python运算学习之Numpy ------ 数组操作:连接数组、拆分数组 、广播机制、结构化数组、文件贮存与读写、np.where、数组去重
数组的连接:
1 # 连接数组
2 A = np.zeros((3, 4))
3 B = np.ones_like(A)
4 print(A, "\n-------分割符--------\n", B)
5 print("np.vstack的效果:\n", np.vstack((A, B))) # 这是多维数组按列拼接,如果A的shape是(3,4,5),拼接之后为(6,4,5)
6 print("np.hstack的效果:\n", np.hstack((A, B))) # 这是多维数组按行拼接,如果A的shape是(3,4,5),拼接之后为(3,8,5)
7 a = np.array([1, 1.2, 1.3])
8 b = np.array([2, 2.2, 2.3])
9 c = np.array([3, 3.2, 3.3])
10 print("np.column_stack的效果:\n", np.column_stack((A, B)))
11 print("np.row_stack的效果:\n", np.row_stack((A, B)))
12 print("np.column_stack的效果:\n", np.column_stack((a, b, c)))
13 print("np.row_stack的效果:\n", np.row_stack((a, b, c)))
14 Out[1]:
15 [[0. 0. 0. 0.]
16 [0. 0. 0. 0.]
17 [0. 0. 0. 0.]]
18 -------分割符--------
19 [[1. 1. 1. 1.]
20 [1. 1. 1. 1.]
21 [1. 1. 1. 1.]]
22 np.vstack的效果:
23 [[0. 0. 0. 0.]
24 [0. 0. 0. 0.]
25 [0. 0. 0. 0.]
26 [1. 1. 1. 1.]
27 [1. 1. 1. 1.]
28 [1. 1. 1. 1.]]
29 np.hstack的效果:
30 [[0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
31 [0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
32 [0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 1. 1. 1.]]
33 np.column_stack的效果:
34 [[0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
35 [0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
36 [0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 1. 1. 1.]]
37 np.row_stack的效果:
38 [[0. 0. 0. 0.]
39 [0. 0. 0. 0.]
40 [0. 0. 0. 0.]
41 [1. 1. 1. 1.]
42 [1. 1. 1. 1.]
43 [1. 1. 1. 1.]]
44 np.column_stack的效果:
45 [[1. 2. 3. ]
46 [1.2 2.2 3.2]
47 [1.3 2.3 3.3]]
48 np.row_stack的效果:
49 [[1. 1.2 1.3]
50 [2. 2.2 2.3]
51 [3. 3.2 3.3]]
|
拆分数组:
1 A = np.arange(0, 12).reshape(2, 6)
2 print("二维数组A:\n", A)
3 [B, C, D] = np.hsplit(A, 3) # hsplit(ary, indices_or_sections), np.hsplit(A, 3)为默认按列均分数组
4 print(B, "\n--------*---------\n", C, "\n")
5 [E, F] = np.vsplit(A, 2) # 默认按行均分数组
6 print(E, "\n--------*---------\n", F, "\n")
7 [A1, A2, A3] = np.split(A, [1, 3], axis=1) # axis=1按列切分,axis=0按行切分
8 print(A1, "\n--------*---------\n", A2, "\n")
9 Out[2]:
10 二维数组A:
11 [[ 0 1 2 3 4 5]
12 [ 6 7 8 9 10 11]]
13 [[0 1]
14 [6 7]]
15 --------*---------
16 [[2 3]
17 [8 9]]
18
19 [[0 1 2 3 4 5]]
20 --------*---------
21 [[ 6 7 8 9 10 11]]
22
23 [[0]
24 [6]]
25 --------*---------
26 [[1 2]
27 [7 8]]
|
数组的广播机制:
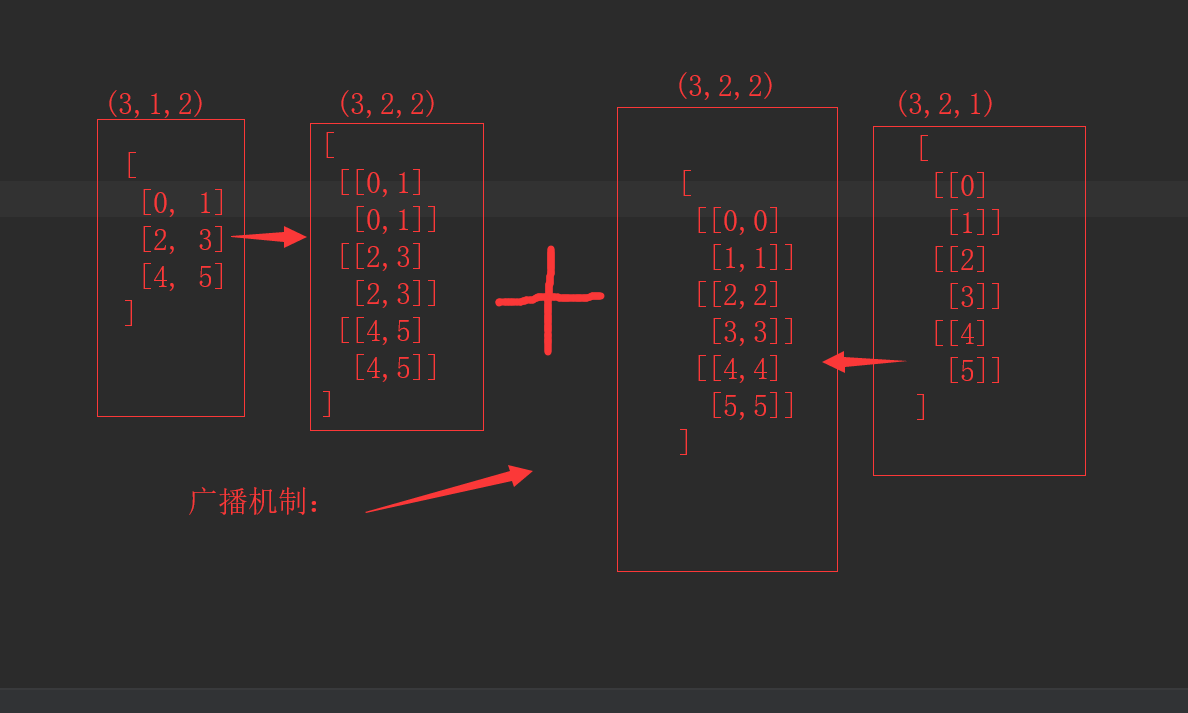
1 A = np.arange(0, 16).reshape(4, 4)
2 b = np.array([1.2, 2.3, 3, 4])
3 print(A + b)
4 m = np.arange(6).reshape((3, 2, 1))
5 n = np.arange(6).reshape((3, 1, 2))
6 print("----*----\n", m, "\n----*----\n", n)
7 print("m + n 的广播:\n", m + n)
8 Out[3]:
9 [[ 1.2 3.3 5. 7. ]
10 [ 5.2 7.3 9. 11. ]
11 [ 9.2 11.3 13. 15. ]
12 [13.2 15.3 17. 19. ]]
13 ----*----
14 [[[0]
15 [1]]
16
17 [[2]
18 [3]]
19
20 [[4]
21 [5]]]
22 ----*----
23 [[[0 1]]
24
25 [[2 3]]
26
27 [[4 5]]]
28 m + n 的广播:
29 [[[ 0 1]
30 [ 1 2]]
31
32 [[ 4 5]
33 [ 5 6]]
34
35 [[ 8 9]
36 [ 9 10]]]
|
示意图如下:
结构化数组:
1 structure_array = np.array([(1, 'First', 0.5, 1+2j), (2, 'Second', 1.3, 2-2j), (3, 'Third', 0.8, 1+3j)])
2 print(structure_array)
3 structure_array_1 = np.array([(1, 'First', 0.5, 1+2j), (2, 'Second', 1.3, 2-2j), (3, 'Third', 0.8, 1+3j)],
4 dtype=[('id', '<i2'), ('position', 'S6'), ('value', 'f4'), ('complex', '<c8')])
5 print(structure_array_1)
6 print(structure_array_1['id'])
7 print(structure_array_1['position'])
8 Out[4]:
9 [['1' 'First' '0.5' '(1+2j)']
10 ['2' 'Second' '1.3' '(2-2j)']
11 ['3' 'Third' '0.8' '(1+3j)']]
12 [(1, b'First', 0.5, 1.+2.j) (2, b'Second', 1.3, 2.-2.j)
13 (3, b'Third', 0.8, 1.+3.j)]
14 [1 2 3]
15 [b'First' b'Second' b'Third']
|
文件贮存与读写:
1 A = np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4)
2 np.save('save_data', A)
3 load_data = np.load('save_data.npy')
4 print("Numpy默认保存的格式:\n", load_data)
5 # 保存为csv格式
6 # savetxt(fname,X,fmt='%.18e',delimiter=' ',newline='\n',header='',footer='',comments='# ', encoding=None)
7 np.savetxt('data_csv.csv', A)
8 txt_csv = np.loadtxt('data_csv.csv')
9 print("Numpy导入csv的格式:\n", txt_csv)
10 # np.genfromtxt()导入数据
11 data = np.genfromtxt('data_csv.csv', delimiter=' ')
12 print("genfromtxt导入csv的格式:\n", data)
13 Out[5]:
14 Numpy默认保存的格式:
15 [[ 0 1 2 3]
16 [ 4 5 6 7]
17 [ 8 9 10 11]]
18 Numpy导入csv的格式:
19 [[ 0. 1. 2. 3.]
20 [ 4. 5. 6. 7.]
21 [ 8. 9. 10. 11.]]
22 genfromtxt导入csv的格式:
23 [[ 0. 1. 2. 3.]
24 [ 4. 5. 6. 7.]
25 [ 8. 9. 10. 11.]]
|
np.where:
np.where实际上是 x if condition else y 的矢量化版本
1 x = np.array([2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
2 y = np.array([10, 11, 12, 13, 14])
3 condition = np.array([True, False, True, True, False])
4 z = np.where(condition, x, y)
5 print(z)
6 data = np.array([[1, 2, np.nan, 4], [np.nan, 2, 3, 4]])
7 print(np.isnan(data))
8 print(np.where(np.isnan(data), 0, data))
9 Out[6]:
10 [ 2 11 4 5 14]
11 [[False False True False]
12 [ True False False False]]
13 [[1. 2. 0. 4.]
14 [0. 2. 3. 4.]]
|
数组去重:
1 print(np.unique([1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 6]))
2 print(np.unique(np.array([[1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 6], [1, 5, 9, 4, 7, 2, 1]])))
3 test = np.unique([[1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 6], [1, 5, 9, 4, 7, 2, 1]])
4 print(test, type(test))
5 Out[7]:
6 [1 2 3 4 6]
7 [1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9]
8 [1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9] <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
|
清澈的爱,只为中国


