实验11-使用keras完成逻辑回归
版本python3.7 tensorflow版本为tensorflow-gpu版本2.6
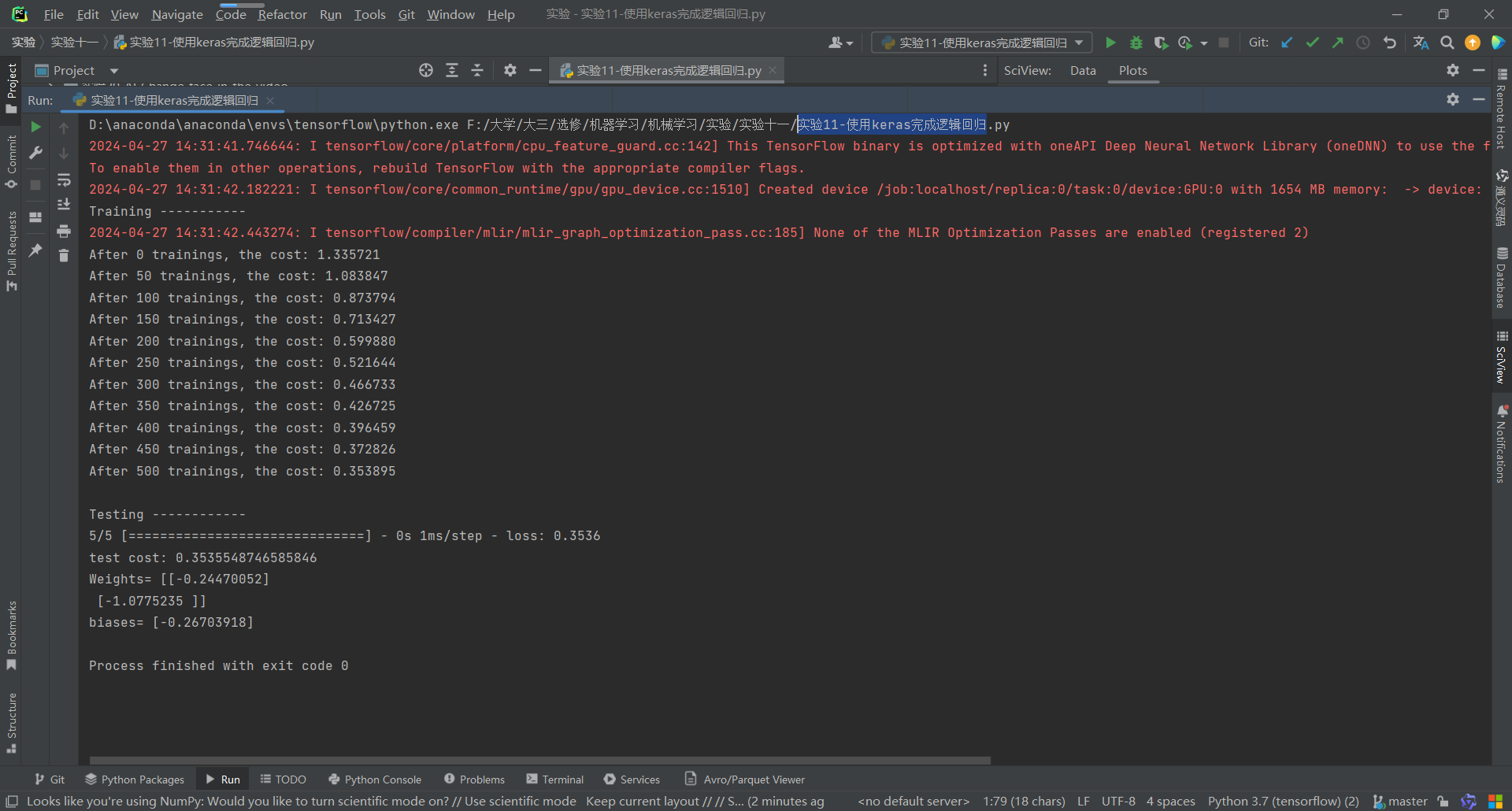
运行结果:
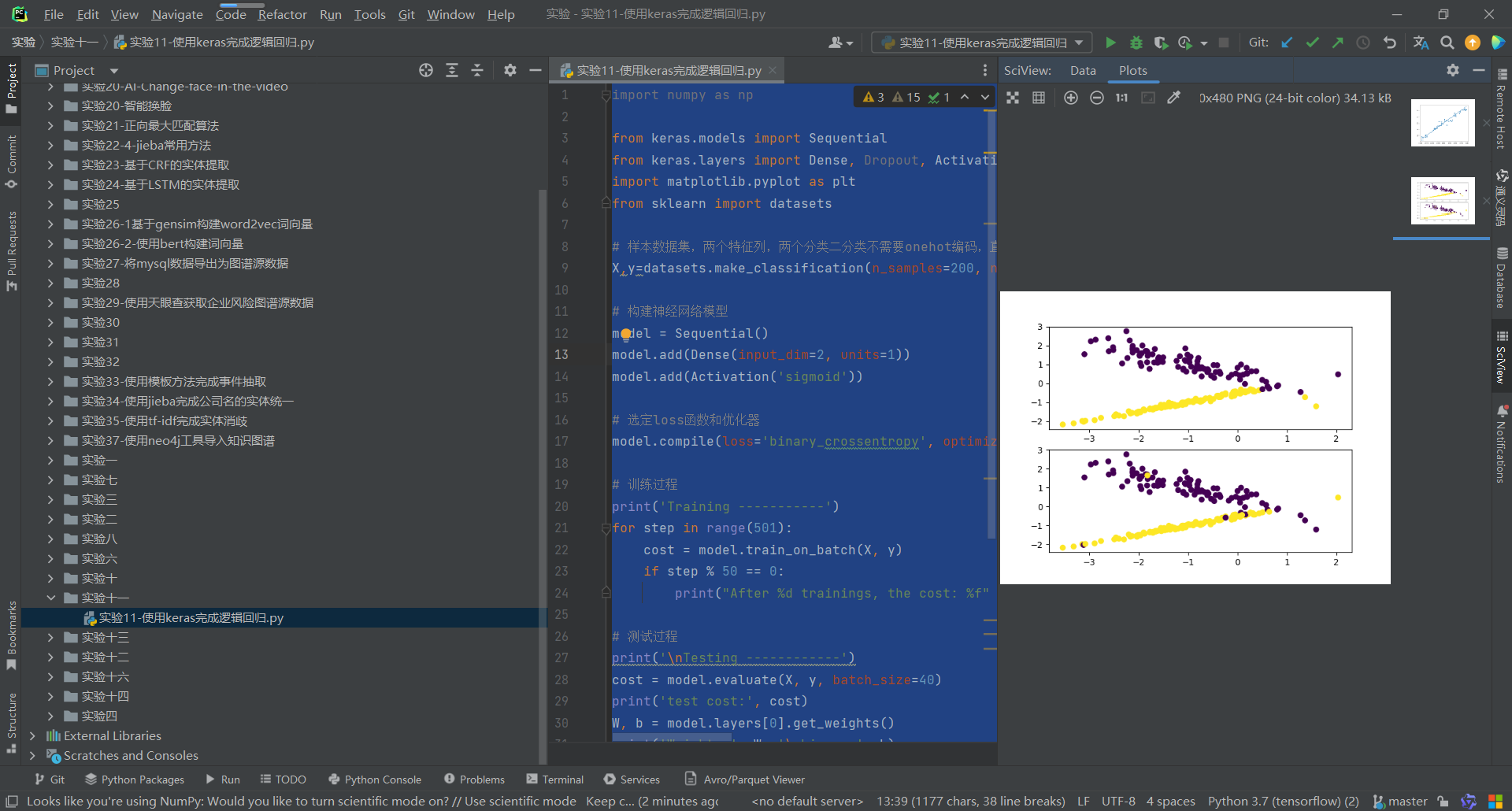
代码:
import numpy as np from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Activation, Flatten import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets # 样本数据集,两个特征列,两个分类二分类不需要onehot编码,直接将类别转换为0和1,分别代表正样本的概率。 X,y=datasets.make_classification(n_samples=200, n_features=2, n_informative=2, n_redundant=0,n_repeated=0, n_classes=2, n_clusters_per_class=1) # 构建神经网络模型 model = Sequential() model.add(Dense(input_dim=2, units=1)) model.add(Activation('sigmoid')) # 选定loss函数和优化器 model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='sgd') # 训练过程 print('Training -----------') for step in range(501): cost = model.train_on_batch(X, y) if step % 50 == 0: print("After %d trainings, the cost: %f" % (step, cost)) # 测试过程 print('\nTesting ------------') cost = model.evaluate(X, y, batch_size=40) print('test cost:', cost) W, b = model.layers[0].get_weights() print('Weights=', W, '\nbiases=', b) # 将训练结果绘出 Y_pred = model.predict(X) Y_pred = (Y_pred*2).astype('int') # 将概率转化为类标号,概率在0-0.5时,转为0,概率在0.5-1时转为1 # 绘制散点图 参数:x横轴 y纵轴 plt.subplot(2,1,1).scatter(X[:,0], X[:,1], c=Y_pred[:,0]) plt.subplot(2,1,2).scatter(X[:,0], X[:,1], c=y) plt.show()



