TreeMap
1.TreeMap的特点
-
概念:
TreeMap是一个双列集合,是Map的子类。底层由红黑树结构构成。
-
特点:
- 元素中键不能重复
- 元素会按照大小顺序排序
2.TreeMap的数据结构
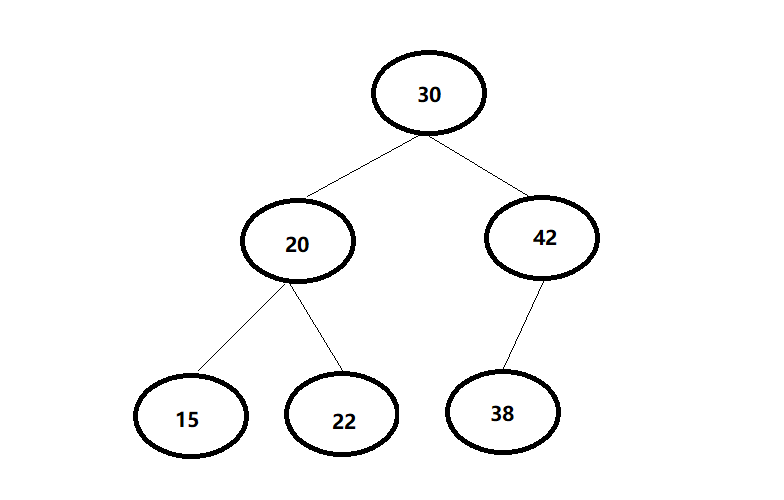
2.1二叉查找树
2.1.1二叉查找树的定义
- 特点:
1.若左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
2.若右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
3.左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树;
4.没有相等的结点;
-
结论:
二叉查找树就是每个结点的值按照大小排列的二叉树,二叉查找树方便对结点的值进行查找。
-
图:
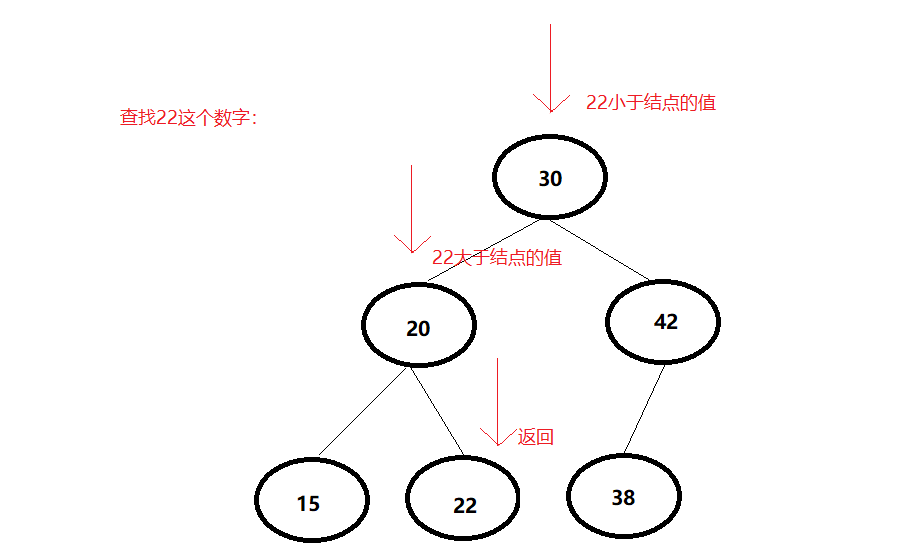
2.1.2二叉查找树的查找操作
- 查找方式:
从根结点开始,如果要查找的数据等于结点的值, 那就返回。
如果要查找的数据小于结点的值,那就在左子树中递归查找;
如果要查找的数据大于结点的值,那就在右子树中递归查找。
- 图:
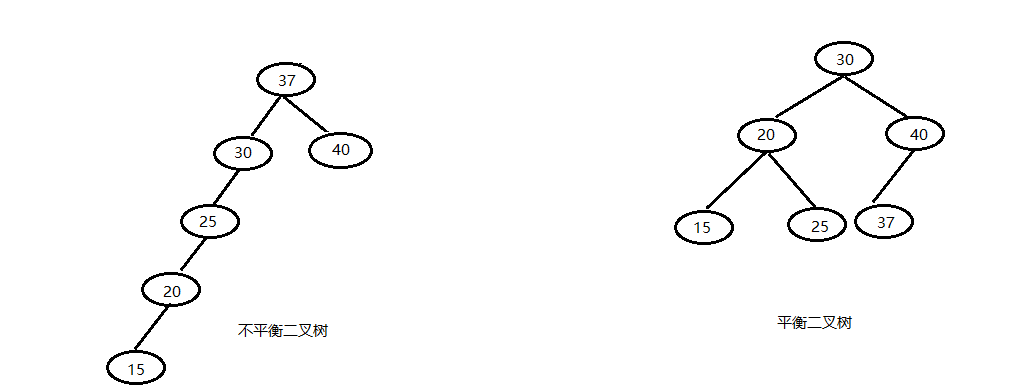
2.2平衡二叉树
2.2.1平衡二叉树的定义
为了避免出现"瘸子"的现象,减少树的高度,提高我们的搜素效率,又存在一种树的结构:"平衡二叉树"
它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树。
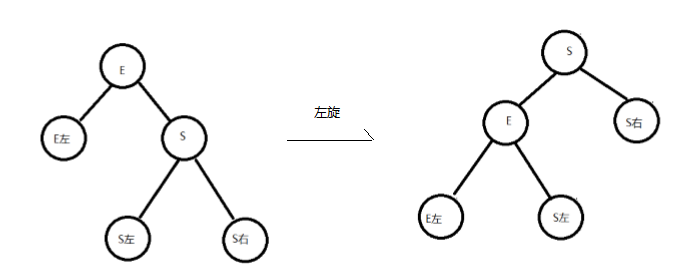
2.2.2平衡二叉树的旋转
- 概念:
在构建一棵平衡二叉树的过程中,当有新的结点要插入时,检查是否因插入后而破坏了树的平衡,如果是,则需要做旋转去改变树的结构。
-
两种旋转方式:
-
左旋:
左旋就是将结点的右支往左拉,右子结点变成父结点,并把晋升之后多余的左子结点出让给降级结点的 右子结点;
-
右旋:
将结点的左支往右拉,左子结点变成了父结点,并把晋升之后多余的右子结点出让给降级结点的左子结 点
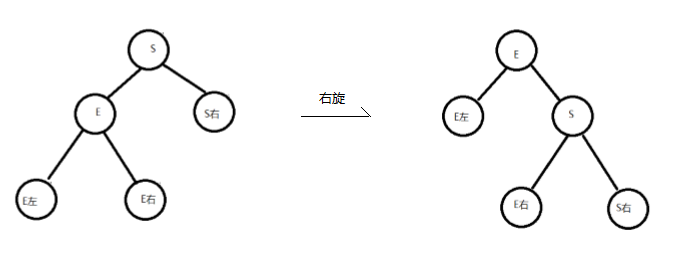
-
-
四种失衡情况:
-
左左情况,需要以10为基准结点进行右旋
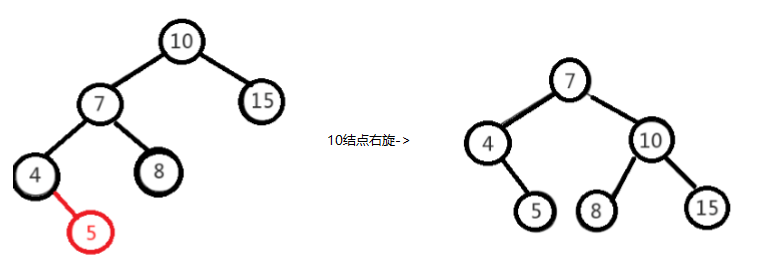
-
左右情况,先以7为基准结点进行左旋,再以11为基准结点进行右旋
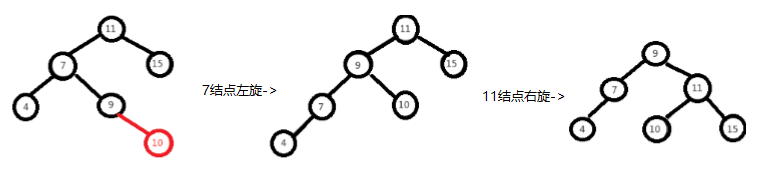
-
右左情况,先以15为基准结点进行右旋,再以11为基准结点进行左旋
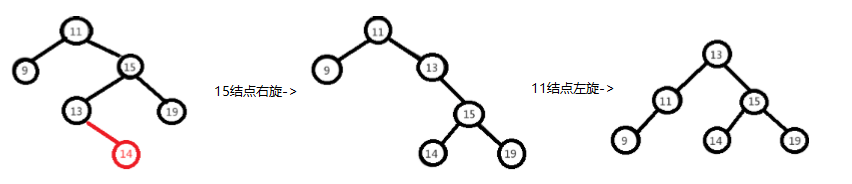
-
右右情况,以11未基准结点进行左旋
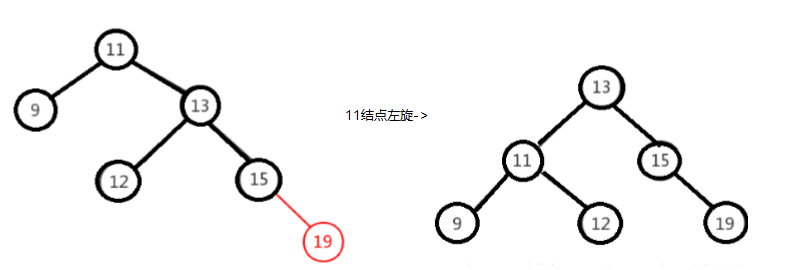
-
2.3红黑树
2.3.1红黑树的定义
-
概述:
红黑树是一种自平衡的二叉查找树。
红黑树的每一个结点上都有存储位表示结点的颜色,可以是红或者黑。
红黑树不是高度平衡的,它的平衡是通过"红黑树的特性"进行实现的。
-
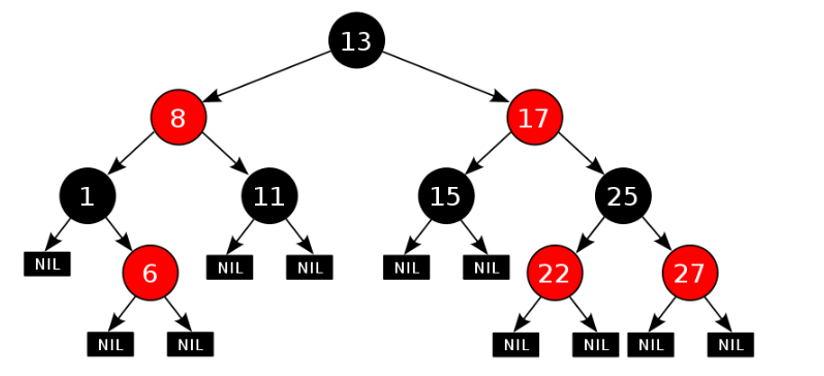
红黑树的特性:
- 每一个结点或是红色的,或者是黑色的;
- 根结点必须是黑色;
- 每个叶结点是黑色的(叶结点是Nil)
- 如果某一个结点是红色,那么它的子结点必须是黑色(不能出现两个红色结点相连的情况)
- 对每一个结点,从该结点到其所有后代叶结点的简单路径上,均包含相同数目的黑色结点;
-
图:
2.TreeMap的源码分析
2.1get()获取方法分析
//Entry类型表示结点
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
K key; //key表示键
V value; //value表示值
Entry<K,V> left; //left表示左子结点的地址
Entry<K,V> right; //rigth表示右子结点的地址
Entry<K,V> parent; //parent表示父结点的地址
boolean color = BLACK; //color表示结点的颜色
//下面方法省略…………
}
public V get(Object key) {
//调用方法根据键获取Entry对象
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
//判断对象如果是null返回null,如果不是null返回对象中的值
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
//判断有没有传入comparator
if (comparator != null)
//调用方法,使用比较器做查询
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
//判断传入的键是否为null
if (key == null)
//如果要查询的键是null则抛出空指针异常
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//把Object类型的键向下转型为Comparable
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
//先把二叉树的根结点赋值给p
Entry<K,V> p = root;
//如果p不为null,一直循环比较
while (p != null) {
//调用Comparable的compareTo()方法进行比较
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
//如果cmp小于0,表示要查找的键小于结点的数字
if (cmp < 0)
//把p左子结点赋值给p对象
p = p.left;
//如果cmp大于0,表示要查找的键大于结点的数字
else if (cmp > 0)
//把P右子结点赋值给p对象
p = p.right;
else
//要查找的键等于结点的值,就把当前Entry对象直接返回
return p;
}
//已经找到叶子结点,没有找到要查找的数字返回null
return null;
}
//传入比较器的情况下
final Entry<K,V> getEntryUsingComparator(Object key) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//把Object类型的Key向下转型为对应的键的类型
K k = (K) key;
//给比较器对象起名字cpr
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
//把二叉树的根结点赋值给P对象
Entry<K,V> p = root;
//循环用要查找的数字和结点中的数字进行比较
while (p != null) {
//调用比较器的compare()
int cmp = cpr.compare(k, p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
}
return null;
}
2.2put()添加方法分析
public V put(K key, V value) {
//获取根结点赋值给变量t
Entry<K,V> t = root;
//判断根结点是否为null
if (t == null) {
//对key进行非空和类型校验
compare(key, key);
//新建一个结点
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
//设置集合长度为1
size = 1;
//记录集合被修改的次数
modCount++;
//添加成功返回null
return null;
}
//如果根结点不是null则执行下面代码
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
//把比较器对象赋值给变量cpr
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
//判断比较器对象如果是空则执行下面代码
if (cpr != null) {
do {
//把当前结点赋值给变量parent
parent = t;
//比较当前结点的键和要存储的键的大小
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
//如果要存储的键小于当前结点,则继续和左边的结点进行比较
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
//如果要存储的键大于当前结点,则继续和右边的结点进行比较
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
//如果要存储的键等于当前结点的键,则调用setValue()方法设置新的值
//并结束循环
return t.setValue(value);
//循环直到遍历到叶子结点结束为止
} while (t != null);
}
//如果比较器对象不是空则执行下面代码
else {
//如果要保存的键为空,抛出空指针异常
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//把键转型为Comparable类型
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
//把当前结点赋值给变量parent
parent = t;
//比较要存储的键和当前结点的键
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
//如果要存储的键小于当前结点,则继续和左边的结点比较
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
//如果要存储的键大于当前结点,则继续和右边的结点比较
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
//如果要存储的键等于当前结点的键,则调用setValue()方法设置新的值
//并结束循环
return t.setValue(value);
//循环直到遍历到叶子结点结束为止
} while (t != null);
}
//遍历结束如果没有找到相同的键,则执行下面代码
//创建新的结点对象,保存键值对,设置父结点
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
//如果新的键小于父结点的键,则保存在左边
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
//如果新的键大于父结点的键,则保存在右边
parent.right = e;
//维持红黑树的平衡
fixAfterInsertion(e);
//集合长度加一
size++;
//集合修改次数加一
modCount++;
//返回被覆盖的值是null
return null;
}
2.3 remove方法
remove方法可以分为两个步骤,先是找到这个节点,直接调用了上面介绍的getEntry(Object key),这个步骤我们就不说了,直接说第二个步骤,找到后的删除操作。
public V remove(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
if (p == null)
return null;
V oldValue = p.value;
deleteEntry(p);
return oldValue;
}
通过deleteEntry(p)进行删除操作,删除操作的原理我们在前面已经讲过
- 删除的是根节点,则直接将根节点置为null;
- 待删除节点的左右子节点都为null,删除时将该节点置为null;
- 待删除节点的左右子节点有一个有值,则用有值的节点替换该节点即可;
- 待删除节点的左右子节点都不为null,则找前驱或者后继,将前驱或者后继的值复制到该节点中,然后删除前驱或者后继(前驱:左子树中值最大的节点,后继:右子树中值最小的节点);
private void deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> p) {
modCount++;
size--;
//当左右子节点都不为null时,通过successor(p)遍历红黑树找到前驱或者后继
if (p.left != null && p.right != null) {
Entry<K,V> s = successor(p);
//将前驱或者后继的key和value复制到当前节点p中,然后删除节点s(通过将节点p引用指向s)
p.key = s.key;
p.value = s.value;
p = s;
}
Entry<K,V> replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right);
/**
* 至少有一个子节点不为null,直接用这个有值的节点替换掉当前节点,给replacement的parent属性赋值,给
* parent节点的left属性和right属性赋值,同时要记住叶子节点必须为null,然后用fixAfterDeletion方法
* 进行自平衡处理
*/
if (replacement != null) {
//将待删除节点的子节点挂到待删除节点的父节点上。
replacement.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = replacement;
else if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = replacement;
else
p.parent.right = replacement;
p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;
/**
* p如果是红色节点的话,那么其子节点replacement必然为红色的,并不影响红黑树的结构
* 但如果p为黑色节点的话,那么其父节点以及子节点都可能是红色的,那么很明显可能会存在红色相连的情
* 况,因此需要进行自平衡的调整
*/
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(replacement);
} else if (p.parent == null) {//这种情况就不用多说了吧
root = null;
} else {
/**
* 如果p节点为黑色,那么p节点删除后,就可能违背每个节点到其叶子节点路径上黑色节点数量一致的规则,
* 因此需要进行自平衡的调整
*/
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(p);
if (p.parent != null) {
if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = null;
else if (p == p.parent.right)
p.parent.right = null;
p.parent = null;
}
}
}
操作的操作其实很简单,场景也不多,我们看一下删除后的自平衡操作方法fixAfterDeletion.
private void fixAfterDeletion(Entry<K,V> x) {
/**
* 当x不是root节点且颜色为黑色时
*/
while (x != root && colorOf(x) == BLACK) {
/**
* 首先分为两种情况,当前节点x是左节点或者当前节点x是右节点,这两种情况下面都是四种场景,这里通过
* 代码分析一下x为左节点的情况,右节点可参考左节点理解,因为它们非常类似
*/
if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
Entry<K,V> sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
/**
* 场景1:当x是左黑色节点,兄弟节点sib是红色节点
* 兄弟节点由红转黑,父节点由黑转红,按父节点左旋,
* 左旋后树的结构变化了,这时重新赋值sib,这个时候sib指向了x的兄弟节点
*/
if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
setColor(sib, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
}
/**
* 场景2:节点x、x的兄弟节点sib、sib的左子节点和右子节点都为黑色时,需要将该节点sib由黑变
* 红,同时将x指向当前x的父节点
*/
if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(sib, RED);
x = parentOf(x);
} else {
/**
* 场景3:节点x、x的兄弟节点sib、sib的右子节点都为黑色,sib的左子节点为红色时,
* 需要将sib左子节点设置为黑色,sib节点设置为红色,同时按sib右旋,再将sib指向x的
* 兄弟节点
*/
if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
setColor(sib, RED);
rotateRight(sib);
sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
}
/**
* 场景4:节点x、x的兄弟节点sib都为黑色,而sib的左右子节点都为红色或者右子节点为红色、
* 左子节点为黑色,此时需要将sib节点的颜色设置成和x的父节点p相同的颜色,
* 设置x的父节点为黑色,设置sib右子节点为黑色,左旋x的父节点p,然后将x赋值为root
*/
setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
x = root;
}
} else {//x是右节点的情况
Entry<K,V> sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
setColor(sib, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
rotateRight(parentOf(x));
sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
}
if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(sib, RED);
x = parentOf(x);
} else {
if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
setColor(sib, RED);
rotateLeft(sib);
sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
}
setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
rotateRight(parentOf(x));
x = root;
}
}
}
setColor(x, BLACK);
3.自定义TreeMap集合
使用二叉树实现TreeMap集合,编写put(),get(),remove()等关键方法。
import java.util.Comparator;
public class TreeMap<K, V> {
//定义比较器变量
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;
//根结点
private Entry<K, V> root;
//定义集合长度
private int size;
//空参构造
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}
//有参构造
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
//定义内部类表示键值对
private class Entry<K, V> {
//键
K k;
//值
V v;
//左子结点
Entry<K, V> left;
//右子结点
Entry<K, V> right;
//父结点
Entry<K, V> parent;
//有参构造
public Entry(K k, V v, Entry<K, V> left, Entry<K, V> right, Entry<K, V> parent) {
this.k = k;
this.v = v;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.parent = parent;
}
}
//获取集合长度
public int size() {
return size;
}
//get()方法的实现
public V get(K key) {
Entry<K, V> entry = getEntry(key);
return entry == null ? null : entry.v;
}
//根据键获取Entry对象的方法
private Entry<K, V> getEntry(Object key) {
//非空校验
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
//给根结点起名
Entry<K, V> t = root;
//判断有没有传入比较器
if (comparator != null) {
K k = (K) key;
//循环
while (t != null) {
int cmp = comparator.compare(k, t.k);
if (cmp < 0) {
t = t.left;
} else if (cmp > 0) {
t = t.right;
} else {
return t;
}
}
} else {
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
while (t != null) {
int cmp = k.compareTo(t.k);
if (cmp < 0) {
t = t.left;
} else if (cmp > 0) {
t = t.right;
} else {
return t;
}
}
}
//如果找不到返回null
return null;
}
//put()方法的实现
public V put(K key, V value) {
//给根结点赋值
Entry<K, V> t = root;
//非空校验
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
//集合是否为空
if (t == null) {
//创建新结点
Entry<K, V> entry = new Entry<>(key, value, null, null, null);
//给根结点赋值
root = entry;
//集合长度加一
size++;
return null;
}
//键值对表示新增结点的父结点
Entry<K, V> parent = t;
//定义变量
int cmp = 0;
if (comparator != null) {
while (t != null) {
//给parent
parent = t;
//判断键
cmp = comparator.compare(key, t.k);
if (cmp < 0) {
t = t.left;
} else if (cmp > 0) {
t = t.right;
} else {
//用新的值替换旧的值 把旧的值作为返回值返回
V v = t.v;
t.v = value;
return v;
}
}
} else {
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
while (t != null) {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.k);
if (cmp < 0) {
t = t.left;
} else if (cmp > 0) {
t = t.right;
} else {
//用新的值替换旧的值 把旧的值返回
V v = t.v;
t.v = value;
return v;
}
}
}
//要添加的键值对 键不重复
Entry<K, V> entry = new Entry<>(key, value, null, null, parent);
if (cmp < 0) {
parent.left = entry;
} else {
parent.right = entry;
}
//集合长度加一
size++;
return null;
}
//remove()方法的实现
public V remove(K key) {
Entry<K, V> entry = getEntry(key);
if (entry == null) {
return null;
}
//删除操作
if (entry.left == null && entry.right != null) {
//有右子结点没有左子结点
if (entry == root) {
root = entry.right;
} else if (entry.parent.right == entry) {
entry.parent.right = entry.right;
} else if (entry.parent.left == entry) {
entry.parent.left = entry.right;
}
//让被删除结点的子结点指向父结点
entry.right.parent = entry.parent;
} else if (entry.left != null && entry.right == null) {
//有左子结点没有右子结点
//要删除的结点是父结点的右子结点
if (entry == root) {
root = entry.left;
} else if (entry.parent.right == entry) {
entry.parent.right = entry.left;
} else if (entry.parent.left == entry) {
entry.parent.left = entry.left;
}
//让被删除结点子结点指向父结点
entry.left.parent = entry.parent;
} else if (entry.left != null && entry.right != null) {
//有左子结点也有右子结点
//要后继结点
Entry<K, V> target = entry.right;
//寻找被删除结点右子结点最左子结点
while (target.left != null) {
target = target.left;
}
//右子结点作为后继结点
if (entry.right == target) {
target.parent = entry.parent;
if (entry == root) {
root = target;
} else if (entry.parent.right == entry) {
entry.parent.right = target;
} else if (entry.parent.left == entry) {
entry.parent.left = target;
}
//被删除结点左子结点重新指向新的父结点
entry.left.parent = target;
target.left = entry.left;
} else {
//右子结点的最左子结点作为后继结点
if (target.right == null) {
//后继结点没有右子结点
target.parent.left = null;
} else {
//后继结点有右子结点
target.parent.left = target.right;
target.right = target.parent;
}
//让后继结点替换被删除结点
if (entry == root) {
root = target;
} else if (entry.parent.right == entry) {
entry.parent.right = target;
} else if (entry.parent.left == entry) {
entry.parent.left = target;
}
//被删除结点左右子树需要指向后继结点
entry.left.parent = target;
entry.right.parent = target;
target.left = entry.left;
target.right = entry.right;
}
} else {
//要删除的结点是叶子结点
if (entry == root) {
root = null;
} else if (entry.parent.right == entry) {
entry.parent.right = null;
} else if (entry.parent.left == entry) {
entry.parent.left = null;
}
}
//给集合长度减一
size--;
return entry.v;
}
//toString()方法的实现
//{1=abc, 3=qwe}
public String toString() {
//非空判断
if (root == null) {
return "{}";
}
String s = "{";
String s1 = method(root);
s = s + s1.substring(0, s1.length() - 2) + "}";
return s;
}
//递归的方法
//1=abc, 3=qwe,
private String method(Entry<K, V> entry) {
String s = "";
//拼接左子结点
if (entry.left != null) {
s += method(entry.left);
}
//拼接中间结点自己
s += entry.k + "=" + entry.v + ", ";
//拼接右子结点
if (entry.right != null) {
s += method(entry.right);
}
return s;
}
}
- 测试类
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建对象
TreeMap<Integer,String> map = new TreeMap<>();
//添加键值对
map.put(5,"aaa");
map.put(1,"bbb");
map.put(9,"ccc");
map.put(98,"ddd");
map.put(65,"eee");
map.put(12,"fff");
//相同的键
map.put(12,"qqq");
//根据键获取值
String s = map.get(5);
System.out.println(s);
String s1 = map.get(4);
System.out.println(s1);
//删除
String s2 = map.remove(9);
System.out.println(s2);
//删除
String s3 = map.remove(5);
System.out.println(s3);
//打印
System.out.println(map);
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号