Jdk新特性之重复注解与类型注解
重复注解的使用
自从Java 5中引入 注解 以来,注解开始变得非常流行,并在各个框架和项目中被广泛使用。不过注解有一个很大的限制是:在同一个地方不能多次使用同一个注解。JDK 8引入了重复注解的概念,允许在同一个地方多次使用同一个注解。在JDK 8中使用@Repeatable注解定义重复注解。
/** * @author WGR * @create 2020/4/1 -- 19:02 */ @MyTest("ta") @MyTest("tb") @MyTest("tc") public class Test { @org.junit.Test @MyTest("ma") @MyTest("mb") public void test() { } public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException { // 4.解析重复注解 // 获取类上的重复注解 // getAnnotationsByType是新增的API用户获取重复的注解 MyTest[] annotationsByType = Test.class.getAnnotationsByType(MyTest.class); for (MyTest myTest : annotationsByType) { System.out.println(myTest); } MyTests[] annotationsByType1 = Test.class.getAnnotationsByType(MyTests.class); for ( MyTests myTests : annotationsByType1){ System.out.println(myTests); } System.out.println("----------"); // 获取方法上的重复注解 MyTest[] tests = Test.class.getMethod("test").getAnnotationsByType(MyTest.class); for (MyTest test : tests) { System.out.println(test); } MyTests[] test = Test.class.getMethod("test").getAnnotationsByType(MyTests.class); for (MyTests t : test) { System.out.println(t); } } } // 1.定义重复的注解容器注解 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @interface MyTests { // 这是重复注解的容器 MyTest[] value(); } // 2.定义一个可以重复的注解 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Repeatable(MyTests.class) @interface MyTest { String value(); }
@com.topcheer.annotation.MyTest(value=ta) @com.topcheer.annotation.MyTest(value=tb) @com.topcheer.annotation.MyTest(value=tc) @com.topcheer.annotation.MyTests(value=[@com.topcheer.annotation.MyTest(value=ta), @com.topcheer.annotation.MyTest(value=tb), @com.topcheer.annotation.MyTest(value=tc)]) ---------- @com.topcheer.annotation.MyTest(value=ma) @com.topcheer.annotation.MyTest(value=mb) @com.topcheer.annotation.MyTests(value=[@com.topcheer.annotation.MyTest(value=ma), @com.topcheer.annotation.MyTest(value=mb)])
类型注解的使用
JDK 8为@Target元注解新增了两种类型: TYPE_PARAMETER , TYPE_USE 。
TYPE_PARAMETER :表示该注解能写在类型参数的声明语句中。 类型参数声明如: <T> 、
TYPE_USE :表示注解可以再任何用到类型的地方使用。
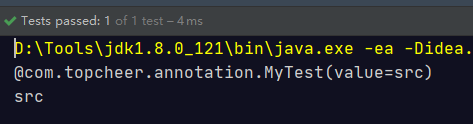
@MyTest("src1")
public int show01(@MyTest("src")String src) {
@MyTest("123")int i = 10;
System.out.println(i + ": " + src);
return i;
}
/**
* 类型参数读取
*/
@org.junit.Test public void testTypeParameter() throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {
Class<?> clazz = this.getClass();
Method method01 = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("show01", String.class);
AnnotatedType[] types = method01.getAnnotatedParameterTypes();
for (AnnotatedType at : types) {
MyTest anno = at.getAnnotation(MyTest.class);
System.out.println(anno);
System.out.println(anno.value());
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号