Spring Framework 简介
官网文档说明
在第2章节
2. Spring Framework 简介
Spring Framework 是一个 Java 平台,为 developing Java applications 提供全面的基础架构支持。 Spring 处理基础结构,因此您可以专注于 application。
Spring 使您能够从“普通旧 Java objects”(POJO)build applications 并将企业服务 non-invasively 应用于 POJO。此功能适用于 Java SE 编程 model 以及完整和部分 Java EE。
作为 application 开发人员,您可以从 Spring 平台中受益的示例如下:
-
使 Java 方法在数据库 transaction 中执行,而不必处理 transaction API。
-
使本地 Java 方法成为 HTTP 端点,而无需处理 Servlet API。
-
使本地 Java 方法成为消息处理程序,而无需处理 JMS API。
-
使本地 Java 方法成为 management 操作,而无需处理 JMX API。
2.1 依赖注入和控制反转
Java application - 一个宽松的术语,从约束的嵌入式应用程序到 n-tier,server-side enterprise applications 运行 - 通常由 objects 合作形成 application 本身。因此,application 中的 objects 彼此依赖。
尽管 Java 平台提供了丰富的 application 开发功能,但它缺乏将基本 building 块组织成一个连贯整体的方法,将该任务留给架构师和开发人员。虽然您可以使用诸如 Factory,Abstract Factory,Builder,Decorator 和 Service Locator 之类的设计模式来组成构成 application 的各种 classes 和 object 实例,但这些模式只是:给出 name 的最佳实践,其描述为 pattern 做什么,在哪里应用它,它解决的问题,等等。模式是您必须在 application 中实现的正式最佳实践。
Spring Framework 控制反转(IoC)component 通过提供一种形式化的方法来解决这个问题,该方法将不同的组件组合成一个可以使用的完全工作的 application。 Spring Framework 将形式化的设计模式编码为 first-class objects,您可以将它们集成到您自己的 application(s 中。许多组织和机构以这种方式使用 Spring Framework 来设计健壮,可维护的应用程序。
2.2 Framework Modules
Spring Framework 由组成大约 20 个模块的 features 组成。这些模块分为 Core Container,Data Access/Integration, Web,AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming),Instrumentation,Messaging 和 Test,如下图所示。
图 1_.Spring Framework 概述
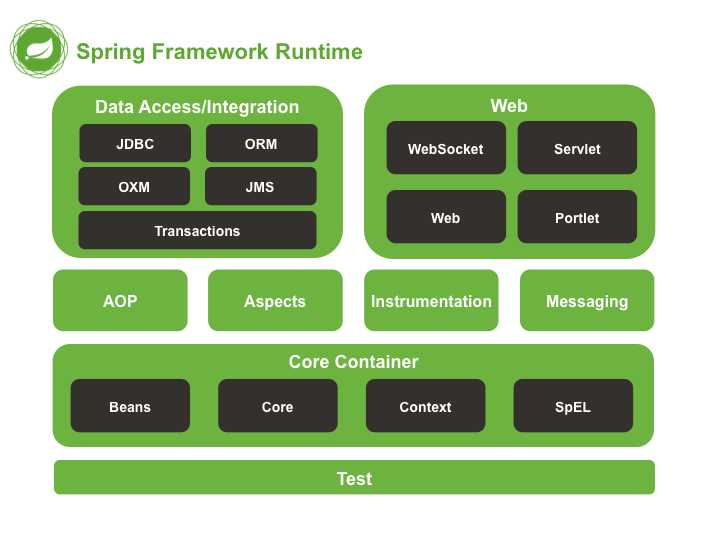
以下部分列出了每个 feature 的可用模块及其 artifact 名称及其涵盖的主题。 Artifact 名称与依赖性管理工具中使用的 artifact ID 相关联。
2.2.1 核心容器
核心容器由spring-core,spring-beans,spring-context,spring-context-support和spring-expression(Spring 表达式语言)模块组成。
spring-core和spring-beans模块提供 framework 的基本部分,包括 IoC 和依赖注入 features。 BeanFactory是工厂 pattern 的复杂 implementation。它消除了对程序化单例的需求,并允许您从实际程序逻辑中分离 configuration 和依赖项规范。
Context(spring-context)模块构建在核心和 Beans模块提供的坚实基础之上:它是一种以 framework-style 方式访问 objects 的方法,类似于 JNDI 注册表。 Context 模块从 Beans 模块继承其 features 并添加对国际化(使用,例如,资源包),event 传播,资源加载以及透明的上下文创建的支持,例如,Servlet 容器。 Context 模块还支持 Java EE features,例如 EJB,JMX 和基本远程处理。 ApplicationContext接口是 Context 模块的焦点。 spring-context-support支持将 common third-party libraries 集成到 Spring application context 中,用于缓存(EhCache,Guava,JCache),邮件(JavaMail),调度(CommonJ,Quartz)和模板引擎(FreeMarker,JasperReports,Velocity)。
spring-expression模块提供了一个强大的表达语言,用于在运行时查询和操作 object 图。它是 JSP 2.1 规范中指定的统一表达式语言(统一 EL)的扩展。该语言支持设置和获取 property 值,property 赋值,方法调用,访问数组,集合和索引器的内容,逻辑和算术操作符,命名变量以及 Spring 的 IoC 容器中的 name 检索 objects。它还支持列表投影和选择以及 common 列表聚合。
2.2.2 AOP 和仪表
spring-aop模块提供AOP Alliance-compliant aspect-oriented 编程 implementation,允许您为 example 定义方法拦截器和切入点,以干净地解耦实现应该分离的功能的 code。使用 source-level 元数据功能,您还可以以类似于.NET 属性的方式将行为信息合并到 code 中。
单独的spring-aspects模块提供与 AspectJ 的 integration。
spring-instrument模块提供 class 检测支持和类加载器 implementations 以在某些 application 服务器中使用。 spring-instrument-tomcat模块包含 Spring 的 Tomcat 检测代理。
2.2.3 消息
Spring Framework 4 包含一个spring-messaging模块,其中包含来自 Spring Integration 项目的 key 抽象,例如Message,MessageChannel,MessageHandler等,以作为 messaging-based applications 的基础。该模块还包括一组 annotations,用于将消息映射到方法,类似于基于 Spring MVC annotation 的编程 model。
2.2.4 数据 Access/Integration
Data Access/Integration 层由 JDBC,ORM,OXM,JMS 和 Transaction 模块组成。
spring-jdbc模块提供JDBC -abstraction 层,无需进行繁琐的 JDBC 编码和解析 database-vendor 特定错误代码。
spring-tx模块支持程序性和声明式 transaction management 用于实现特殊接口的 classes 和所有 POJO(Plain Old Java Objects)。
spring-orm模块为流行的object-relational 映射 API 提供 integration 层,包括JPA,JDO和Hibernate。使用spring-orm模块,您可以将所有这些 O/R-mapping 框架与 Spring 提供的所有其他 features 结合使用,例如前面提到的简单声明 transaction management feature。
spring-oxm模块提供了一个支持Object/XML 映射 __mplementation 的抽象层,例如 JAXB,Castor,XMLBeans,JiBX 和 XStream。
spring-jms模块(Java 消息传递服务)包含用于 producing 和 consuming 消息的 features。从 Spring Framework 4.1 开始,它为spring-messaging模块提供了 integration。
2.2.5 Web
Web 层由spring-web,spring-webmvc,spring-websocket和spring-webmvc-portlet模块组成。
spring-web模块提供基本的 web-oriented integration features,例如 multipart 文件上载功能和使用 Servlet listeners 和 web-oriented application context 初始化 IoC 容器。它还包含 HTTP client 和 Spring 远程支持的 web-related 部分。
spring-webmvc模块(也称为 Web-Servlet 模块)包含 Spring 的 model-view-controller(MVC)和 REST Web Services implementation for web applications。 Spring 的 MVC framework 提供了域 model code 和 web 表单之间的清晰分离,并与 Spring Framework 的所有其他 features 集成。
spring-webmvc-portlet模块(也称为 Web-Portlet 模块)提供了在 Portlet 环境中使用的 MVC implementation,并且 mirrors Servlet-based spring-webmvc模块的功能。
2.2.6 测试
spring-test模块使用 JUnit 或 TestNG 支持单元测试和整合测试 Spring 组件。它提供了loading的 Spring ApplicationContext和高速缓存这些上下文。它还提供mock objects,您可以使用它来隔离测试您的 code。
2.3 使用场景
前面描述的 building 块使 Spring 成为许多场景中的逻辑选择,从设备上运行的嵌入式应用程序到使用 Spring 的 transaction management 功能和 web framework integration 的 full-fledged enterprise applications。
图 1_.典型的 full-fledged Spring web application
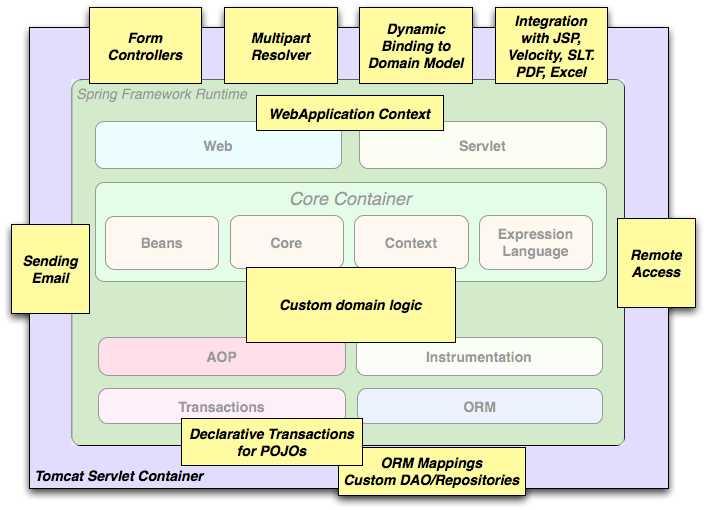
Spring 的声明性 transaction management features使 web application 完全 transactional,就像你使用 EJB container-managed transactions 一样。您可以使用简单的 POJO 实现所有自定义业务逻辑,并由 Spring 的 IoC 容器管理。其他服务包括支持发送独立于 web 层的电子邮件和验证,这使您可以选择执行验证规则的位置。 Spring 的 ORM 支持与 JPA,Hibernate 和 JDO 集成在一起;对于 example,当使用 Hibernate 时,您可以继续使用现有的映射 files 和标准 Hibernate SessionFactory configuration。表单控制器将 web-layer 与域 model 无缝集成,无需使用ActionForms或其他 classes 将 HTTP 参数转换为域 model 的值。
图 1_.Spring middle-tier 使用 third-party web framework
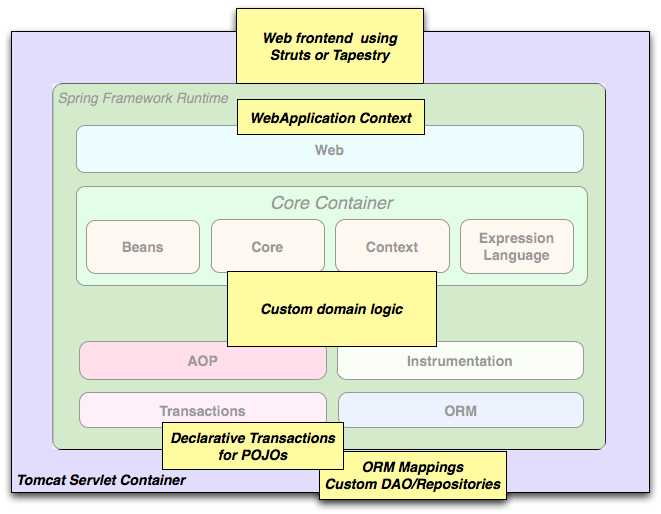
有时情况不允许您完全切换到不同的 framework。 Spring Framework 不会强迫您使用其中的所有内容;它不是 all-or-nothing 解决方案。使用 Struts,Tapestry,JSF 或其他 UI 框架构建的现有 front-ends 可以与 Spring-based middle-tier 集成,这允许您使用 Spring transaction features。您只需使用ApplicationContext连接业务逻辑并使用WebApplicationContext来集成 web 层。
图 1_.远程处理使用场景
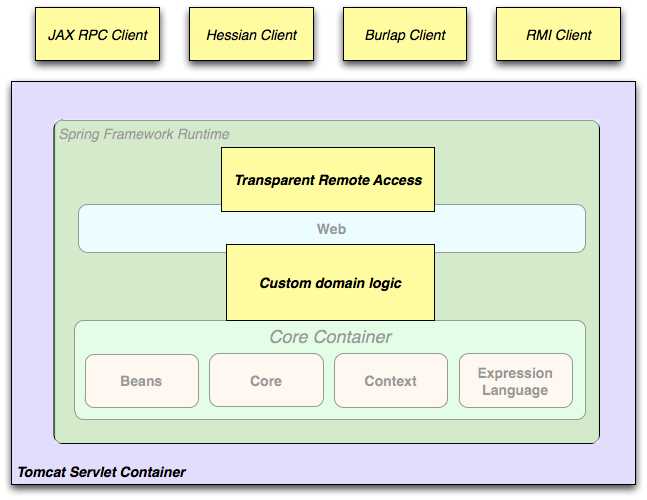
当您需要通过 web services 访问现有 code 时,可以使用 Spring 的Hessian-,Burlap-,Rmi-或JaxRpcProxyFactory classes。启用对现有 applications 的 remote 访问并不困难。
图 1_.EJB - 包装现有的 POJO
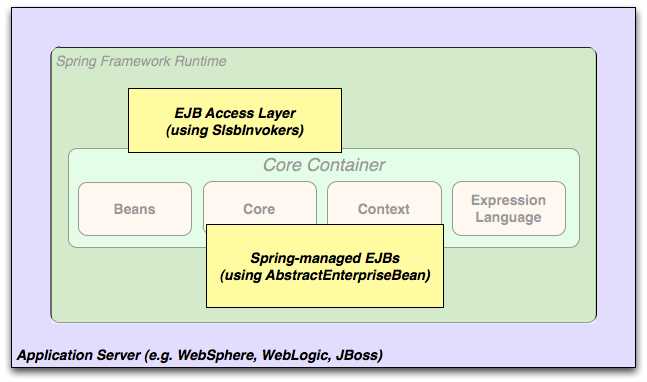
Spring Framework 还为 Enterprise JavaBeans 提供访问和抽象层,使您可以重用现有的 POJO 并将它们包装在 stateless session beans 中,以用于可能需要声明性安全性的可伸缩的 fail-safe web applications。
2.3.1 依赖管理和命名约定
依赖管理和依赖注入是不同的事情。要将 Spring 的那些好 features 放入你的 application(比如依赖注入),你需要组装所有需要的 libraries(jar files)并在运行时将它们放到 classpath 上,并且可能在 compiletime 上。这些依赖项不是注入的虚拟组件,而是文件系统中的物理资源(通常)。依赖 management 的 process 涉及定位这些资源,存储它们并将它们添加到类路径中。依赖关系可以是直接的(e.g. 我的 application 依赖于运行时的 Spring),或者是间接的(e.g. 我的 application 取决于依赖于commons-pool的commons-dbcp)。间接依赖性也称为“传递性”,并且最难识别和管理的是那些依赖性。
如果你打算使用 Spring,你需要获得一个 jar libraries 的副本,它包含你需要的 Spring 部分。为了使这更容易 Spring 被打包为一组模块,尽可能地分离依赖关系,因此对于 example,如果你不想编写 web application,则不需要 spring-web 模块。要在本指南中引用 Spring library 模块,我们使用简写命名约定spring-*或spring-*.jar,,其中*表示模块的短 name(e.g. spring-core,spring-webmvc,spring-jms,etc.)。您使用的实际 jar 文件 name 通常是模块 name 与 version number(e.g. spring-core-4.3.21.RELEASE.jar)连接。
Spring Framework 的每个版本都会将 artifacts 发布到以下位置:
-
Maven Central,它是 Maven 查询的默认 repository,不需要使用任何特殊的 configuration。 Spring 依赖的许多 common libraries 也可以从 Maven Central 获得,而 Spring 社区的很大一部分使用 Maven 进行依赖管理,所以这对他们来说很方便。这里 jars 的名称是
spring-*-<version>.jar形式,Maven groupId 是org.springframework。 -
在专门为 Spring 托管的公共 Maven repository 中。除了最终的 GA 版本之外,这个 repository 还托管了开发快照和里程碑。 jar 文件名与 Maven Central 的格式相同,因此这是一个有用的地方,可以让 Spring 的开发版本与 Maven Central 中部署的其他_lib 库一起使用。此 repository 还包含一个 bundle distribution zip 文件,其中包含所有捆绑在一起的 Spring jars 以便于下载。
因此,首先需要决定如何管理依赖项:我们通常建议使用自动系统,如 Maven,Gradle 或 Ivy,但您也可以通过自己下载所有 jars 来手动完成。
您可以在下面找到 Spring artifacts 列表。有关每个模块的更完整描述,请参阅第 2.2 节,“框架模块”。
表格 1_.Spring Framework Artifacts
| GroupId | artifactId | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| org.springframework | spring-aop | Proxy-based AOP 支持 |
| org.springframework | spring-aspects | AspectJ 基于方面 |
| org.springframework | spring-beans | Beans 支持,包括 Groovy |
| org.springframework | spring-context | Application context 运行时,包括调度和远程抽象 |
| org.springframework | spring-context-support | 支持 classes 将 common third-party libraries 集成到 Spring application context 中 |
| org.springframework | spring-core | 核心实用程序,由许多其他 Spring 模块使用 |
| org.springframework | spring-expression | Spring 表达语言(SpEL) |
| org.springframework | spring-instrument | 用于 JVM 引导的检测代理程序 |
| org.springframework | spring-instrument-tomcat | Tomcat 的检测代理 |
| org.springframework | spring-jdbc | JDBC 支持包,包括 DataSource 设置和 JDBC 访问支持 |
| org.springframework | spring-jms | JMS 支持包,包括 send/receive JMS 消息的辅助 classes |
| org.springframework | spring-messaging | 支持消息传递体系结构和协议 |
| org.springframework | spring-orm | Object/Relational Mapping,包括 JPA 和 Hibernate 支持 |
| org.springframework | spring-oxm | Object/XML 映射 |
| org.springframework | spring-test | 支持单元测试和 integration 测试 Spring 组件 |
| org.springframework | spring-tx | Transaction 基础设施,包括 DAO 支持和 JCA integration |
| org.springframework | spring-web | 基础 web 支持,包括 web client 和 web-based 远程处理 |
| org.springframework | spring-webmvc | Servlet 堆栈的 HTTP-based Model-View-Controller 和 REST endpoints |
| org.springframework | spring-webmvc-portlet | 要在 Portlet 环境中使用的 MVC implementation |
| org.springframework | spring-websocket | WebSocket 和 SockJS 基础架构,包括 STOMP 消息传递支持 |
Spring 依赖关系并取决于 Spring
尽管 Spring 为大量企业和其他外部工具提供了集成和支持,但它有意将其强制依赖性保持在绝对最低限度:您不必在 order 中找到并下载(甚至自动)大量 jar libraries 将 Spring 用于简单的用例。对于基本依赖注入,只有一个强制性外部依赖,即 logging(有关 logging 选项的更详细描述,请参见下文)。
接下来,我们概述了配置依赖于 Spring 的 application 所需的基本步骤,首先使用 Maven,然后使用 Gradle,最后使用 Ivy。在所有情况下,如果有任何不清楚的地方,请参阅您的依赖管理系统的文档,或者查看一些 sample code - Spring 本身使用 Gradle 来管理依赖项,当它是 building 时,我们的 samples 主要使用 Gradle 或 Maven。
Maven Dependency Management
如果您使用Maven进行依赖管理,则甚至不需要显式提供 logging 依赖项。对于 example,要创建一个 application context 并使用依赖注入来配置 application,Maven 依赖项将如下所示:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>4.3.21.RELEASE</version> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>
而已。请注意,如果您不需要针对 Spring API 进行编译,则可以将范围声明为运行时,这通常是基本依赖项注入用例的情况。
上面的 example 与 Maven Central repository 一起使用。要使用 Spring Maven repository(e.g. 用于里程碑或开发人员快照),您需要在 Maven configuration 中指定 repository 位置。对于完整版本:
<repositories> <repository> <id>io.spring.repo.maven.release</id> <url>http://repo.spring.io/release/</url> <snapshots><enabled>false</enabled></snapshots> </repository> </repositories>
对于里程碑:
<repositories> <repository> <id>io.spring.repo.maven.milestone</id> <url>http://repo.spring.io/milestone/</url> <snapshots><enabled>false</enabled></snapshots> </repository> </repositories>
对于快照:
<repositories> <repository> <id>io.spring.repo.maven.snapshot</id> <url>http://repo.spring.io/snapshot/</url> <snapshots><enabled>true</enabled></snapshots> </repository> </repositories>
Maven“物料清单”依赖
使用 Maven 时,可能会意外混合不同版本的 Spring JAR。对于 example,您可能会发现 third-party library 或另一个 Spring 项目将传递依赖项拉入旧版本。如果您忘记自己明确声明直接依赖,则可能会出现各种意外问题。
为了克服这些问题,Maven 支持“物料清单”(BOM)依赖的概念。您可以 import dependencyManagement部分中的spring-framework-bom以确保所有 spring 依赖项(直接和传递)都在同一个 version 中。
<dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-framework-bom</artifactId> <version>4.3.21.RELEASE</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement>
使用 BOM 的另一个好处是,在依赖 Spring Framework artifacts 时,您不再需要指定<version>属性:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependencies>
Gradle Dependency Management
要将 Spring repository 与Gradle build 系统一起使用,请在repositories部分中包含相应的 URL:
repositories {
mavenCentral()
// and optionally...
maven { url "http://repo.spring.io/release" }
}
您可以根据需要将repositories URL 从/release更改为/milestone或/snapshot。一旦配置了 repository,就可以用通常的 Gradle 方式声明依赖项:
dependencies {
compile("org.springframework:spring-context:4.3.21.RELEASE")
testCompile("org.springframework:spring-test:4.3.21.RELEASE")
}
Ivy 依赖管理
如果您更喜欢使用常春藤来管理依赖项,那么有类似的 configuration 选项。
要将 Ivy 配置为指向 Spring repository,请将以下解析程序添加到ivysettings.xml:
<resolvers>
<ibiblio name="io.spring.repo.maven.release"
m2compatible="true"
root="http://repo.spring.io/release/"/>
</resolvers>
您可以根据需要将root URL 从/release/更改为/milestone/或/snapshot/。
配置完成后,您可以按常规方式添加依赖项。对于 example(在ivy.xml中):
<dependency org="org.springframework"
name="spring-core" rev="4.3.21.RELEASE" conf="compile->runtime"/>
分发 Zip Files
尽管使用支持依赖管理的 build 系统是获取 Spring Framework 的推荐方法,但仍然可以下载分发 zip 文件。
分发拉链发布到 Spring Maven Repository(这只是为了方便起见,你不需要 Maven 或 order 中的任何其他 build 系统来下载它们)。
要下载分发 zip,请打开 web 浏览器到http://repo.spring.io/release/org/springframework/spring并选择所需的 version 的相应子文件夹。分发 files 结束-dist.zip,对于 example spring-framework - {。 174} -RELEASE-dist.zip。也为里程碑和快照发布了发行版。
2.3.2 Logging
Logging 是 Spring 的一个非常重要的依赖项,因为 a)它是唯一的强制外部依赖项,b)每个人都喜欢从他们正在使用的工具中看到一些输出,并且 c)Spring 集成了许多其他工具,所有这些工具也都做了选择 logging 依赖。 application 开发人员的目标之一通常是在整个 application 的中心位置配置统一的 logging,包括所有外部组件。由于 logging framework 有很多选择,因此这比以往更难。
Spring 中的强制 logging 依赖是 Jakarta Commons Logging _API(JCL)。我们针对 JCL 进行编译,并且我们还为扩展 Spring Framework 的 classes 显示 JCL Log objects。对于用户来说重要的是 Spring 的所有版本都使用相同的 logging library:迁移很容易,因为即使使用扩展 Spring 的 applications 也可以保留向后兼容性。我们这样做的方法是让 Spring 中的一个模块明确依赖commons-logging(JCL 的规范 implementation),然后让所有其他模块依赖于 compile time。如果你正在使用 Maven 进行 example,并想知道你在哪里找到了对commons-logging的依赖,那么它来自 Spring,特别是来自名为spring-core的中央模块。
关于commons-logging的好处是你不需要任何其他东西来使你的 application 工作。它有一个运行时发现算法,可以在 classpath 中的众所周知的位置查找其他 logging 框架,并使用它认为合适的一个(或者如果需要,可以告诉它哪一个)。如果没有其他可用的东西,你可以从 JDK(简称 java.util.logging 或 JUL)获得相当漂亮的日志。在大多数情况下,您应该发现 Spring application 正常工作并快乐地记录到 console 开箱即用,这很重要。
使用 Log4j 1.2 或 2.x
Log4j 1.2 同时也是 EOL。此外,Log4j 2.3 是最后一个 Java 6 兼容版本,新版本的 Log4j 2.x 版本需要 Java 7。
许多人使用Log4j作为 logging framework 进行 configuration 和 management 目的。它是高效的 well-established,实际上它是我们 build Spring 时在运行时使用的。 Spring 还提供了一些用于配置和初始化 Log4j 的实用程序,因此在某些模块中它对 Log4j 具有可选的 compile-time 依赖性。
要使 Log4j 1.2 使用默认的 JCL 依赖项(commons-logging),您需要做的就是将 Log4j 放在 classpath 上,并为其提供 configuration 文件(classpath 的根目录中的log4j.properties或log4j.xml)。所以对于 Maven 用户来说这是你的依赖声明:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-core</artifactId> <version>4.3.21.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <version>1.2.17</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
这是一个 sample log4j.properties for logging 到 console:
log4j.rootCategory=INFO, stdout
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{ABSOLUTE} %5p %t %c{2}:%L - %m%n
log4j.category.org.springframework.beans.factory=DEBUG
要将 Log4j 2.x 与 JCL 一起使用,您需要做的就是将 Log4j 放在 classpath 上,并为其提供 configuration 文件(log4j2.xml,log4j2.properties或其他支持的 configuration 格式)。对于 Maven 用户,所需的最小依赖项是:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId> <version>2.6.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j-jcl</artifactId> <version>2.6.2</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
如果您还希望启用 SLF4J 委派给 Log4j,e.g. 对于默认使用 SLF4J 的其他 libraries,还需要以下依赖项:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j-slf4j-impl</artifactId> <version>2.6.2</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
这是一个 example log4j2.xml for logging 到 console:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <Configuration status="WARN"> <Appenders> <Console name="Console" target="SYSTEM_OUT"> <PatternLayout pattern="%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%t] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n"/> </Console> </Appenders> <Loggers> <Logger name="org.springframework.beans.factory" level="DEBUG"/> <Root level="error"> <AppenderRef ref="Console"/> </Root> </Loggers> </Configuration>
避免 Commons Logging
遗憾的是,标准commons-logging API 中的运行时发现算法虽然方便了 end-user,但可能会出现问题。如果您想避免使用 JCL 的标准查找,基本上有两种方法可以将其关闭:
-
从
spring-core模块中排除依赖关系(因为它是唯一明确依赖于commons-logging的模块) -
依赖于一个特殊的
commons-logging依赖项,用 jar 替换 library(更多细节可以在SLF4J 常见问题中找到)
要排除 commons-logging,请将以下内容添加到dependencyManagement部分:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-core</artifactId> <version>4.3.21.RELEASE</version> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>commons-logging</groupId> <artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> </dependencies>
现在这个 application 目前已经被破坏,因为 class 路径上没有_Lmple API 的 implementation,所以为了修复它,必须提供一个新的。在下一节中,我们将向您展示如何使用 SLF4J 提供 JCL 的替代 implementation。
将 SLF4J 与 Log4j 或 Logback 一起使用
Simple Logging Facade for Java(SLF4J)是一个流行的 API,由 Spring 常用的其他 libraries 使用。它通常与logback一起使用,这是 SLF4J API 的原生 implementation。
SLF4J 提供了对许多 common logging 框架的绑定,包括 Log4j,它也反过来了:其他 logging 框架和它自己之间的桥梁。因此,要将 SLF4J 与 Spring 一起使用,您需要将commons-logging依赖项替换为 SLF4J-JCL bridge。完成后,Spring 中的 logging calls 将被转换为 logging calls 到 SLF4J API,因此如果 application 中的其他 libraries 使用该 API,那么您只需一个地方来配置和管理 logging。
common 的选择可能是 bridge Spring 到 SLF4J,然后从 SLF4J 向 Log4j 提供显式的 binding。您需要提供多个依赖项(并排除现有的commons-logging):JCL bridge,SLF4j binding 到 Log4j,以及 Log4j 提供程序本身。在 Maven 你会这样做
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-core</artifactId> <version>4.3.21.RELEASE</version> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>commons-logging</groupId> <artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>jcl-over-slf4j</artifactId> <version>1.7.21</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId> <version>1.7.21</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <version>1.2.17</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
SLF4J 用户中使用较少步骤并产生较少依赖关系的更常见选择是直接绑定到logback。这删除了额外的 binding step,因为 Logback 直接实现了 SLF4J,所以你只需要依赖两个 libraries,即jcl-over-slf4j和logback):
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>jcl-over-slf4j</artifactId> <version>1.7.21</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId> <artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId> <version>1.1.7</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
使用 JUL(java.util.logging)
Commons Logging _will 默认委托给java.util.logging,前提是在 classpath 上没有检测到 Log4j。所以没有特殊的依赖关系来设置:只需在 log输出到java.util.logging时使用没有外部依赖关系的 Spring,或者在独立的 application(在 JDK level 中使用自定义或默认 JUL 设置)或者使用 application 服务器的 log 系统(和它的 system-wide JUL 设置)。
Commons Logging _on WebSphere
Spring applications 可能会在一个容器上运行,该容器本身提供_Lmple 的实现,e.g. IBM 的 WebSphere Application Server(WAS)。这不会导致问题本身,但会导致需要理解的两种不同情况:
在“parent first”ClassLoader 委托 model(WAS 中的默认值)中,applications 将始终获取 Commons Logging 的 server-provided version,委托给 WAS logging 子系统(实际上是基于 JUL)。 JCL 的 application-provided 变体,无论是标准 Commons Logging 还是 JCL-over-SLF4J bridge,都将被有效地忽略,以及任何本地包含的 log 提供者。
使用“parent last”委托 model(常规 Servlet 容器中的默认值,但 WAS 上的显式 configuration 选项),将拾取 application-provided Commons Logging _variant,使您能够设置本地包含的 log 提供程序 e.g. 您的 application 中的 Log4j 或 Logback。如果没有本地 log 提供程序,则默认情况下,常规 Commons Logging _will 委托给 JUL,有效 logging 到 WebSphere 的 logging 子系统,就像在“parent first”场景中一样。
总而言之,我们建议在“parent last”model 中部署 Spring applications,因为它自然允许本地提供程序以及服务器的 log 子系统。

