框架设计之魂——反射
反射是框架设计的灵魂
一、什么是反射
JAVA反射机制是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法和属性;这种动态获取的信息以及动态调用对象的方法的功能称为java语言的反射机制。
要想解剖一个类,必须先要获取到该类的字节码文件对象。而解剖使用的就是Class类中的方法.所以先要获取到每一个字节码文件对应的Class类型的对象.
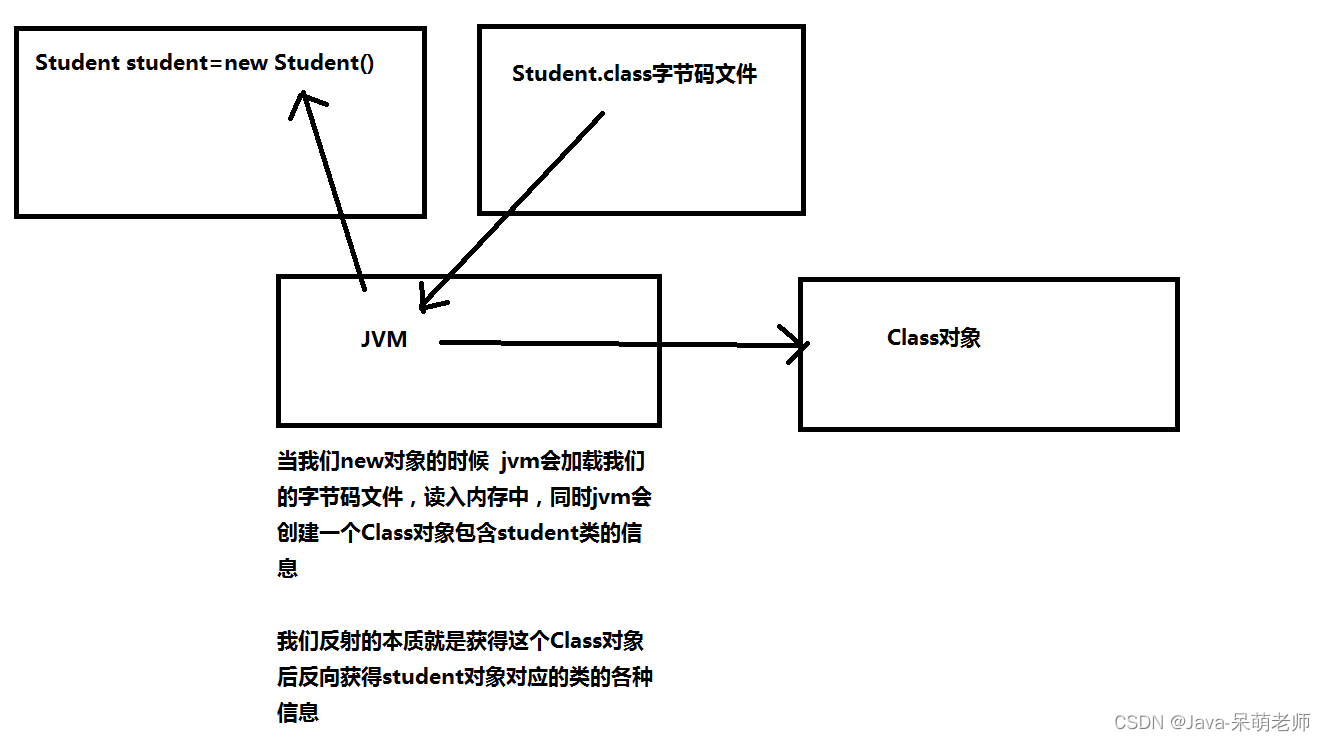
二、反射的原理
反射就是把java类中的各种成分映射成一个个的Java对象
例如:一个类有:成员变量、方法、构造方法、包等等信息,利用反射技术可以对一个类进行解剖,把个个组成部分映射成一个个对象。
其实:一个类中这些成员方法、构造方法、在加入类中都有一个类来描述
三、反射机制主要提供以下功能:
①在运行时判断任意一个对象所属的类;
②在运行时构造任意一个类的对象;
③在运行时判断任意一个类所具有的成员变量和方法;
④在运行时调用任意一个对象的方法;
⑤生成动态代理。
四、Class类
1.获取Class对象的三种方式
1、Class clazz1 = Class.forName("全限定类名"); //通过Class类中的静态方法forName,直接获取到一个类的字节码文件对象,此时该类还是源文件阶段,并没有变为字节码文件。
2、Class clazz2 = Person.class; //当类被加载成.class文件时,此时Person类变成了.class,在获取该字节码文件对象,也就是获取自己, 该类处于字节码阶段。
3、Class clazz3 = p.getClass(); //通过类的实例获取该类的字节码文件对象,该类处于创建对象阶段
通过类名获取Class对象,Class<T> c = Class.forName("类的完全路径");
通过Class对象获取具体的类对象:Object o = (Object) c.newInstance();
2、获取类中的构造方法:
3、获取类中的属性:
4、获取类中的方法:
五、反射的使用
注意:在运行期间,一个类,只有一个Class对象产生。
1.通过反射获取构造方法并使用
2 .通过反射获取不同的构造方法。
4、通过反射获取方法











【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)