IoC容器简介
官网说明:
在核心的第7章节
1 Spring IoC 容器和 beans 简介
本章介绍了 Spring Framework implementation of the Inversion of Control(IoC)[1]原理。 IoC 也称为依赖注入(DI)。它是一个 process,其中 objects 定义它们的依赖关系,即它们使用的其他 objects,只能通过构造函数 arguments,工厂方法的 arguments,或者 object 实例在构造或从工厂方法返回后设置的 properties 。然后容器在创建 bean 时注入这些依赖项。这个 process 基本上是反向的,因此 name 控制反转(IoC),bean 本身通过使用 classes 的直接构造或诸如 Service Locator pattern 之类的机制来控制其依赖关系的实例化或位置。
org.springframework.beans和org.springframework.context包是 Spring Framework 的 IoC 容器的基础。 Bean 工厂接口提供了一种高级 configuration 机制,能够管理任何类型的 object。 ApplicationContext是BeanFactory的 sub-interface。它增加了 Spring 的 AOP features 更容易整合;消息资源处理(用于国际化),事件发布;和 application-layer 特定的上下文,例如用于 web applications。
简而言之,BeanFactory提供 configuration framework 和基本功能,ApplicationContext添加更多 enterprise-specific 功能。 ApplicationContext是BeanFactory的完整超集,在本章中专门用于 Spring 的 IoC 容器的描述。
在 Spring 中,构成 application 主干并由 Spring IoC 容器管理的 objects 称为 beans。 _ bean 是一个 object,它由 Spring IoC 容器实例化,组装和管理。否则,bean 只是 application 中许多 object 之一。 Beans 及其之间的依赖关系反映在容器使用的 configuration 元数据中。
2 容器概述
接口org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext表示 Spring IoC 容器,负责实例化,配置和组装上述 beans。容器通过读取 configuration 元数据获取有关 objects 实例化,配置和汇编的指令。 configuration 元数据以 XML,Java annotations 或 Java code 表示。它允许您表达组成您的 application 的 objects 以及这些 objects 之间丰富的相互依赖关系。
使用 Spring 为ApplicationContext提供了ApplicationContext接口的几个 implementation。在独立的 applications 中,创建ClassPathXmlApplicationContext或FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 来的实例是 common。虽然 XML 是定义 configuration 元数据的传统格式,但您可以通过提供少量 XML configuration 来声明性地启用对这些其他元数据格式的支持,从而指示容器使用 Java annotations 或 code 作为元数据格式。
在大多数 application 场景中,不需要显式用户 code 来实例化 Spring IoC 容器的一个或多个实例。
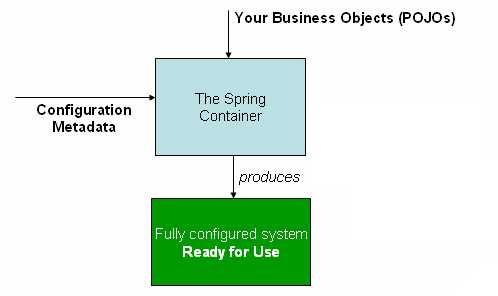
下图是 Spring 如何工作的 high-level 视图。您的 application classes 与 configuration 元数据结合使用,以便在创建和初始化ApplicationContext之后,您拥有一个完全配置且可执行的系统或 application。
图 1_.Spring IoC 容器
7.2.1 配置元数据
如上图所示,Spring IoC 容器使用一种 configuration 元数据形式;此 configuration 元数据表示您作为 application 开发人员如何告诉 Spring 容器在 application 中实例化,配置和组装 objects。
Configuration 元数据传统上以简单直观的 XML 格式提供,本章大部分内容用于传达 Spring IoC 容器的 key 概念和 features。
有关在 Spring 容器中使用其他形式的元数据的信息,请参阅:
-
Annotation-based configuration:Spring 2.5 引入了对 annotation-based configuration 元数据的支持。
-
Java-based configuration:从 Spring 3.0 开始,Spring JavaConfig 项目提供的许多 features 成为核心 Spring Framework 的一部分。因此,您可以使用 Java 而不是 XML files 定义 application classes 外部的 beans。要使用这些新的 features,请参阅
@Configuration,@Bean,@Import和@DependsOn注释。
Spring configuration 包含容器必须管理的至少一个且通常不止一个 bean 定义。 XML-based configuration 元数据显示这些 beans 在 top-level <beans/>元素内配置为<bean/>元素。 Java configuration 通常在@Configuration class 中使用@Bean带注释的方法。
这些 bean 定义对应于构成 application 的实际 objects。通常,您可以定义服务层对象,数据访问对象(DAO),表示对象(如 Struts Action实例),基础结构对象(如 Hibernate SessionFactories,JMS Queues等)。通常,不会在容器中配置 fine-grained domain objects,因为创建和加载域 objects 通常是 DAO 和业务逻辑的责任。但是,您可以使用 Spring 与 AspectJ 的 integration 来配置在 IoC 容器控制之外创建的 objects。
以下 example 显示了 XML-based configuration 元数据的基本结构:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="..." class="..."> <!-- collaborators and configuration for this bean go here --> </bean> <bean id="..." class="..."> <!-- collaborators and configuration for this bean go here --> </bean> <!-- more bean definitions go here --> </beans>
id属性是一个 string,用于标识单个 bean 定义。 class属性定义 bean 的类型并使用完全限定的类名。 id 属性的 value 指的是协作 objects。用于引用协作 objects 的 XML 未在此 example 中显示;有关详细信息,请参阅依赖。
7.2.2 实例化容器
实例化 Spring IoC 容器非常简单。提供给ApplicationContext构造函数的位置路径或_path 实际上是资源 strings,它允许容器从各种外部资源(如本地文件系统,Java CLASSPATH等)加载 configuration 元数据。
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml");
以下 example 显示了服务层 objects (services.xml) configuration 文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- services --> <bean id="petStore" class="org.springframework.samples.jpetstore.services.PetStoreServiceImpl"> <property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/> <property name="itemDao" ref="itemDao"/> <!-- additional collaborators and configuration for this bean go here --> </bean> <!-- more bean definitions for services go here --> </beans>
以下 example 显示了数据访问 objects daos.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="accountDao" class="org.springframework.samples.jpetstore.dao.jpa.JpaAccountDao"> <!-- additional collaborators and configuration for this bean go here --> </bean> <bean id="itemDao" class="org.springframework.samples.jpetstore.dao.jpa.JpaItemDao"> <!-- additional collaborators and configuration for this bean go here --> </bean> <!-- more bean definitions for data access objects go here --> </beans>
在前面的示例中,服务层由 class PetStoreServiceImpl和两个数据访问 object 组成,类型为JpaAccountDao和JpaItemDao(基于 JPA Object/Relational 映射标准)。 property name元素引用 JavaBean property 的 name,ref元素引用另一个 bean 定义的 name。 id和ref元素之间的这种联系表达了协作 objects 之间的依赖关系。
编写 XML-based configuration 元数据
使 bean 定义 span 多个 XML files 非常有用。通常,每个单独的 XML configuration 文件都代表 architecture 中的逻辑层或模块。
您可以使用 application context 构造函数从所有这些 XML 片段加载 bean 定义。此构造函数需要多个Resource位置,如上一节中所示。或者,使用一个或多个<import/>元素来从另一个文件或 files 加载 bean 定义。例如:
<beans> <import resource="services.xml"/> <import resource="resources/messageSource.xml"/> <import resource="/resources/themeSource.xml"/> <bean id="bean1" class="..."/> <bean id="bean2" class="..."/> </beans>
在前面的 example 中,外部 bean 定义从三个 files 加载:services.xml,messageSource.xml和themeSource.xml。所有位置_path 都与执行 importing 的定义文件相关,因此services.xml必须与执行 importing 的文件位于同一目录或 classpath 位置,而messageSource.xml和themeSource.xml必须位于 importing 文件位置下方的resources位置。如您所见,忽略前导斜杠,但鉴于这些_path 是相对的,最好不要使用斜杠。根据 Spring Schema,导入的 files 的内容(包括 top level <beans/>元素)必须是有效的 XML bean 定义。
使用相对“../”路径在 parent 目录中 reference files 是可能的,但不建议这样做。这样做会对当前 application 之外的文件创建依赖关系。特别是,不建议将此 reference 用于“classpath:”URL(对于 example,“classpath:../services.xml”),其中运行时解析 process 选择“最近的”classpath 根,然后查看其 parent 目录。 Classpath configuration 更改可能导致选择不同的,不正确的目录。
您始终可以使用完全限定的资源位置而不是相对的 paths:for example,“file:C:/config/services.xml”或“classpath:/config/services.xml”。但是,请注意您将 application 的 configuration 与特定的绝对位置耦合。通常最好为这样的绝对位置保持间接,例如,通过在运行时针对 JVM 系统 properties 解析的“$ {}”占位符。
import 指令是 beans 命名空间本身提供的 feature。 Spring,e.g 提供的一系列 XML 命名空间中提供了进一步 configuration features 以外的普通 bean 定义。 “context”和“util”命名空间。
2.3 使用容器
ApplicationContext是高级工厂的接口,能够维护不同 beans 及其依赖项的注册表。使用方法T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType),您可以检索 beans 的实例。
ApplicationContext使您能够读取 bean 定义并按如下方式访问它们:
// create and configure beans ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml"); // retrieve configured instance PetStoreService service = context.getBean("petStore", PetStoreService.class); // use configured instance List<String> userList = service.getUsernameList();
如果需要,这些 reader 委托可以在相同的ApplicationContext上混合和匹配,从不同的 configuration 源读取 bean 定义。
然后,您可以使用getBean来检索 beans 的实例。 ApplicationContext接口有一些其他方法可以检索 beans,但理想情况下你的 application code 应该永远不会使用它们。实际上,你的 application code 根本不应该对getBean()方法有 calls,因此根本不依赖于 Spring API。例如,Spring 与 web 框架的 integration 为各种 web framework 组件(如控制器和 JSF-managed beans)提供依赖注入,允许您通过元数据声明对特定 bean 的依赖(e.g. 自动装配 annotation)。
3 BeanFactory
BeanFactory API 为 Spring 的 IoC 功能提供了基础。它的特定 contracts 主要用于与 Spring 和相关 third-party 框架的其他部分进行整合,其DefaultListableBeanFactory implementation 是 higher-level GenericApplicationContext容器中的 key 委托。
BeanFactory和相关接口(如BeanFactoryAware,InitializingBean,DisposableBean)是其他 framework 组件的重要集成点:不需要任何注释甚至反射,它们允许容器与其组件之间的非常有效的交互。 Application-level beans 可以使用相同的回调接口,但通常更喜欢通过 annotations 或通过编程 configuration 进行声明性依赖注入。
请注意,核心BeanFactory API level 及其DefaultListableBeanFactory implementation 不会对 configuration 格式或要使用的任何 component annotations 进行假设。所有这些风格都通过诸如XmlBeanDefinitionReader和AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor之类的 extensions 进行,在共享BeanDefinition objects 上作为核心元数据表示进行操作。这就是 Spring 容器如此灵活和可扩展的本质。
以下部分解释了BeanFactory和ApplicationContext容器级别之间的差异以及对引导的影响。
3.1 BeanFactory 或 ApplicationContext?
使用ApplicationContext,除非你有充分的理由不这样做,GenericApplicationContext及其子类AnnotationConfigApplicationContext作为自定义引导的 common implementations。这些是 Spring 的核心容器的主要入口点,适用于所有 common 目的:配置 files,触发 classpath 扫描,以编程方式注册 bean 定义和带注释的 classes。
因为ApplicationContext包含BeanFactory的所有功能,所以通常建议使用BeanFactory,除了需要完全控制 bean 处理的场景。在诸如GenericApplicationContext implementation 之类的ApplicationContext中,将按惯例检测到几种 beans(i.e.由 bean name 或 bean 类型),特别是 post-processors,而普通的DefaultListableBeanFactory与任何特殊的 beans 无关。
对于许多扩展容器 features,例如 annotation 处理和 AOP 代理,BeanPostProcessor 扩展点是必不可少的。如果仅使用普通DefaultListableBeanFactory,则默认情况下不会检测到并激活此类 post-processors。这种情况可能令人困惑,因为你的 bean configuration 没有任何问题;它更像是在这种情况下需要通过附加设置完全自举的容器。
以下 table lists features 由BeanFactory和ApplicationContext接口和 implementations 提供。
表格 1_.Feature Matrix
| 特征 | BeanFactory | ApplicationContext |
|---|---|---|
| Bean实例化/装配 | 是 | 是 |
| 集成生命周期管理 | 没有 | 是 |
BeanPostProcessor自动注册 |
没有 | 是 |
BeanFactoryPostProcessor自动注册 |
没有 | 是 |
| MessageSource便捷访问(针对i18n) | 没有 | 是 |
ApplicationEvent发布机制 |
没有 | 是 |
要使用DefaultListableBeanFactory显式注册 bean post-processor,您需要以编程方式调用addBeanPostProcessor:
DefaultListableBeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); // populate the factory with bean definitions // now register any needed BeanPostProcessor instances factory.addBeanPostProcessor(new AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor()); factory.addBeanPostProcessor(new MyBeanPostProcessor()); // now start using the factory
要将BeanFactoryPostProcessor应用于普通DefaultListableBeanFactory,您需要调用其postProcessBeanFactory方法:
DefaultListableBeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory); reader.loadBeanDefinitions(new FileSystemResource("beans.xml")); // bring in some property values from a Properties file PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer cfg = new PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer(); cfg.setLocation(new FileSystemResource("jdbc.properties")); // now actually do the replacement cfg.postProcessBeanFactory(factory);
在这两种情况下,显式注册步骤都不方便,这就是为什么各种ApplicationContext变体比 Spring-backed applications 中的普通DefaultListableBeanFactory更受欢迎,尤其是在典型企业设置中依赖BeanFactoryPostProcessor s 和BeanPostProcessor s 来扩展容器功能时。

