为是对象,所以打印结果是Object
console.log(box1.style); //打印结果是对象
</script>
</body>
</html>
```
打印结果:
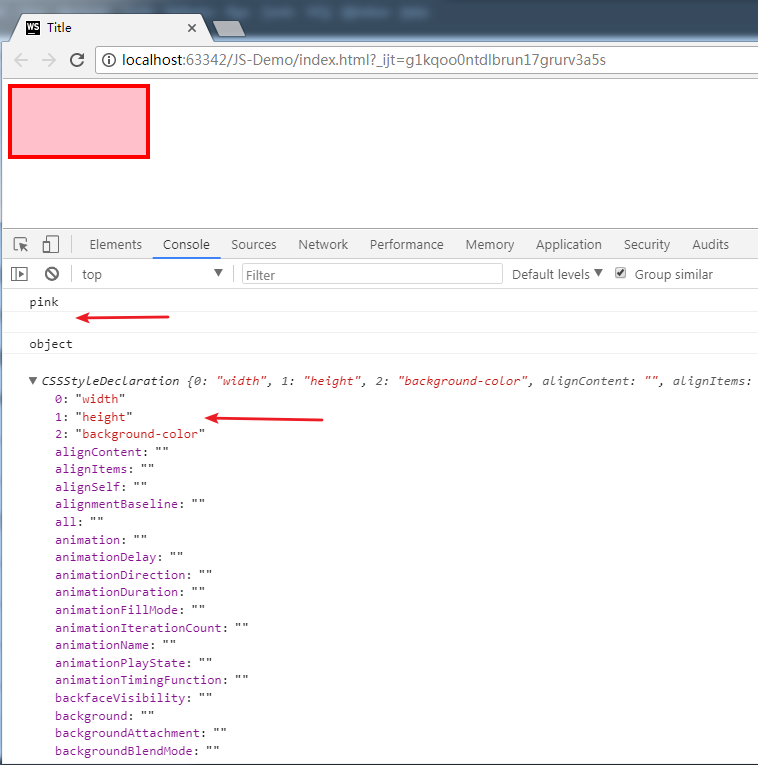
上图显示,因为border属性不是行内样式,所以无法通过style对象获取。
1、通过 js 读取元素的样式
语法:(方式一)
```javascript
元素.style.样式名
```
备注:我们通过style属性读取的样式都是**行内样式**。
语法:(方式二)
```javascript
元素.style["属性"]; //格式
box.style["width"]; //举例
```
方式二最大的优点是:可以给属性传递参数。
2、通过 js 设置元素的样式
语法:
```javascript
元素.style.样式名 = 样式值;
```
举例:
```
box1.style.width = "300px";
box1.style.backgroundColor = "red"; // 驼峰命名法
```
备注:我们通过style属性设置的样式都是**行内样式**,而行内样式有较高的优先级。但是如果在样式中的其他地方写了`!important`,则此时`!important`会有更高的优先级。
3、style属性的注意事项
style属性需要注意以下几点:
(1)样式少的时候使用。
(2)style是对象。我们在上方已经打印出来,typeof的结果是Object。
(3)值是字符串,没有设置值是“”。
(4)命名规则,驼峰命名。
(5)只能获取行内样式,和内嵌和外链无关。
(6)box.style.cssText = “字符串形式的样式”。
`cssText`这个属性,其实就是把行内样式里面的值当做字符串来对待。在上方代码的基础之上,举例:
```html
<script>
var box1 = document.getElementsByTagName("div")[0];
//通过cssText一次性设置行内样式
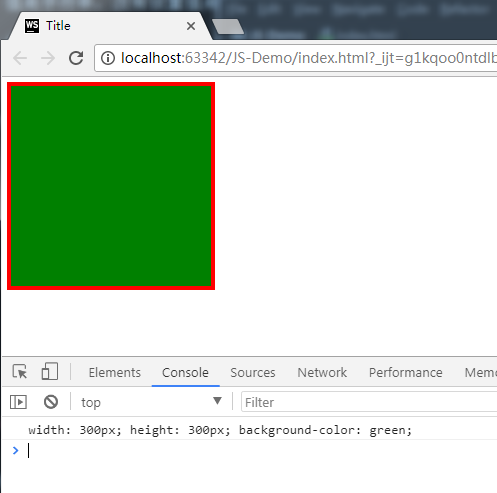
box1.style.cssText = "width: 300px;height: 300px;background-color: green;";
console.log(box1.style.cssText); //这一行更加可以理解,style是对象
</script>
```
打印结果:
4、style的常用属性
style的常用属性包括:
- backgroundColor
- backgroundImage
- color
- width
- height
- border
- opacity 设置透明度 (IE8以前是filter: alpha(opacity=xx))
注意DOM对象style的属性和标签中style内的值不一样,因为在JS中,`-`不能作为标识符。比如:
- DOM中:backgroundColor
- CSS中:background-color
二、style属性的举例
我们针对上面列举的几个style的样式,来举几个例子:
- 举例1、改变div的大小和透明度
- 举例2、当前输入的文本框高亮显示
- 举例3、高级隔行变色、高亮显示
下面来逐一实现。
### 举例1:改变div的大小和透明度
代码举例:
```html
<body>
<div style="width: 100px;height: 100px;background-color: pink;"></div>
<script>
var div = document.getElementsByTagName("div")[0];
div.onmouseover = function () {
div.style.width = "200px";
div.style.height = "200px";
div.style.backgroundColor = "black";
div.style.opacity = "0.2"; //设置背景色的透明度。单位是0.1
div.style.filter = "alpha(opacity=20)"; //上一行代码的兼容性写法。注意单位是百进制
}
</script>
</body>
```
### 举例2:当前输入的文本框高亮显示
代码实现:
```html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style>
input {
display: block;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<input type="text"/>
<input type="text"/>
<input type="text"/>
<input type="text"/>
<input type="text"/>
</ul>
<script>
//需求:让所有的input标签获取焦点后高亮显示
//1.获取事件源
var inpArr = document.getElementsByTagName("input");
//2.绑定事件
//3.书写事件驱动程序
for (var i = 0; i < inpArr.length; i++) {
//获取焦点后,所有的input标签被绑定onfocus事件
inpArr[i].onfocus = function () {
this.style.border = "2px solid red";
this.style.backgroundColor = "#ccc";
}
//绑定onblur事件,取消样式
inpArr[i].onblur = function () {
this.style.border = "";
this.style.backgroundColor = "";
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
```
### 举例3:高级隔行变色、高亮显示
```html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
text-align: center;
}
.wrap {
width: 500px;
margin: 100px auto 0;
}
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
border-spacing: 0;
border: 1px solid #c0c0c0;
width: 500px;
}
th,
td {
border: 1px solid #d0d0d0;
color: #404060;
padding: 10px;
}
th {
background-color: #09c;
font: bold 16px "微软雅黑";
color: #fff;
}
td {
font: 14px "微软雅黑";
}
tbody tr {
background-color: #f0f0f0;
cursor: pointer;
}
.current {
background-color: red !important;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrap">
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>序号</th>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>课程</th>
<th>成绩</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody id="target">
<tr>
<td>
1
</td>
<td>生命壹号</td>
<td>语文</td>
<td>100</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
2
</td>
<td>生命贰号</td>
<td>日语</td>
<td>99</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
3
</td>
<td>生命叁号</td>
<td>营销学</td>
<td>98</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
4
</td>
<td>生命伍号</td>
<td>数学</td>
<td>90</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
5
</td>
<td>许嵩</td>
<td>英语</td>
<td>96</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
6
</td>
<td>vae</td>
<td>体育</td>
<td>90</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
<script>
//需求:让tr各行变色,鼠标放入tr中,高亮显示。
//1.隔行变色。
var tbody = document.getElementById("target");
var trArr = tbody.children;
//循环判断并各行赋值属性(背景色)
for (var i = 0; i < trArr.length; i++) {
if (i % 2 !== 0) {
trArr[i].style.backgroundColor = "#a3a3a3";
} else {
trArr[i].style.backgroundColor = "#ccc";
}
//鼠标进入高亮显示
//难点:鼠标移开的时候要回复原始颜色。
//计数器(进入tr之后,立刻记录颜色,然后移开的时候使用记录好的颜色)
var myColor = "";
trArr[i].onmouseover = function () {
//赋值颜色之前,先记录颜色
myColor = this.style.backgroundColor;
this.style.backgroundColor = "#fff";
}
trArr[i].onmouseout = function () {
this.style.backgroundColor = myColor;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
```
实现的效果如下:

代码解释:
上方代码中,我们**用到了计数器myColor来记录每一行最原始的颜色**(赋值白色之前)。如果不用计数器,可能很多人以为代码是写的:(错误的代码)
```html
<script>
//需求:让tr各行变色,鼠标放入tr中,高亮显示。
//1.隔行变色。
var tbody = document.getElementById("target");
var trArr = tbody.children;
//循环判断并各行赋值属性(背景色)
for (var i = 0; i < trArr.length; i++) {
if (i % 2 !== 0) {
trArr[i].style.backgroundColor = "#a3a3a3";
} else {
trArr[i].style.backgroundColor = "#ccc";
}
//鼠标进入高亮显示
//难点:鼠标移开的时候要回复原始颜色。
//计数器(进入tr之后,立刻记录颜色,然后移开的时候使用记录好的颜色)
trArr[i].onmouseover = function () {
this.style.backgroundColor = "#fff";
}
trArr[i].onmouseout = function () {
this.style.backgroundColor = "#a3a3a3";
}
}
</script>
```
这种错误的代码,实现的效果却是:(未达到效果)

三、通过 js 获取元素当前显示的样式
我们在上面的内容中,通过`元素.style.className`的方式只能获取**行内样式**。但是,有些元素,也写了**内嵌样式或外链样式**。
既然样式有这么种,那么,如何获取元素当前显示的样式(包括行内样式、内嵌样式、外链样式)呢?我们接下来看一看。
1、获取元素当前正在显示的样式
(1)w3c的做法:
```javascript
window.getComputedStyle("要获取样式的元素", "伪元素");
```
两个参数都是必须要有的。参数二中,如果没有伪元素就用 null 代替(一般都传null)。
(2)IE和opera的做法:
```javascript
obj.currentStyle;
```
注意:
- 如果当前元素没有设置该样式,则获取它的默认值。
- 该方法会返回一个**对象**,对象中封装了当前元素对应的样式,可以通过`对象.样式名`来读取具体的某一个样式。
- 通过currentStyle和getComputedStyle()读取到的样式都是只读的,不能修改,如果要修改必须通过style属性。
综合上面两种写法,就有了一种兼容性的写法,同时将其封装。代码举例如下:
```html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style>
div {
background-color: pink;
/*border: 1px solid #000;*/
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div style="width: 100px;height: 100px;"></div>
<script>
var div1 = document.getElementsByTagName("div")[0];
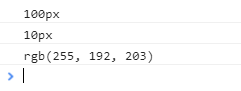
console.log(getStyle(div1, "width"));
console.log(getStyle(div1, "padding"));
console.log(getStyle(div1, "background-color"));
/*
* 兼容方法,获取元素当前正在显示的样式。
* 参数:
* obj 要获取样式的元素
*. name 要获取的样式名
*/
function getStyle(ele, attr) {
if (window.getComputedStyle) {
return window.getComputedStyle(ele, null)[attr];
}
return ele.currentStyle[attr];
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
```
打印结果:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号