Ajax属于客户端网络技术,属于js范畴。
一 数据的传输格式json
| 说明 | 语法 | 总结 | |||
| json |
json指的是类似于javascript对象的一种数据格式。 与json类似的还有xml,yaml,ini,text,protobuf。 作用是 |
|
1. json文件的后缀是json |
二 json数据的数据转换
| 方法 | 参数 | 返回值 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| stringify | json对象 | 字符串 | json对象转成字符串 |

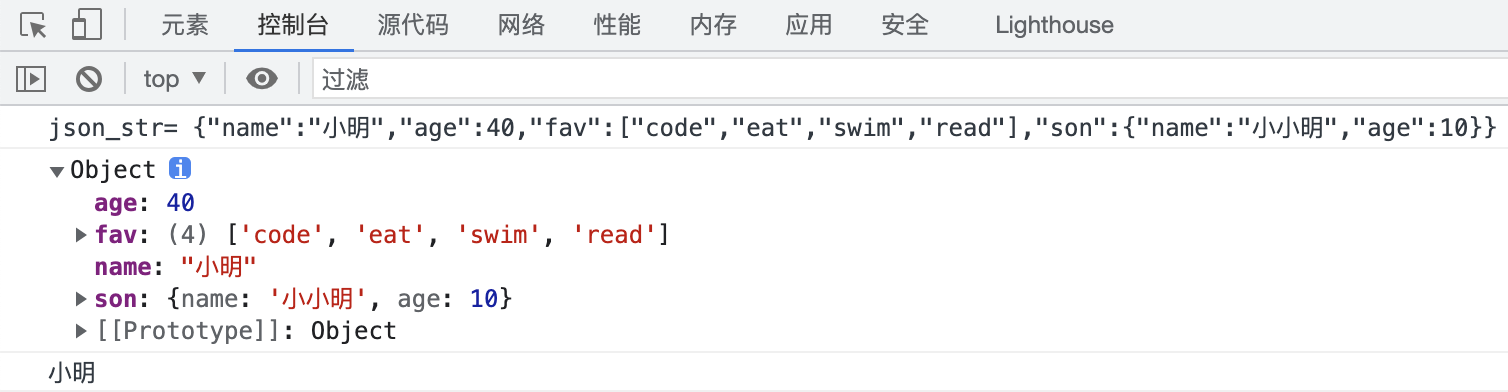
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <script> // js原生对象 var js_obj = { name:"小明", age:40, fav:["code","eat","swim",'read',], son:{ name:'小小明', age:10, } }; // json对象转换成字符串格式的json数据 var json_str = JSON.stringify(js_obj); console.log( "json_str=", json_str ); // 字符串格式的json数据转换成json对象 data_str = `{"name":"小明","age":40,"fav":["code","eat","swim","read"],"son":{"name":"小小明","age":10}}` var json_obj = JSON.parse(data_str); console.log( json_obj ); console.log( json_obj.name ); </script> </head> <body> </body> </html> 代码执行结果:
|
| parse | 字符串 | json对象 | 字符串格式的json数据转成json对象 |
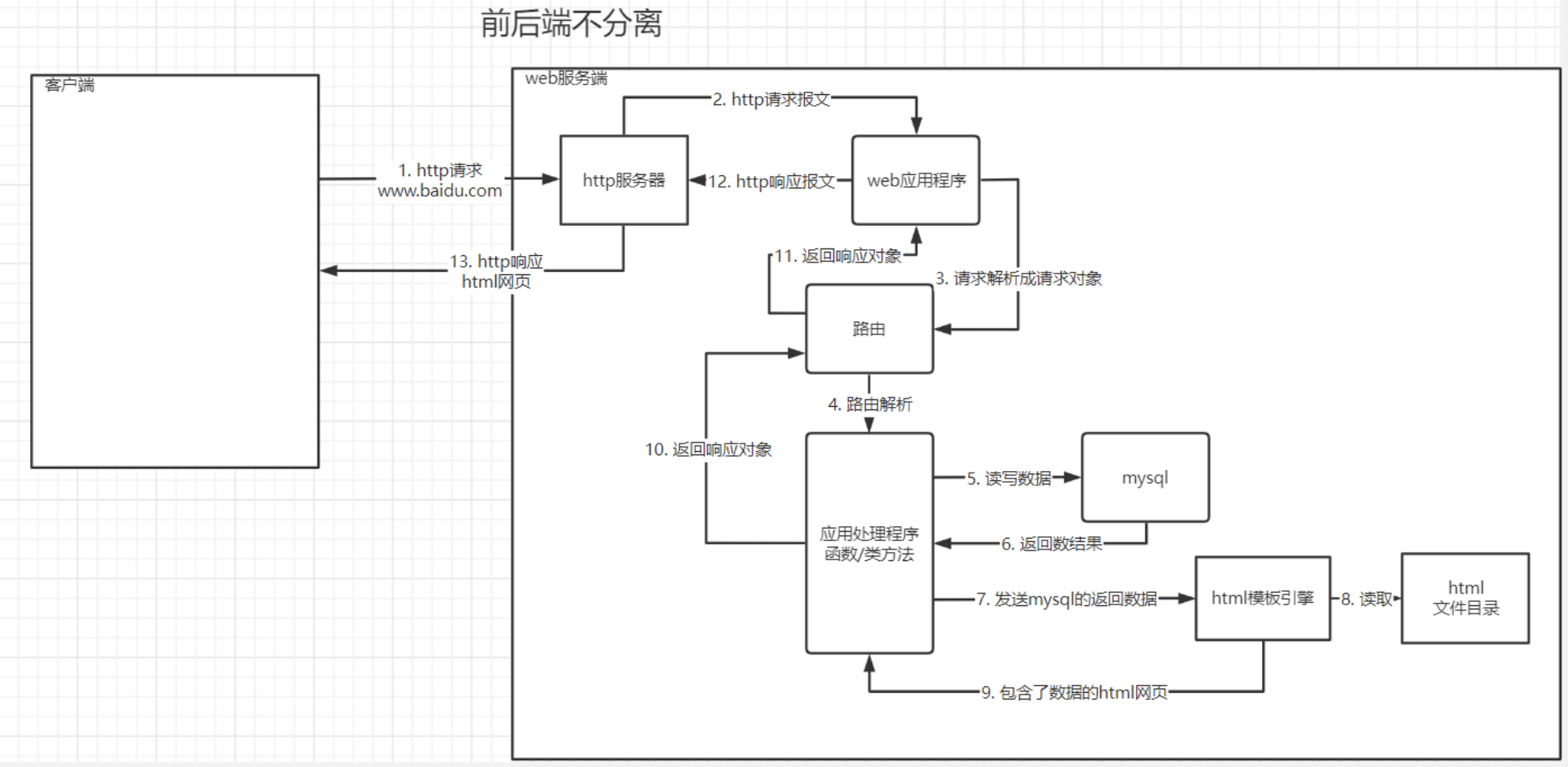
三 ajax
1 相关说明
ajax:Async Javascript And Xml 译作:异步js和xml传输数据技术。现为异步js和json传输数据技术。
| 接口 | 地址 |
|---|---|
| 天气接口 | http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city=城市名称 |
| 音乐接口搜索 | http://msearchcdn.kugou.com/api/v3/search/song?keyword=歌曲标题 |

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .data-table{ border-collapse: collapse; width: 800px; display: none; } .data-table td, .data-table th{ font-weight: normal; border:1px solid red; text-align: center; width: 200px; } </style> </head> <body> <input type="text" name="city" value="北京" placeholder="请输入一个国内的城市名称"><button>获取天气</button> <table class="data-table"> <tr> <th>日期</th> <th>类型</th> <th>风力</th> <th>温度</th> </tr> </table> </body> <script> var btn = document.querySelector("button") var city = document.querySelector('input[name="city"]') let data = document.querySelector(".data-table") let old_conent = data.innerHTML // 原来的内容 btn.addEventListener("click", get_weather) function get_weather(){ // 原生js的ajax: 基于XMLHttpRequest实现ajax1.0版本,有5个步骤 // 1. 创建ajax对象 var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest() // console.log(xhr.readyState) // 0 // 2. 打开网络请求 // 参数1:method,http请求,默认XMLHttpRequest只实现了get与post请求 // 参数2:url,请求的资源路径,可以携带查询字符串 xhr.open("get", `http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city=${city.value}`) // console.log(xhr.readyState) // 1 // 3. 发送网络请求 // 参数1:可选参数,如果是post请求,则填写请求体 // 请求体必须按查询字符串格式编写,属性=值&属性=值&属性=值..... xhr.send() // 4. 监听http通信状态 xhr.onreadystatechange = ()=>{ // 4.1 判断ajax的状态 /** * readyState属性表示ajax的使用状态 * 0 表示刚创建ajax对象,还没有创建http网络请求 * 1 表示ajax对象已经创建http网络请求,但是还没有发送请求 * 2 表示ajax已经发送了http请求,但是服务端还没有接收到请求 * 3 表示服务端已经接收到客户端的http请求,但是没有处理完成 * 4 表示服务端已经处理完成客户端的http请求,并把处理结果返回给客户端了 */ // 5. 判断xhr执行状态已经执行完成,并且http响应状态码是200才获取服务端的数据 if(xhr.readyState === 4){ if(xhr.status === 200){ // console.log(xhr.response) // 获取原生的响应数据[例如图片,音频等] // console.log(xhr.responseText) // 获取纯文本格式数据 // console.log(xhr.responseXML) // 获取xml格式的数据 let response = JSON.parse(xhr.response) console.log(response) data.style.display = "block" data.innerHTML = old_conent console.log(response.data.forecast) for (let info of response.data.forecast) { data.innerHTML+=`<tr> <td>${info.date}</td> <td>${info.type}</td> <td>${info.fengxiang} ${info.fengli.replace(/<!\[CDATA\[(.*?)\]\]>/,"$1")}</td> <td>${info.low} ~ ${info.high}</td> </tr>` } } } } } </script> </html>
方式二:使用fetch全局方法实现ajax2.0,内置本质上就是XMLHttpRequest与Promise(ES6,es2015)来封装的一个函数
1

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .data-table{ border-collapse: collapse; width: 800px; display: none; } .data-table td, .data-table th{ font-weight: normal; border:1px solid red; text-align: center; width: 200px; } </style> </head> <body> <input type="text" name="city" value="北京" placeholder="请输入一个国内的城市名称"><button>获取天气</button> <table class="data-table"> <tr> <th>日期</th> <th>类型</th> <th>风力</th> <th>温度</th> </tr> </table> </body> <script> var btn = document.querySelector("button") var city = document.querySelector('input[name="city"]') let data = document.querySelector(".data-table") let old_conent = data.innerHTML // 原来的内容 btn.addEventListener("click", get_weather) function get_weather(){ // ajax2.0 // 基于fetch全局方法来实现 // fetch使用方式1: // 参数1:Request对象 // fetch使用方式2: // 参数1:字符串格式的url地址, // 参数2:Request对象 // 返回值:Promise回调对象 fetch(`http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city=${city.value}`, { method: "GET", mode: 'cors', }).then(response => { // 此处可以简写成 then(res=>res.json()) // 如果要接收来自服务端的json数据,则先要使用return response.json()来处理 //then对前边的返回值进行处理 // 如果要接收来自服务端的纯文本数据,则先要使用return response.text()来处理 // 如果要接收来自服务端的二进制数据,则先要使用return response.blob()来处理 return response.json() }) .then(response => { // 显示表格 data.style.display = "block" data.innerHTML = old_conent for (let info of response.data.forecast) { data.innerHTML += ` <tr> <td>${info.date}</td> <td>${info.type}</td> <td>${info.fengxiang} ${info.fengli.replace(/<!\[CDATA\[(.*?)\]\]>/, "$1")}</td> <td>${info.low} ~ ${info.high}</td> </tr> ` } }).catch((err) => { // 如果ajax请求失败,或者then方法中的匿名函数中有代码异常,则自动执行catch方法 console.log("错误:", err); // 如果要转换处理来自服务端的异常错误 console.log("来自服务端的错误:", err.response); }); console.log("hello!!!!") } </script> </html>
2服务端代码提供接口:

from aiohttp import web
import aiohttp_cors
# 路由对象
# 路由[router],是一种用于绑定url地址与服务端应用处理程序[python里面的函数/类方法]之间的映射关系。
# /a1 ---> a函数
# /a2 ---> b函数
# 路由的格式类似hash映射(字典结构)
# {
# "/a1": a函数,
# "/a2": b函数,
# }
# 在实际开发中,我们所说的路由,往往也表示在服务端中实现路由关系的类,也叫路由类。
routes = web.RouteTableDef()
@routes.get("/")
async def get_index(request):
print("hello!, 用户访问进来了!")
data = [
{"name": "xiaoming", "age": 17},
{"name": "xiaoming", "age": 18},
{"name": "xiaoming", "age": 19},
]
# 返回json数据
return web.json_response(data)
@routes.post("/")
async def post_index(request):
# 接受客户端上传过来的请求体数据,并使用json.loads()转换成字典
data = await request.json()
print("data=", data)
# 返回json数据
return web.json_response(data)
@routes.put("/{name}") # {name} 变量,当用户通过地址栏使用get请求时,会自动/斜杠后面的内容作为值赋值给name变量
async def num(request):
# 获取url地址的一部分,这个叫路由参数
name = request.match_info.get('name', "Anonymous")
# 返回json数据
return web.json_response({"name": name, "age": 19})
class Application(web.Application):
def __init__(self, routes):
"""
:param routes: url和服务端处理程序之间的绑定关系, 这种绑定关系,我们一般称之为路由,当然,在服务端开发中,我们也会经常把具有路由功能功能的类/对象,称之为"路由类"或"路由对象"
"""
print(routes._items) # 路由列表
# 先让官方的aiohttp的web框架先进行初始化
super(Application, self).__init__()
# 注册路由信息到web框架中,routes是一个list列表
self.add_routes(routes)
# 这里内部完成了一个for循环,把routes里面每一个路由信息都了遍历,添加一个返回值用于实现跨域资源共享[CORS]。
cors = aiohttp_cors.setup(self, defaults={
"*": aiohttp_cors.ResourceOptions(
allow_credentials=True,
expose_headers="*",
allow_headers="*",
)
})
# Configure CORS on all routes.
for route in list(self.router.routes()):
cors.add(route)
if __name__ == '__main__':
web.run_app(Application(routes),host="0.0.0.0",port=8000)

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <button class="btn1">点击获取服务端的数据1</button> <button class="btn2">点击获取服务端的数据2</button> <button class="btn3">点击获取服务端的数据3</button> <script> var btn1 = document.querySelector(".btn1") var btn2 = document.querySelector(".btn2") var btn3 = document.querySelector(".btn3") btn1.onclick = function(){ fetch("http://127.0.0.1:8000/",{ method: "get", mode: "cors", }).then(response=>{ console.log(response.text()); }) } btn2.onclick = function(){ fetch("http://127.0.0.1:8000/",{ method: "post", mode: "cors", headers:{ "Content-Type": "application/json", }, body: JSON.stringify({'name': 'abc'}) // 发送json数据到服务端 }).then(response=>{ console.log(response.text()); }) } btn3.onclick = function(){ fetch("http://127.0.0.1:8000/xiaohong",{ method: "put", mode: "cors", }).then(response=>{ console.log(response.json()); }) } </script> </body> </html>
3 同源策略
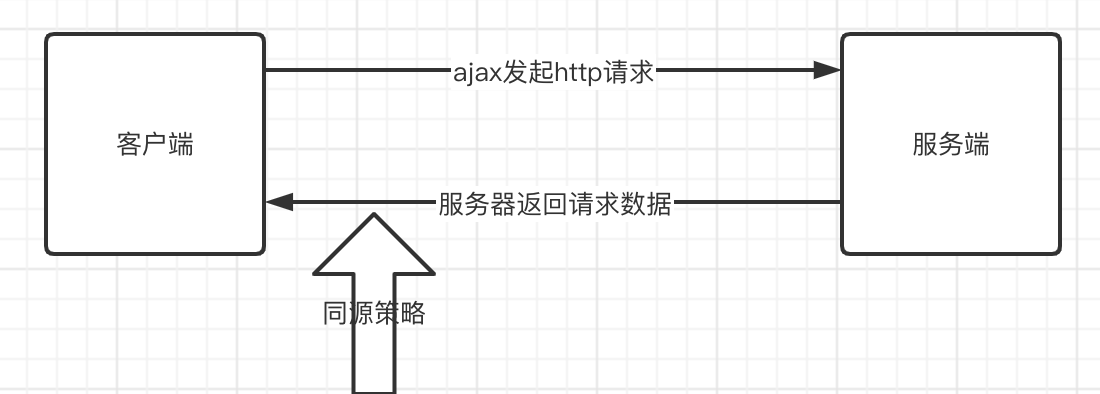
ajax本质上是javascript,是运行在浏览器中的脚本语言,所以会被受到浏览器的同源策略所限制。
如下图示例:
前端地址:http://www.fuguang.cn/index.html | 是否同源 | 原因 |
|---|---|---|
http://www.fuguang.cn/user/login.html |
是 | 协议、域名、端口相同 |
http://www.fuguang.cn/about.html |
是 | 协议、域名、端口相同 |
https://www.fuguang.cn/user/login.html |
否 | 协议不同 ( https和http ),端口不同 |
http:/www.fuguang.cn:5000/user/login.html |
否 | 端口不同( 5000和80) |
http://bbs.fuguang.cn/user/login.html |
否 | 域名不同 ( bbs和www ) |
代码示例:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <input type="text" name="music" value="月亮之上"> <button class="btn">搜索歌曲</button> <script> let btn = document.querySelector(".btn") let music = document.querySelector("input[name=music]") btn.onclick = function(){ fetch(`http://msearchcdn.kugou.com/api/v3/search/song?keyword=${music.value}`,{ method: "get", }).then(response=>response.json()).then(response=>{ console.log(response) }).catch(error=>{ console.log(error) }) } </script> </body> </html>
效果
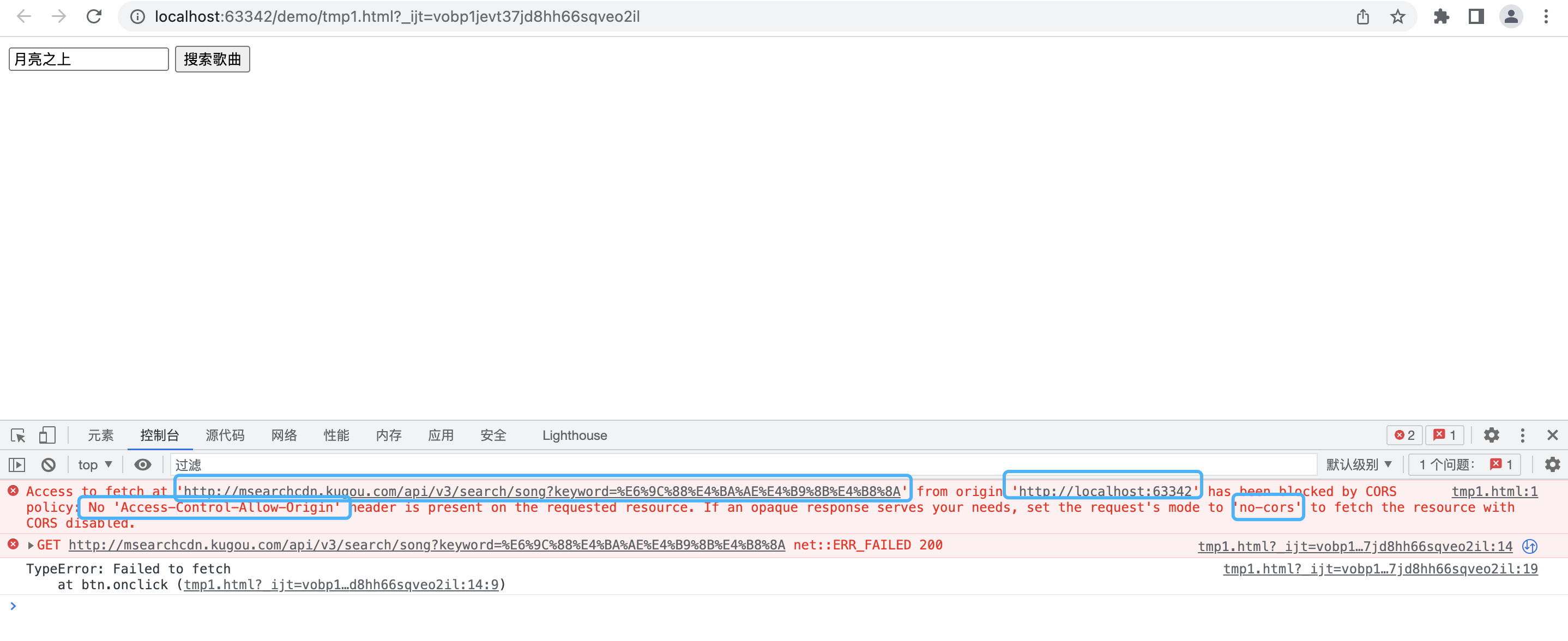
上面的错误不一定是同源策略的问题,也有可能是因为以下原因:
1. 服务端代码报错,或者服务端没有正确的返回授权
2. 客户端请求的服务端的请求报文出错[错误的url地址,错误的请求方法,错误的请求头]
3. 客户端携带了不明来历的cookie信息
4 ajax跨域(跨源)方案
跨域的解决方案一般以下三种:
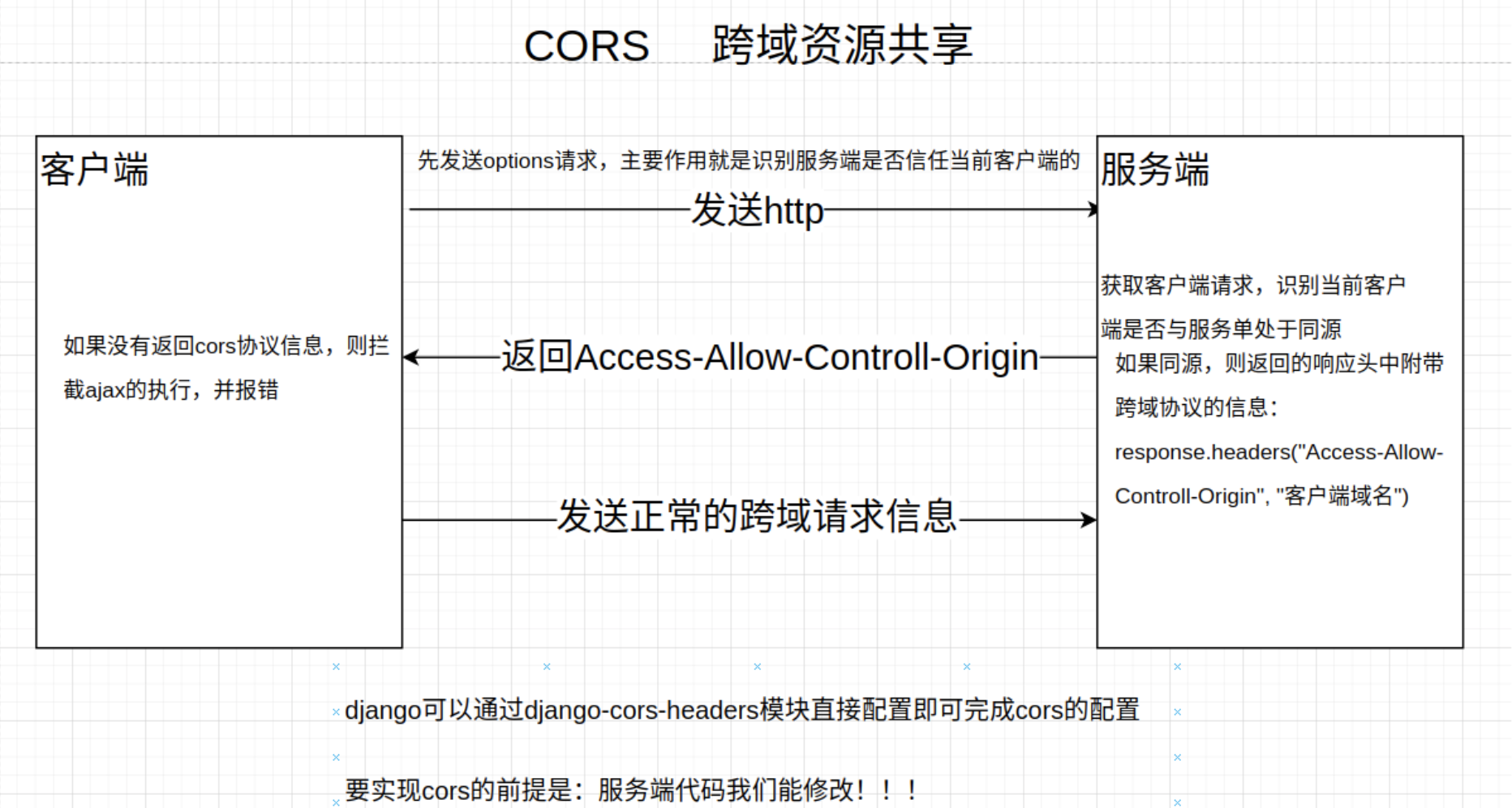
1 cors方案,W3C维护的一个跨域资源共享的协议。这个协议要求服务端通过响应头的方式告知浏览器,当前跨域访问的客户端是否属于可信任客户端。cors方案的使用前提是服务端已经支持了cors。
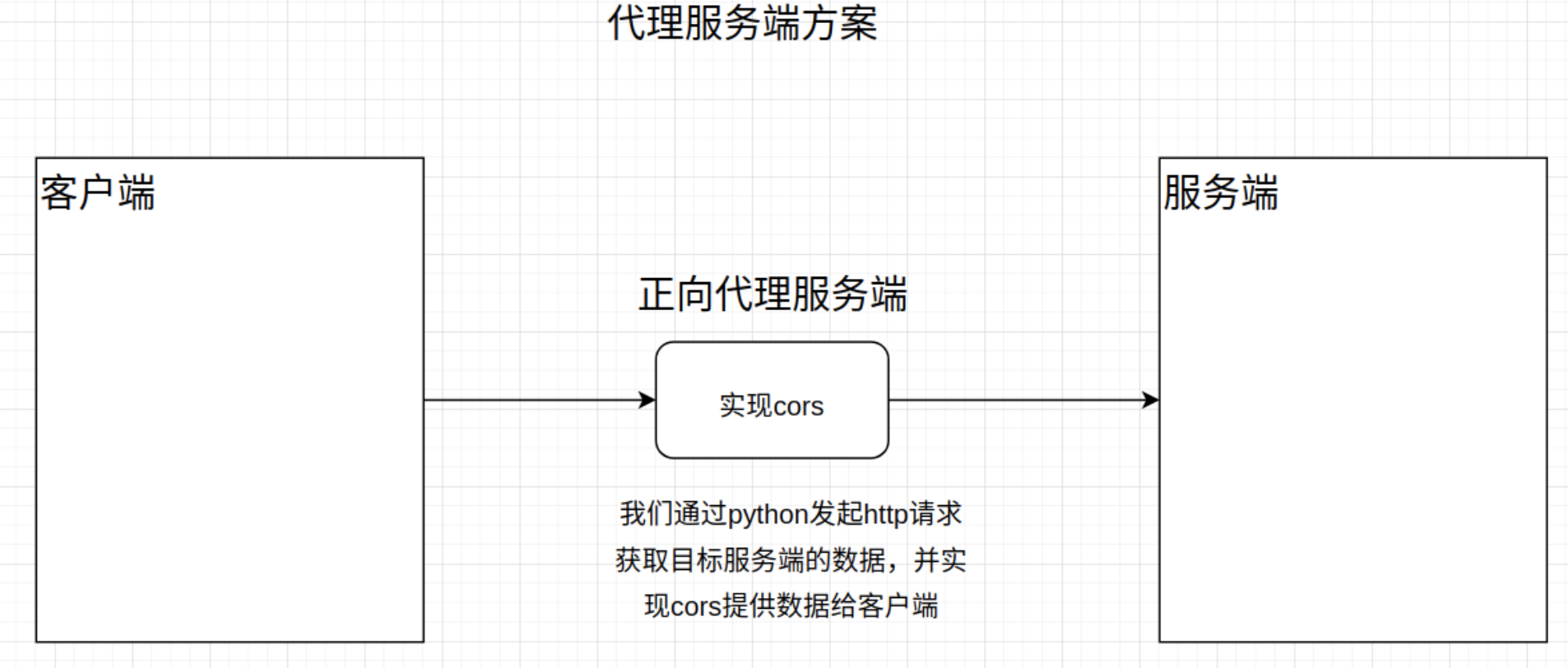
2 服务端代理(Proxy Server),自己搭建一个可控的代理服务端(自己的服务端项目),因为同源策略只存在于浏览器,所以我们让客户端直接请求代理服务端,然后代理服务端接收客户端请求以后,执行代码请求目标服务端那边获取到客户端需要的数据,最终由代理服务端把数据返回给客户端。

import json from aiohttp import web, ClientSession import aiohttp_cors routes = web.RouteTableDef() @routes.get("/") async def get_index(request): # 返回json数据 music = request.query.get("music", None) if music is None: return web.json_response({"errno": -1, "errmsg": "参数有误!"}) # 发起请求,搜索音乐 # http://msearchcdn.kugou.com/api/v3/search/song?keyword= url = f"http://msearchcdn.kugou.com/api/v3/search/song?keyword={music}" async with ClientSession() as session: async with session.get(url) as response: print("status:{}".format(response.status)) if response.status == 200: data = await response.text() data = json.loads(data) print(data) return web.json_response(data) else: return web.json_response({"errno": -1, "errmsg": "搜索失败!"}) class Application(web.Application): def __init__(self, routes): """ :param routes: url和服务端处理程序之间的绑定关系, 这种绑定关系,我们一般称之为路由,当然,在服务端开发中,我们也会经常把具有路由功能功能的类/对象,称之为"路由类"或"路由对象" """ print(routes._items) # 路由列表 # 先让官方的aiohttp的web框架先进行初始化 super(Application, self).__init__() # 注册路由信息到web框架中,routes是一个list列表 self.add_routes(routes) # 这里内部完成了一个for循环,把routes里面每一个路由信息都了遍历,添加一个返回值用于实现跨域资源共享[CORS]。 cors = aiohttp_cors.setup(self, defaults={ "*": aiohttp_cors.ResourceOptions( allow_credentials=True, expose_headers="*", allow_headers="*", ) }) # Configure CORS on all routes. for route in list(self.router.routes()): cors.add(route) if __name__ == '__main__': web.run_app(Application(routes),host="0.0.0.0",port=8000)

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <input type="text" name="music" value="月亮之上"> <button class="btn">搜索歌曲</button> <script> let btn = document.querySelector(".btn") let music = document.querySelector("input[name=music]") btn.onclick = function(){ fetch(`http://127.0.0.1:8000/?music=${music.value}`,{ method: "get", }).then(response=>response.json()).then(response=>{ console.log(response) }).catch(error=>{ console.log(error) }) } </script> </body> </html>
3 jsonp方案,原则上来说jsonp不是ajax技术,而是利用了HTML中的某些默认能跨域的标签来实现的。script,link,src属性,iframe,…客户端先预定义一个js函数。然后服务端生成js代码,代码里面把数据作为函数的参数,在客户端请求的时候返回。
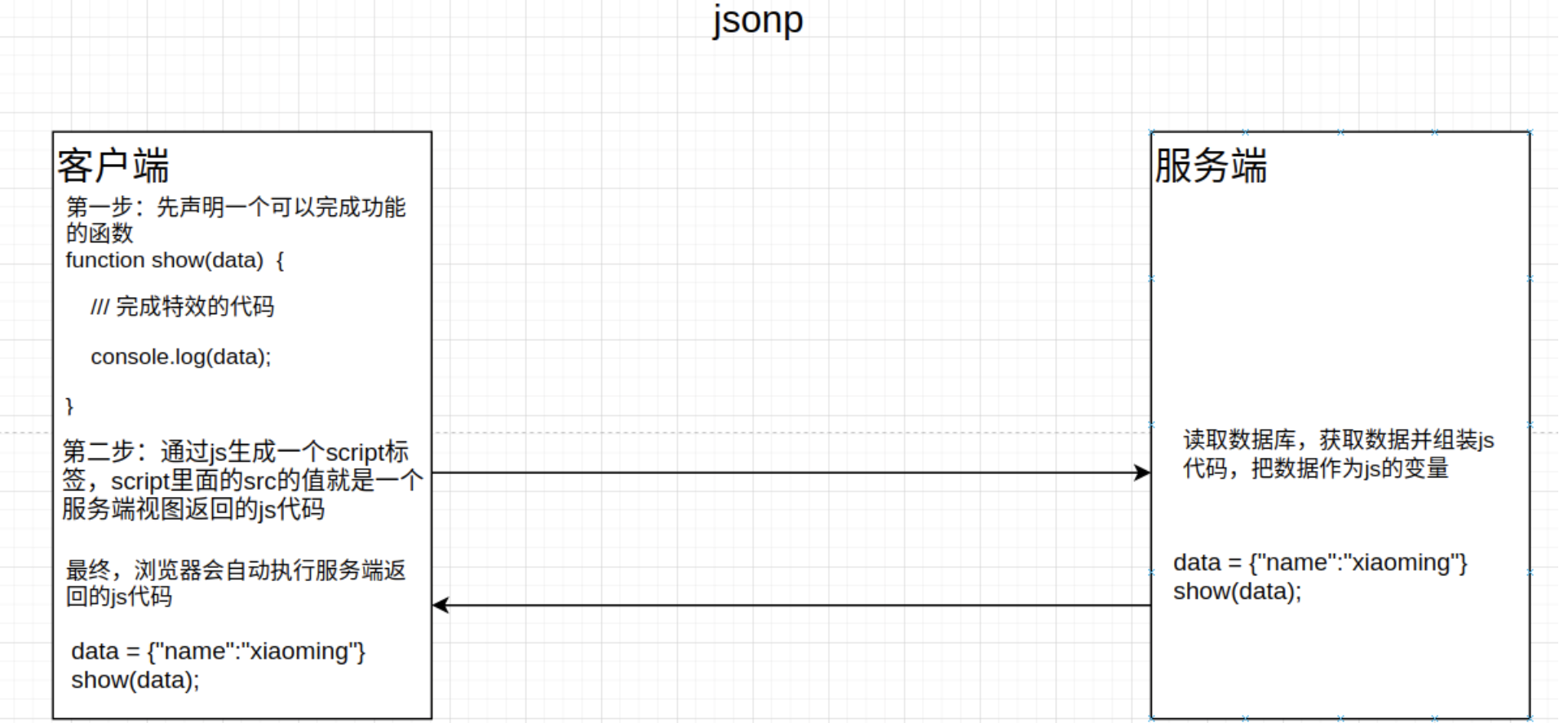

import json from aiohttp import web routes = web.RouteTableDef() @routes.get("/search") async def get_js(request): # 接受客户端上传过来的请求体数据,并使用json.loads()转换成字典 username = request.query.get("username") func = request.query.get("func", "callback") # 假设根据username到数据库中查询数据 data = { "id": 1, "username": username, "age": 20 } return web.Response(text=f"{func}({json.dumps(data)})", content_type="text/javascript") class Application(web.Application): def __init__(self, routes): """ :param routes: url和服务端处理程序之间的绑定关系, 这种绑定关系,我们一般称之为路由,当然,在服务端开发中,我们也会经常把具有路由功能功能的类/对象,称之为"路由类"或"路由对象" """ print(routes._items) # 路由列表 # 先让官方的aiohttp的web框架先进行初始化 super(Application, self).__init__() # 注册路由信息到web框架中,routes是一个list列表 self.add_routes(routes) if __name__ == '__main__': web.run_app(Application(routes),host="0.0.0.0",port=8000)

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <input type="text" name="username" value="小明"> <button class="btn">发送数据</button> <script> var btn = document.querySelector('.btn') var user = document.querySelector('input[name="username"]') btn.onclick = function(){ // <script src="http://127.0.0.1:8000/1.js?username=xiaoming&func=callback"><//script> let script = document.createElement("script") // 定义引用外部脚本的URI,这可以用来代替直接在文档中嵌入脚本 script.src= `http://127.0.0.1:8000/search?username=${user.value}&func=callback` document.head.append(script) //返回当前文档中的 <head> 元素 } function callback(data){ console.log(data); } </script> </body> </html>
四 异步编程
js默认是单线程运行的。为了实现javascript的异步编程,常用的方式有定时器、ajax、Promise、Generator、async/await、服务器推技术(WebSocket,Worker,EventSource)。
1 promise
Promise 是一个代理对象(代理一个值),被代理的值在 Promise 对象创建时可能是未知的。它允许你为异步操作的成功和失败分别绑定相应的处理方法(handlers)。 这让异步方法可以像一个 Promise 对象代表一个在这个 promise 被创建出来时不一定已知值的代理。它让你能够把异步操作最终的成功返回值或者失败原因和相应的处理程序关联起来。这样使得异步方法可以像同步方法那样返回值:异步方法并不会立即返回最终的值,而是会返回一个 promise,以便在未来某个时候把值交给使用者。
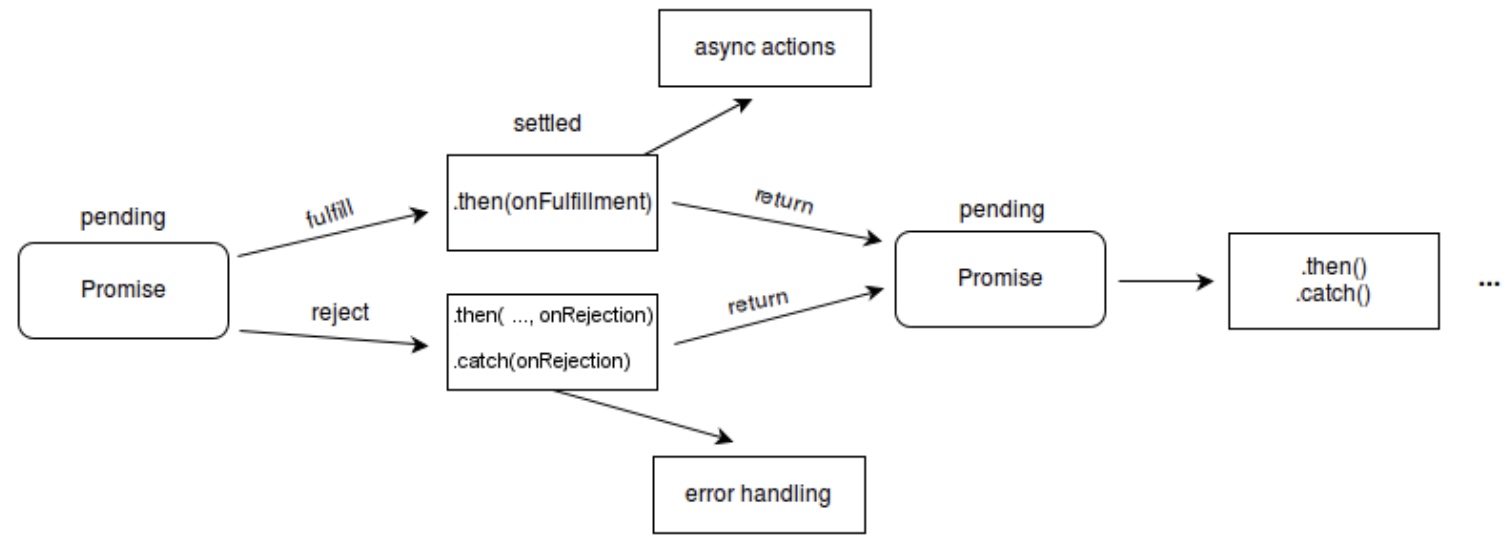
一个 Promise 必然处于以下几种状态之一:
- 待定(pending):初始状态,既没有被兑现,也没有被拒绝。
- 已兑现(fulfilled):意味着操作成功完成。
- 已拒绝(rejected):意味着操作失败。
如果一个 promise 已经被兑现或被拒绝,那么我们也可以说它处于 已敲定(settled) 状态。
一个经常跟 promise 一起使用的术语:已决议(resolved),它表示 promise 已经处于已敲定状态,或者为了匹配另一个 promise 的状态被“锁定”了。
示例

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <script> var status = false; var response = new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{ // 下载/读取文件等耗时操作,容易阻塞的代码 // .... if(status === "false"){ // 写耗时的代码,结果放在resolve作为参数提供给调用者 resolve("成功的结果"); }else{ reject("错误了!!!你玩大了!"); } }); console.log("1") response.then(response=>{ console.log(response); }).catch(error=>{ console.log(error) }) console.log("2") </script> </body> </html>
2 生成器Generator

<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <script> // 生成器函数 function* gen(){ // yield 暂停 yield 100 yield 200 yield 300 yield 400 return 500 } // 生成器函数的返回值就是生成器对象 let g = gen() console.log(g) console.log(g.next()) console.log(g.next()) console.log(g.next()) console.log(g.next()) console.log(g.next()) // 可以获取retrun返回值 // for循环无法获取生成器的return返回值,仅能回去yield的返回值 for(let item of gen()){ console.log(item) } </script> </body> </html>
3 协程异步async/await

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <script> // async 标记当前函数为异步 async function request() { try { // await 等待 const data1 = await fetch("http://127.0.0.1:8000",{method: "get", mode:"cors"}).then(response=>response.json()); const data2 = await fetch("http://127.0.0.1:8000",{method: "get", mode:"cors"}).then(response=>response.json()); console.log(data1); console.log(data2); } catch (e) { console.log('出错啦'); } } request() console.log("hello!!") </script> </body> </html>







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现