Jdk8新特性之Stream(2)
Stream流中的结果到集合中
Stream流提供 collect 方法,其参数需要一个 java.util.stream.Collector<T,A, R> 接口对象来指定收集到哪
种集合中。java.util.stream.Collectors 类提供一些方法,可以作为 Collector`接口的实例:
public static <T> Collector<T, ?, List<T>> toList() :转换为 List 集合。 public static <T> Collector<T, ?, Set<T>> toSet() :转换为 Set 集合。
下面是这两个方法的基本使用代码:
// 将流中数据收集到集合中 @Test public void testStreamToCollection() { Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("aa", "bb", "cc"); ArrayList<String> arrayList = stream.collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new)); HashSet<String> hashSet = stream.collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new)); }
Stream流中的结果到数组中
Stream提供 toArray 方法来将结果放到一个数组中,返回值类型是Object[]的:
@Test public void testStreamToArray() { Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("aa", "bb", "cc"); String[] strings = stream.toArray(String[]::new); for (String str : strings) { System.out.println(str); } }
对流中数据进行聚合计算
当我们使用 Stream流处理数据后,可以像数据库的聚合函数一样对某个字段进行操作。比如获取最大值,获取最小
值,求总和,平均值,统计数量。
@Test public void test(){ Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of( new Student("赵丽颖", 58, 95), new Student("杨颖", 56, 88), new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 99), new Student("柳岩", 52, 77)); //1. 最大值 Optional<Student> collect = studentStream.collect(Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(Student::getSocre))); //studentStream.collect(Collectors.maxBy((o1,o2) ->( o1.getSocre() - o2.getSocre()))); System.out.println(collect.get()); //Student{name='迪丽热巴', age=56, socre=99} }
@Test public void test(){ Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of( new Student("赵丽颖", 58, 95), new Student("杨颖", 56, 88), new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 99), new Student("柳岩", 52, 77)); //最小值 Optional<Student> collect = studentStream.collect(Collectors.minBy(Comparator.comparing(Student::getSocre))); //studentStream.collect(Collectors.minBy((o1,o2) ->( o1.getSocre() - o2.getSocre()))); System.out.println(collect.get()); //Student{name='柳岩', age=52, socre=77} }
@Test public void test(){ Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of( new Student("赵丽颖", 58, 95), new Student("杨颖", 56, 88), new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 99), new Student("柳岩", 52, 77)); // studentStream.map(Student::getSocre).reduce(Integer::sum); Integer collect = studentStream.collect(Collectors.summingInt(Student::getSocre)); System.out.println(collect); }
@Test public void test(){ Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of( new Student("赵丽颖", 58, 95), new Student("杨颖", 56, 88), new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 99), new Student("柳岩", 52, 77)); Double collect = studentStream.collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(Student::getSocre)); System.out.println(collect); }
对流中数据进行分组
当我们使用Stream流处理数据后,可以根据某个属性将数据分组:
@Test public void test(){ Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of( new Student("赵丽颖", 58, 95), new Student("杨颖", 56, 88), new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 99), new Student("柳岩", 52, 77)); Map<Integer, List<Student>> collect = studentStream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getAge)); collect.forEach( (k,v) -> { System.out.println(k + "::" + v); }); }
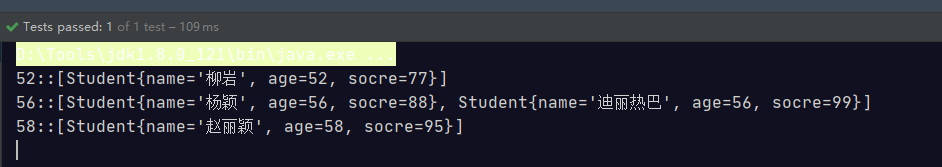
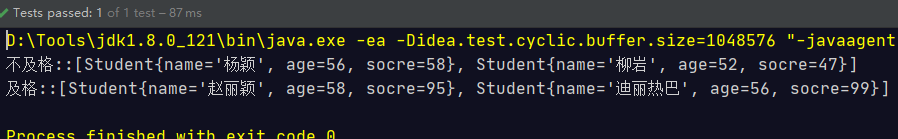
@Test public void test(){ Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of( new Student("赵丽颖", 58, 95), new Student("杨颖", 56, 58), new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 99), new Student("柳岩", 52, 47)); Map<String, List<Student>> collect = studentStream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(s -> s.getSocre() > 60 ? "及格" : "不及格")); collect.forEach( (k,v) -> { System.out.println(k + "::" + v); }); }
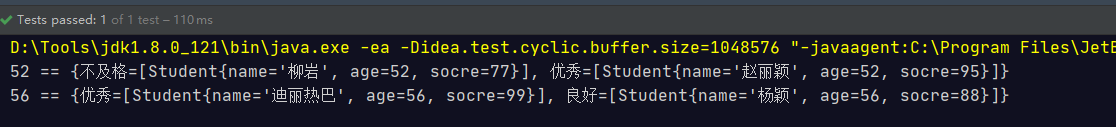
对流中数据进行多级分组
@Test public void test(){ Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of( new Student("赵丽颖", 52, 95), new Student("杨颖", 56, 88), new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 99), new Student("柳岩", 52, 77)); Map<Integer, Map<String, List<Student>>> map = studentStream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getAge, Collectors.groupingBy(s -> { if (s.getSocre() >= 90) { return "优秀"; } else if (s.getSocre() >= 80 && s.getSocre() < 90) { return "良好"; } else if (s.getSocre() >= 80 && s.getSocre() < 80) { return "及格"; } else { return "不及格"; } }))); map.forEach((k, v) -> { System.out.println(k + " == " + v); }); }
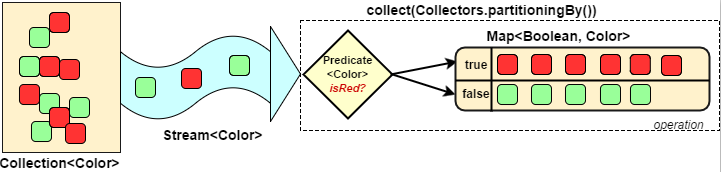
对流中数据进行分区
Collectors.partitioningBy 会根据值是否为true,把集合分割为两个列表,一个true列表,一个false列表。
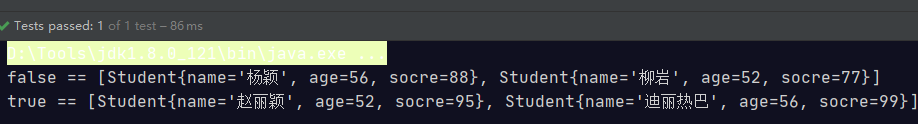
@Test public void test(){ Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of( new Student("赵丽颖", 52, 95), new Student("杨颖", 56, 88), new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 99), new Student("柳岩", 52, 77)); // partitioningBy会根据值是否为true,把集合分割为两个列表,一个true列表,一个false列表。 Map<Boolean, List<Student>> map = studentStream.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(s -> s.getSocre() > 90)); map.forEach((k, v) -> { System.out.println(k + " == " + v); }); }
对流中数据进行拼接
Collectors.joining 会根据指定的连接符,将所有元素连接成一个字符串。
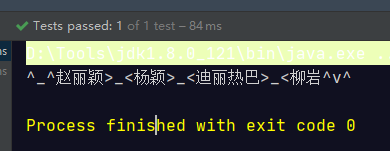
@Test public void test(){ Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of( new Student("赵丽颖", 52, 95), new Student("杨颖", 56, 88), new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 99), new Student("柳岩", 52, 77)); String collect = studentStream .map(Student::getName) .collect(Collectors.joining(">_<", "^_^", "^v^")); System.out.println(collect); }
/** * 测试flatMap */ @Test public void testFlatMap() { List<String> strs = Arrays.asList("孙悟空", "猪八戒"); String collect = strs.stream() .map(s -> { char[] arr01 = s.toCharArray(); Character[] arr02 = new Character[arr01.length]; for (int i = 0; i < arr02.length; i++) { arr02[i] = arr01[i]; } return arr02; }) .flatMap(Arrays::stream) // 扁平化 .map(String::valueOf) .collect(Collectors.joining(",")); System.out.println(collect); // 孙,悟,空,猪,八,戒 }
/** * SQL与Stream * */ @Test public void testStreamCompSql() { // select name, max(age) from person where name in ('孙悟空','猪八戒') and age is not null group by name order by name LinkedHashMap<String, Optional<Integer>> map = plist.stream() .filter(p -> Arrays.asList("孙悟空","猪八戒").contains(p.getName())) // name in ('孙悟空','猪八戒') .filter(p -> nonNull(p.getAge())) // age is not null .sorted(comparing(Person::getName,nullsLast(naturalOrder()))) // order by name, 注意空值问题 //.collect(groupingBy(Person::getName) // Map<String, List<Person>>, 此处搜集到的还是人,但需要的是年龄,继续downstream搜集 .collect(groupingBy(Person::getName,LinkedHashMap::new,mapping(Person::getAge, maxBy(Integer::compare)))) // group by name ; System.out.println(map); // {孙悟空=Optional[18], 猪八戒=Optional[28]} // select * from person where age = (select max(age) from person) limit 1 Optional<Person> first = plist.stream().sorted((p1,p2) -> p2.getAge() - p1.getAge()).findFirst(); System.out.println(first.get()); // Person [name=沙悟净, age=48, salary=40000.0] }


