java集合LinkedList
基于jdk_1.8.0
关于List,主要是有序的可重复的数据结构。jdk主要实现类有ArrayList(底层使用数组)、LinkedList(底层使用双向链表)
LinkedList:
(一)继承关系图
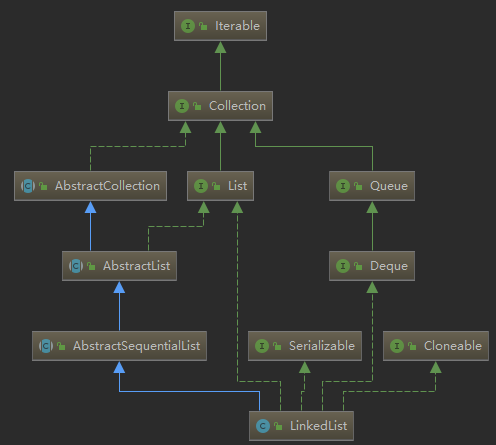
(二)源码分析
1. 关键字段

1 /** 2 * 当前链表元素个数 3 */ 4 transient int size = 0; 5 6 /** 7 * 指向第一个节点的指针 8 */ 9 transient Node<E> first; 10 11 /** 12 * 指向最后一个节点的指针 13 */ 14 transient Node<E> last;
2. 构造方法

1 public LinkedList() { 2 } 3 4 public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { 5 this(); 6 addAll(c); //详见 3. public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) 7 }
3. 常用方法
a. public boolean add(E e)

1 /** 2 * 向链表的尾部追加元素 3 * 等效于调用addLast方法,只不过addLast没有返回值 4 * @param e 5 * @return 6 */ 7 public boolean add(E e) { 8 linkLast(e); 9 return true; 10 } 11 12 /** 13 * 链表尾部追加元素 14 * 第一个添加的元素节点作为链表的头结点 15 * @param e 16 */ 17 void linkLast(E e) { 18 final Node<E> l = last; 19 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); // 构造新的node节点 20 last = newNode; //尾节点指向新节点 21 if (l == null) 22 first = newNode; //空表时,头节点也指向新节点 23 else 24 l.next = newNode; //将新节点添加到链表 25 size++; 26 modCount++; 27 } 28 29 // LinkedList$Node.class 30 private static class Node<E> { 31 E item; //储存的元素 32 Node<E> next; //后继节点 33 Node<E> prev; //前继节点 34 35 Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { 36 this.item = element; 37 this.next = next; 38 this.prev = prev; 39 } 40 }
b. public void add(int index, E element)

1 /** 2 * 将指定的元素插入到列表中的指定位置。 3 * 4 * @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted 5 * @param element element to be inserted 6 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException 7 */ 8 public void add(int index, E element) { 9 checkPositionIndex(index); 10 11 if (index == size) 12 linkLast(element); // 详见 a. public void add(E element) 13 else 14 linkBefore(element, node(index)); 15 } 16 17 private void checkPositionIndex(int index) { 18 if (!isPositionIndex(index)) 19 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); 20 } 21 22 private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) { 23 return index >= 0 && index <= size; 24 } 25 26 /** 27 * 在 succ节点前插入 28 * @param e 29 * @param succ 30 */ 31 void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { 32 // assert succ != null; 33 final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; 34 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); // newNode.prev = pred; newNode.next = succ; 35 succ.prev = newNode; //更新succ的前继节点 36 if (pred == null) 37 first = newNode; // 在第一个元素节点前插入,更新头节点 38 else 39 pred.next = newNode; //将新节点加入链表 40 size++; 41 modCount++; 42 } 43 44 /** 45 * 最坏的情况需要遍历size/2个节点找到 index位置的节点 46 * @param index 47 * @return 48 */ 49 Node<E> node(int index) { 50 // assert isElementIndex(index); 51 52 if (index < (size >> 1)) { //节点位置在链表前半部分 从头节点往后找 53 Node<E> x = first; 54 for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) 55 x = x.next; 56 return x; 57 } else { //节点位置在链表后半部分 从尾节点往前找 58 Node<E> x = last; 59 for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) 60 x = x.prev; 61 return x; 62 } 63 }
c. public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)

1 /** 2 * 将指定集合中的所有元素追加到链表 3 * 默认尾插 4 * @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list 5 * @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call 6 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null 7 */ 8 public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { 9 return addAll(size, c); //详见 4. public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) 10 }
d. public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)

1 /** 2 * 从指定位置开始插入,性能不如尾插 3 * 虽然说,链表的随机插入较快,但是node(int index) 最坏也要遍历size/2个节点才能找到该位置的节点 4 * @param index index at which to insert the first element 5 * from the specified collection 6 * @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list 7 * @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call 8 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 9 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null 10 */ 11 public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { 12 checkPositionIndex(index); // index < 0 || index > size throws IndexOutOfBoundsException 13 14 Object[] a = c.toArray(); 15 int numNew = a.length; 16 if (numNew == 0) 17 return false; 18 19 Node<E> pred, succ; 20 if (index == size) { // 尾插(包括空表情况) 21 succ = null; 22 pred = last; // 待插入节点的前继节点 23 } else { 24 succ = node(index); // 获取index位置的节点 25 pred = succ.prev; // 待插入节点的前继节点 26 } 27 28 for (Object o : a) { 29 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o; 30 Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null); // newNode.prev = pred; newNode.next = null; 31 if (pred == null) //空表更新头节点 32 first = newNode; 33 else 34 pred.next = newNode; //更新前继节点的next指向当前新节点 35 pred = newNode; 36 } 37 38 if (succ == null) { // 空表更新尾节点 39 last = pred; 40 } else { 41 pred.next = succ; // 更新最后添加新节点的后继节点为原index位置节点 42 succ.prev = pred; // 更新原index位置节点的前继节点为最后新添加元素的节点 43 } 44 45 size += numNew; 46 modCount++; 47 return true; 48 }
e. public void addFirst(E e) // override for Deque

1 /** 2 * 头插法,对应的就是尾插法 addLast(E e) 3 * 头插,尾插性能想同,不过默认的add(E e)使用的是尾插法 4 * @param e 5 */ 6 public void addFirst(E e) { 7 linkFirst(e); 8 } 9 10 private void linkFirst(E e) { 11 final Node<E> f = first; 12 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f); 13 first = newNode; 14 if (f == null) 15 last = newNode; 16 else 17 f.prev = newNode; 18 size++; 19 modCount++; 20 }
f. public void addLast(E e) // override for Deque

1 /** 2 * 尾插法,对应的头插法 addFirst(E e),性能想同 3 * @param e 4 */ 5 public void addLast(E e) { 6 linkLast(e); 7 } 8 9 void linkLast(E e) { 10 final Node<E> l = last; 11 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); 12 last = newNode; 13 if (l == null) 14 first = newNode; 15 else 16 l.next = newNode; 17 size++; 18 modCount++; 19 }
g. public E remove() // override for Deque

1 /** 2 * 从链表中移除并返回第一个元素。 3 * @return 4 */ 5 public E remove() { 6 return removeFirst(); 7 } 8 9 /** 10 * 从链表中移除并返回第一个元素。 11 * 12 * @return the first element from this list 13 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty 14 */ 15 public E removeFirst() { 16 final Node<E> f = first; // 很多地方都采用了局部变量 17 if (f == null) 18 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 19 return unlinkFirst(f); 20 } 21 22 /** 23 * 该方法并没有判断参数是否null并且为第一个节点 需要调用者去保证 24 * 不过不理解的地方是,明明有first成员变量,为什么还要当做参数传进来 25 * @param f 头节点 26 * @return 移除掉的元素 27 */ 28 private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) { 29 // assert f == first && f != null; 30 final E element = f.item; 31 final Node<E> next = f.next; 32 f.item = null; 33 f.next = null; // help GC 34 first = next; 35 if (next == null) 36 last = null; 37 else 38 next.prev = null; 39 size--; 40 modCount++; 41 return element; 42 }
h. public E remove(int index)

1 /** 2 * 移除列表中指定位置的元素 3 * 4 * @param index the index of the element to be removed 5 * @return the element previously at the specified position 6 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 7 */ 8 public E remove(int index) { 9 checkElementIndex(index); 10 return unlink(node(index)); 11 } 12 13 /** 14 * 从链表中移除节点x 15 * @param x 16 * @return x.item 17 */ 18 E unlink(Node<E> x) { 19 // assert x != null; 20 final E element = x.item; 21 final Node<E> next = x.next; 22 final Node<E> prev = x.prev; 23 24 if (prev == null) { // x为第一个节点 25 first = next; 26 } else { 27 prev.next = next; // 把待移除节点的前继节点的next指向待移除节点的next 28 x.prev = null; 29 } 30 31 if (next == null) { // x为最后一个节点 32 last = prev; 33 } else { 34 next.prev = prev; // 把待移除节点的后继节点的prev指向待移除节点的prev 35 x.next = null; 36 } 37 38 x.item = null; 39 size--; 40 modCount++; 41 return element; 42 }
i. public boolean remove(Object o)

1 /** 2 * 删除第一个存在链表中的 o 3 * 4 * @param o element to be removed from this list, if present 5 * @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element 6 */ 7 public boolean remove(Object o) { 8 if (o == null) { 9 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { 10 if (x.item == null) { 11 unlink(x); //移除x节点 详情 h. public E remove(int index) 12 return true; 13 } 14 } 15 } else { 16 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { 17 if (o.equals(x.item)) { 18 unlink(x); //移除x节点 详情 h. public E remove(int index) 19 return true; 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 return false; 24 }
j. public E set(int index, E element)

1 /** 2 * 更新指定位置的元素 3 * 4 * @param index index of the element to replace 5 * @param element element to be stored at the specified position 6 * @return the element previously at the specified position 7 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 8 */ 9 public E set(int index, E element) { 10 checkElementIndex(index); // index < 0 || index >= size throws IndexOutOfBoundsException 11 Node<E> x = node(index); // 获取index位置的节点 12 E oldVal = x.item; 13 x.item = element; 14 return oldVal; 15 }
k. public E get(int index)

1 /** 2 * 获取链表指定位置的元素 3 * 4 * @param index index of the element to return 5 * @return the element at the specified position in this list 6 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 7 */ 8 public E get(int index) { 9 checkElementIndex(index); // index < 0 || index >= size throws IndexOutOfBoundsException 10 return node(index).item; 11 }
l. public int indexOf(Object o)

1 /** 2 * 查找链表中元素o所在的第一个下标 3 * 4 * @param o element to search for 5 * @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in 6 * this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element 7 */ 8 public int indexOf(Object o) { 9 int index = 0; 10 if (o == null) { 11 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { 12 if (x.item == null) 13 return index; 14 index++; 15 } 16 } else { 17 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { 18 if (o.equals(x.item)) // 需要重写实体类的equals方法 19 return index; 20 index++; 21 } 22 } 23 return -1; 24 }
m. public int lastIndexOf(Object o)

1 /** 2 * 从后往前遍历查找元素o所在的位置 3 * 4 * @param o element to search for 5 * @return the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in 6 * this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element 7 */ 8 public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { 9 int index = size; 10 if (o == null) { 11 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { 12 index--; 13 if (x.item == null) 14 return index; 15 } 16 } else { 17 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { 18 index--; 19 if (o.equals(x.item)) 20 return index; 21 } 22 } 23 return -1; 24 }
n. public Iterator<E> iterator() //AbstractSequentialList.class

1 // LinkedList ——> AbstractSequentialList ——> AbstractList 2 3 // AbstractSequentialList.class 4 public Iterator<E> iterator() { 5 return listIterator(); // AbstractList.listIterator() 6 } 7 8 public abstract ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index); 9 10 // AbstractList.class 11 public ListIterator<E> listIterator() { 12 return listIterator(0); // LinkedList.listIterator(0) 13 } 14 15 // LinkedList.class 16 public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) { 17 checkPositionIndex(index); 18 return new ListItr(index); 19 } 20 21 // LinkedList$ListItr.class 22 private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> { 23 /** 24 * 主要是提供给 remove、set方法用,在调用remove、set方法前 务必首先调用next() 或者 previous,否则lastReturned为null 会抛IllegalStateException 25 * 也要注意调用remove、add方法后lastReturned会置为null 26 */ 27 private Node<E> lastReturned; // next() 或者 previous()返回的最新节点 28 private Node<E> next; // 当前游标节点 29 private int nextIndex; // 当前游标位置 30 private int expectedModCount = modCount; 31 32 ListItr(int index) { 33 // assert isPositionIndex(index); 34 next = (index == size) ? null : node(index); 35 nextIndex = index; 36 } 37 38 public boolean hasNext() { 39 return nextIndex < size; 40 } 41 42 public E next() { 43 checkForComodification(); 44 if (!hasNext()) 45 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 46 47 lastReturned = next; 48 next = next.next; 49 nextIndex++; 50 return lastReturned.item; 51 } 52 53 public boolean hasPrevious() { 54 return nextIndex > 0; //第一个节点没有前继节点 55 } 56 57 /** 58 * 调用previous()要小心默认 listIterator() { 59 * listIterator(0); // 此种情况下使用hasPrevious()遍历,返回的永远都是false 60 * } 61 * 对应next() 应调用listIterator(list.size()) 62 * @return 63 */ 64 public E previous() { 65 checkForComodification(); 66 if (!hasPrevious()) 67 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 68 69 lastReturned = next = (next == null) ? last : next.prev; // 从后往前遍历 70 nextIndex--; 71 return lastReturned.item; 72 } 73 74 public int nextIndex() { 75 return nextIndex; 76 } 77 78 public int previousIndex() { 79 return nextIndex - 1; 80 } 81 82 public void remove() { 83 checkForComodification(); 84 if (lastReturned == null) 85 throw new IllegalStateException(); 86 87 Node<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next; 88 unlink(lastReturned); 89 if (next == lastReturned) 90 next = lastNext; 91 else 92 nextIndex--; 93 lastReturned = null; // 防止再次remove 94 expectedModCount++; 95 } 96 97 public void set(E e) { 98 if (lastReturned == null) 99 throw new IllegalStateException(); 100 checkForComodification(); 101 lastReturned.item = e; 102 } 103 104 public void add(E e) { 105 checkForComodification(); 106 lastReturned = null; 107 if (next == null) 108 linkLast(e); // 尾插 109 else 110 linkBefore(e, next); // 在next节点前插入e 111 nextIndex++; 112 expectedModCount++; 113 } 114 115 public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) { 116 Objects.requireNonNull(action); 117 while (modCount == expectedModCount && nextIndex < size) { 118 action.accept(next.item); 119 lastReturned = next; 120 next = next.next; 121 nextIndex++; 122 } 123 checkForComodification(); 124 } 125 126 /** 127 * 防止使用iterator遍历的时候,还操作list 128 */ 129 final void checkForComodification() { 130 if (modCount != expectedModCount) 131 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 132 } 133 }
o. public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index)

1 /** 2 * 指定从index位置开始遍历链表 3 * 如果使用previous ,必须调用该方法,指定index > 0 4 * @param index 5 * @return 6 */ 7 public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) { 8 checkPositionIndex(index); 9 return new ListItr(index); //参考 n. public Iterator<E> iterator() 10 }
p. public Object[] toArray()

1 public Object[] toArray() { 2 Object[] result = new Object[size]; 3 int i = 0; 4 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) 5 result[i++] = x.item; 6 return result; 7 }
q. public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a)

1 public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { 2 if (a.length < size) 3 a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance( 4 a.getClass().getComponentType(), size); 5 int i = 0; 6 Object[] result = a; 7 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) 8 result[i++] = x.item; 9 10 if (a.length > size) 11 a[size] = null; 12 13 return a; 14 }
r. 其他基本方法

1 /** 2 * 清空列表 3 */ 4 public void clear() { 5 // Clearing all of the links between nodes is "unnecessary", but: 6 // - helps a generational GC if the discarded nodes inhabit 7 // more than one generation 8 // - is sure to free memory even if there is a reachable Iterator 9 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) { 10 Node<E> next = x.next; 11 x.item = null; 12 x.next = null; 13 x.prev = null; 14 x = next; 15 } 16 first = last = null; 17 size = 0; 18 modCount++; 19 } 20 21 /** 22 * 克隆列表 ,需要实体类自行重写Object.clone()方法,才可实现深度复制 23 * @return 24 */ 25 public Object clone() { 26 LinkedList<E> clone = superClone(); 27 28 // Put clone into "virgin" state 29 clone.first = clone.last = null; 30 clone.size = 0; 31 clone.modCount = 0; 32 33 // Initialize clone with our elements 34 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) 35 clone.add(x.item); 36 37 return clone; 38 } 39 40 /** 41 * 列表是否包含元素o 42 * @param o 43 * @return 44 */ 45 public boolean contains(Object o) { 46 return indexOf(o) != -1; 47 } 48 49 /** 50 * 当前列表节点数量 51 * @return 52 */ 53 public int size() { 54 return size; 55 } 56 57 // 序列化相关 58 private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) 59 throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { 60 // Read in any hidden serialization magic 61 s.defaultReadObject(); 62 63 // Read in size 64 int size = s.readInt(); 65 66 // Read in all elements in the proper order. 67 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) 68 linkLast((E)s.readObject()); 69 } 70 71 private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) 72 throws java.io.IOException { 73 // Write out any hidden serialization magic 74 s.defaultWriteObject(); 75 76 // Write out size 77 s.writeInt(size); 78 79 // Write out all elements in the proper order. 80 for (LinkedList.Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) 81 s.writeObject(x.item); 82 }
s. Deque方法

1 public void addFirst(E e) { 2 linkFirst(e); 3 } 4 5 public void addLast(E e) { 6 linkLast(e); 7 } 8 9 public E element() { 10 return getFirst(); 11 } 12 13 public boolean offer(E e) { 14 return add(e); 15 } 16 17 public boolean offerFirst(E e) { 18 addFirst(e); 19 return true; 20 } 21 22 public boolean offerLast(E e) { 23 addLast(e); 24 return true; 25 } 26 27 public E peek() { 28 final Node<E> f = first; 29 return (f == null) ? null : f.item; 30 } 31 32 public E peekFirst() { 33 final Node<E> f = first; 34 return (f == null) ? null : f.item; 35 } 36 37 public E peekLast() { 38 final Node<E> l = last; 39 return (l == null) ? null : l.item; 40 } 41 42 public E poll() { 43 final Node<E> f = first; 44 return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f); 45 } 46 47 public E pollFirst() { 48 final Node<E> f = first; 49 return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f); 50 } 51 52 public E pollLast() { 53 final Node<E> l = last; 54 return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l); 55 } 56 57 public E pop() { 58 return removeFirst(); 59 } 60 61 public void push(E e) { 62 addFirst(e); 63 } 64 65 public E remove() { 66 return removeFirst(); 67 } 68 69 public E removeFirst() { 70 final Node<E> f = first; 71 if (f == null) 72 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 73 return unlinkFirst(f); 74 } 75 76 public E removeLast() { 77 final Node<E> l = last; 78 if (l == null) 79 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 80 return unlinkLast(l); 81 } 82 83 public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) { 84 return remove(o); 85 } 86 87 public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) { 88 if (o == null) { 89 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { 90 if (x.item == null) { 91 unlink(x); 92 return true; 93 } 94 } 95 } else { 96 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { 97 if (o.equals(x.item)) { 98 unlink(x); 99 return true; 100 } 101 } 102 } 103 return false; 104 }
写在最后:
通过构造方法,还有add方法,可以看出,没有构造没有存储任何元素的头结点,第一个存储的元素作为链表的头结点;
通过Node内部类prev,next可以看出LinkedList是双向链表,既可以从尾部向头部遍历,也可以从头部向尾部遍历;
非必要情况下,尽可能不要调用按位置插入方法,会多一步按位置查找节点影响性能。对于插入时选择头插法还是尾插法,性能都是一样的。默认add(E e) 调用的是addLast;
通过对比ArrayList,发现LinkedList除了实现了AbstractList还实现了Deque,可以把LinkedList当做队列、栈操作,比如addFirst、addLast、remove、pop、push等;
使用listIterator.hasPrevious()从后往前遍历的时候,应注意list.listIterator(list.size());
LinkedList理论上只要内存足够,几乎没有最大元素上限;
和ArrayList一样,LinkedList也是非线程安全的,存放其中的实体,同样也需要重写Object.equals()方法。如果需要调用list.clone(),还应重写Object.clone()方法;
LinkedList,在随机插入由于不需要移动元素,故比ArrayList要快,但在get(int index)、set(int index, E e)随机访问要比ArrayList慢





