1. Two Sum
Given an array of integers, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to a specific target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
Example:
Given nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9, Because nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9, return [0, 1].
IDE:
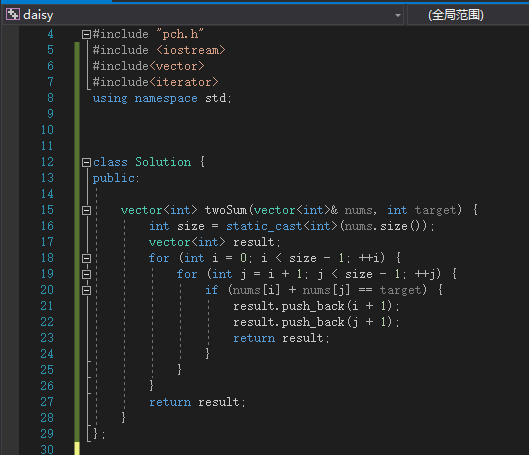
// daisy.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将在此处开始并结束。
//
#include "pch.h"
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<iterator>
using namespace std;
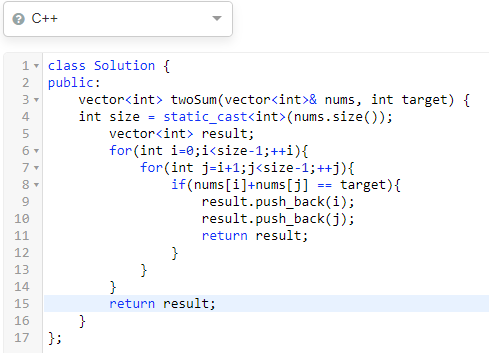
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int size = static_cast<int>(nums.size());
vector<int> result;
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; ++i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < size - 1; ++j) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
result.push_back(i + 1);
result.push_back(j + 1);
return result;
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
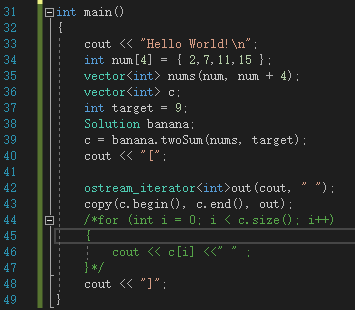
int main()
{
cout << "Hello World!\n";
int num[4] = { 2,7,11,15 };
vector<int> nums(num, num + 4);
vector<int> c;
int target = 9;
Solution banana;
c = banana.twoSum(nums, target);
cout << "[";
ostream_iterator<int>out(cout, " ");
copy(c.begin(), c.end(), out);
/*for (int i = 0; i < c.size(); i++)
{
cout << c[i] <<" " ;
}*/
cout << "]";
}