Jdk8新特性之4大函数式接口
函数式接口介绍
它们主要在 java.util.function 包中。下面是最常用的几个接口。
1. Supplier接口
@FunctionalInterface public interface Supplier<T> { /** * Gets a result. * * @return a result */ T get(); }
2. Consumer接口
@FunctionalInterface public interface Consumer<T> { /** * Performs this operation on the given argument. * * @param t the input argument */ void accept(T t); }
3. Function接口
@FunctionalInterface public interface Function<T, R> { /** * Applies this function to the given argument. * * @param t the function argument * @return the function result */ R apply(T t); }
4. Predicate接口
@FunctionalInterface public interface Predicate<T> { /** * Evaluates this predicate on the given argument. * * @param t the input argument * @return {@code true} if the input argument matches the predicate, * otherwise {@code false} */ boolean test(T t); }
Supplier 接口
java.util.function.Supplier<T> 接口,它意味着"供给" , 对应的Lambda表达式需要“对外提供”一个符合泛型类型的对象数据。
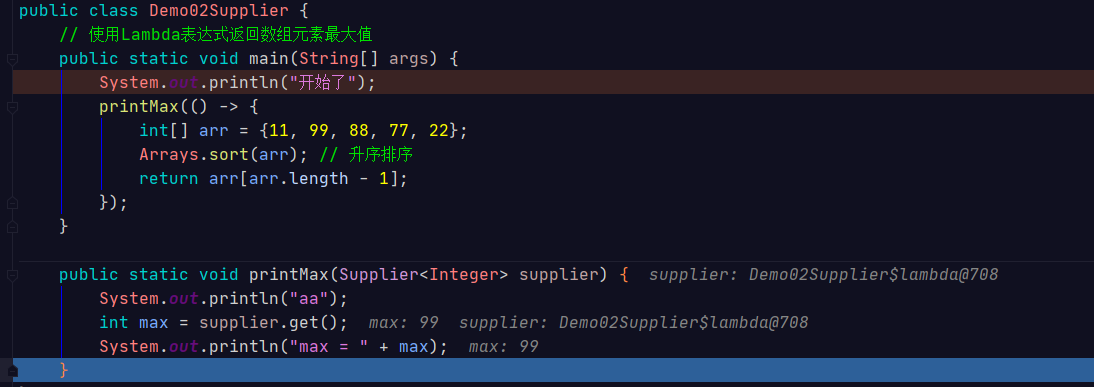
/** * @author WGR * @create 2020/3/24 -- 21:46 */ public class Demo02Supplier { // 使用Lambda表达式返回数组元素最大值 public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("开始了"); printMax(() -> { int[] arr = {11, 99, 88, 77, 22}; Arrays.sort(arr); // 升序排序 return arr[arr.length - 1]; }); } public static void printMax(Supplier<Integer> supplier) { System.out.println("aa"); int max = supplier.get(); System.out.println("max = " + max); } }
Consumer 接口
java.util.function.Consumer<T> 接口则正好相反,它不是生产一个数据,而是消费一个数据,其数据类型由泛型参数决定。
public class Demo03Consumer { public static void main(String[] args) { printHello( str ->{ //HELLO JDK8 System.out.println(str.toUpperCase()); }); } public static void printHello(Consumer<String> consumer) { consumer.accept("hello jdk8"); } }
public class Demo04ConsumerAndThen { public static void main(String[] args) { printHello( str1 ->{ System.out.println(str1.toUpperCase()); },str2 ->{ System.out.println(str2.toLowerCase()); }); } public static void printHello(Consumer<String> c1, Consumer<String> c2) { String str = "Hello Jdk8"; // default Consumer<T> andThen(Consumer<? super T> after) { // Objects.requireNonNull(after); // return (T t) -> { accept(t); after.accept(t); }; // } c2.andThen(c1).accept(str); } }
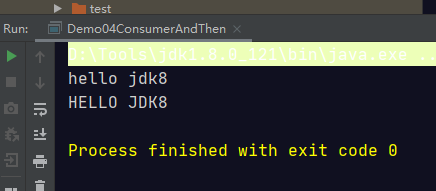
由于c2在前面,所以先操作c2再去操作c1,结果如图所示。
Function 接口
java.util.function.Function<T,R> 接口用来根据一个类型的数据得到另一个类型的数据,前者称为前置条件,后者称为后置条件。有参数有返回值。
public class Demo05Function { public static void main(String[] args) { getNumber( str ->{ return Integer.parseInt(str); }); } public static void getNumber(Function<String, Integer> function) { String num = "20"; Integer apply = function.apply(num); System.out.println(apply); } }
public class Demo06FunctionAndThen { public static void main(String[] args) { getNumber(str -> { return Integer.parseInt(str); }, num -> { return num * 5; }); } public static void getNumber(Function<String, Integer> f1, Function<Integer, Integer> f2) { String num = "20"; Integer integer = f1.andThen(f2).apply(num); System.out.println(integer); //100 } }
Predicate 接口
有时候我们需要对某种类型的数据进行判断,从而得到一个boolean值结果。这时可以使用java.util.function.Predicate<T> 接口。
public class Demo07Predicate { public static void main(String[] args) { isLongName( str -> { return str.length() > 3; }); } public static void isLongName(Predicate<String> predicate) { boolean test = predicate.test("新年快乐"); System.out.println(test); } }
public class Demo08Predicate_And_Or_Negate { // 使用Lambda表达式判断一个字符串中即包含W,也包含H // 使用Lambda表达式判断一个字符串中包含W或者包含H // 使用Lambda表达式判断一个字符串中不包含W public static void main(String[] args) { test((String str) -> { // 判断是否包含W return str.contains("W"); }, (String str) -> { // 判断是否包含H return str.contains("H"); }); } public static void test(Predicate<String> p1, Predicate<String> p2) { String str = "Hello World"; boolean b = p1.and(p2).test(str); if (b) { System.out.println("即包含W,也包含H"); } // 使用Lambda表达式判断一个字符串中包含W或者包含H boolean b1 = p1.or(p2).test(str); if (b1) { System.out.println("包含W或者包含H"); } // 使用Lambda表达式判断一个字符串中不包含W boolean b2 = p1.negate().test("Hello W"); // negate相当于取反 !boolean if (b2) { System.out.println("不包含W"); } } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号