SpringMvc组件初始化
SpringMVC 9大组件初始化
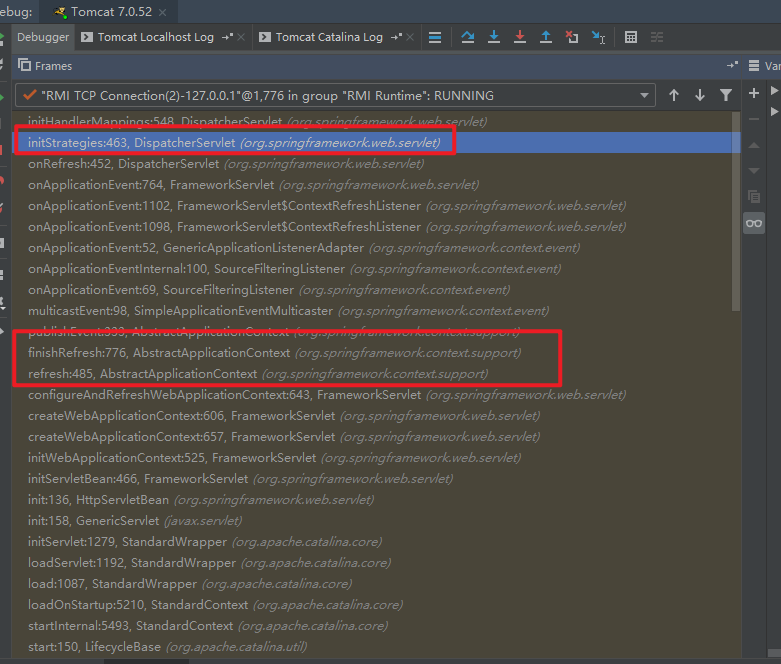
由上面的断点流程,可以看出来其实是在spring容器初始化完成的最后一步,通过发送event事件
@Override
public void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Publishing event in " + getDisplayName() + ": " + event);
}
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(event);
if (this.parent != null) {
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}
然后进入下面的SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster的类中,去遍历所有的监听类
@Override
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event) {
for (final ApplicationListener listener : getApplicationListeners(event)) {
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
});
}
else {
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
}
}
onApplicationEvent这个方法一直被重写,最后执行的是FrameworkServlet的onApplicationEvent方法,在去调用DispatcherServlet的onRefresh方法。
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses.
* <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects.
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
再去初始化9大组件,这里就简单的介绍其中的一个组件的初始化过程。
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<HandlerMapping>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.
OrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering
// a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found.
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No HandlerMappings found in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default");
}
}
}
其中:detectAllHandlerMappings这个值为true,也可以在配置文件里面设置false,当true的时候,值为下面。
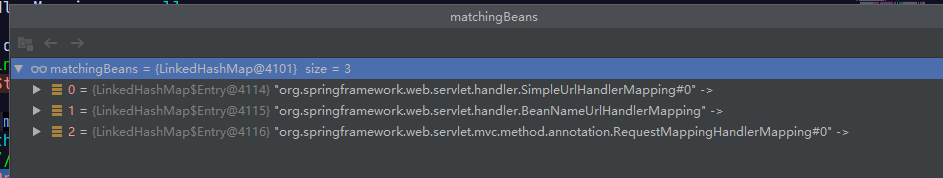
其中:this.handlerMappings == null,当走进这个方法的时候,回去读取配置文件中默认的处理器映射器。
protected <T> List<T> getDefaultStrategies(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) {
String key = strategyInterface.getName();
String value = defaultStrategies.getProperty(key);
if (value != null) {
String[] classNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(value);
List<T> strategies = new ArrayList<T>(classNames.length);
for (String className : classNames) {
try {
Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName(className, DispatcherServlet.class.getClassLoader());
Object strategy = createDefaultStrategy(context, clazz);
strategies.add((T) strategy);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException(
"Could not find DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" + className +
"] for interface [" + key + "]", ex);
}
catch (LinkageError err) {
throw new BeanInitializationException(
"Error loading DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" + className +
"] for interface [" + key + "]: problem with class file or dependent class", err);
}
}
return strategies;
}
else {
return new LinkedList<T>();
}
}
其中
private static final Properties defaultStrategies;
static {
// Load default strategy implementations from properties file.
// This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized
// by application developers.
try {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, DispatcherServlet.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'DispatcherServlet.properties': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
回去加载配置文件里面的默认值。
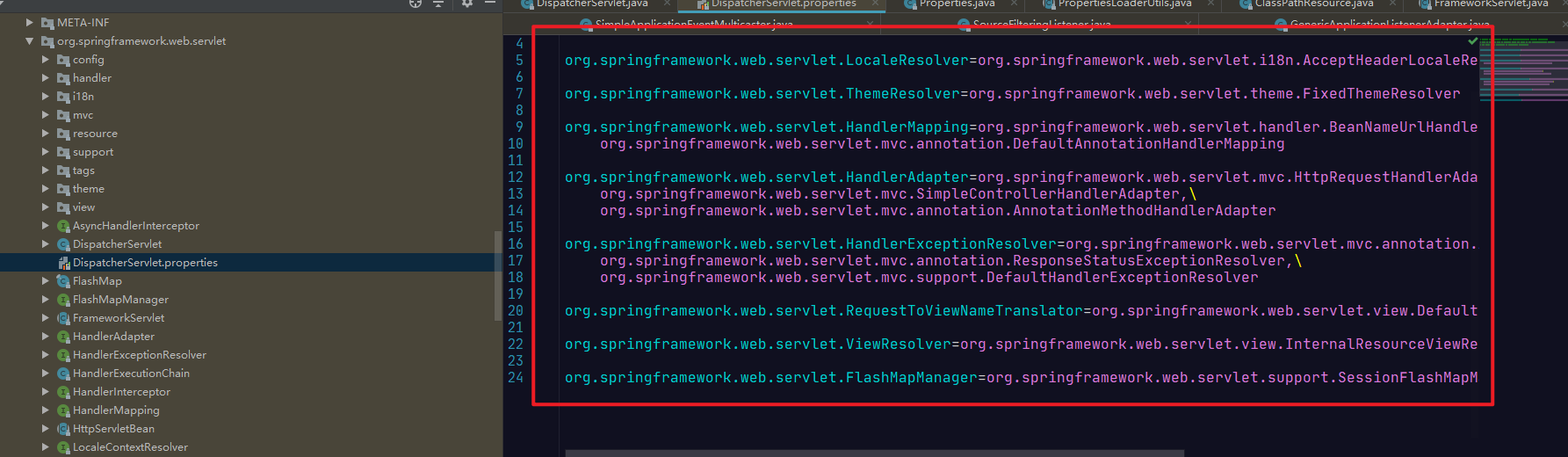
先简单的记录一下,等后面在结合SpringMVC源码的书,在进行补充。
个人感觉这个工具类还是挺有用的,其中springboot的自动配置原理也有用到,下面就简单测试一下。
/**
* @author WGR
* @create 2021/4/14 -- 22:27
*/
public class Test {
@SneakyThrows
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("test.properties", Test.class);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
System.out.println(properties.getProperty("org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter"));
}
}
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter
我这里是idea,跑起来的时候,直接报错,然后百度了一下,要在pom.xml配置.因为IDEA有个配置项,默认只把.class的文件放到编译目录中,也就是target目录。
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.*</include>
</includes>
<excludes>
<exclude>**/*.java</exclude>
</excludes>
</resource>
</resources>



