【源码笔记】浅析HashMap的构造方法及put方法(JDK1.7)
引言
数据结构中,Hash的核心是使用一个hash函数将值映射到一个地址上,在后续查找的时候再通过这个hash函数计算得到这个地址。所以理想情况下Hash查找的时间复杂度是O(1)。
但是hash映射有可能会有冲突,两个不同的值,通过hash函数算出来的地址相同。比如,hash函数是:x%5,则5和10通过这个函数计算得到的地址都是0。这种情况就被称为hash冲突。
常见的Hash冲突解决办法有开放地址法、再哈希法、链地址法。
Hash函数+Hash冲突解决方法 就构成了一套hash算法
JDK1.7的HashMap的Hash函数是一个位运算计算公式:h & (length-1)。
- Java位运算符:Java移位运算符、复合位赋值运算符及位逻辑运算符
- 位运算比取余运算更高效
JDK1.7的HashMap的Hash冲突解决办法是:链地址法。
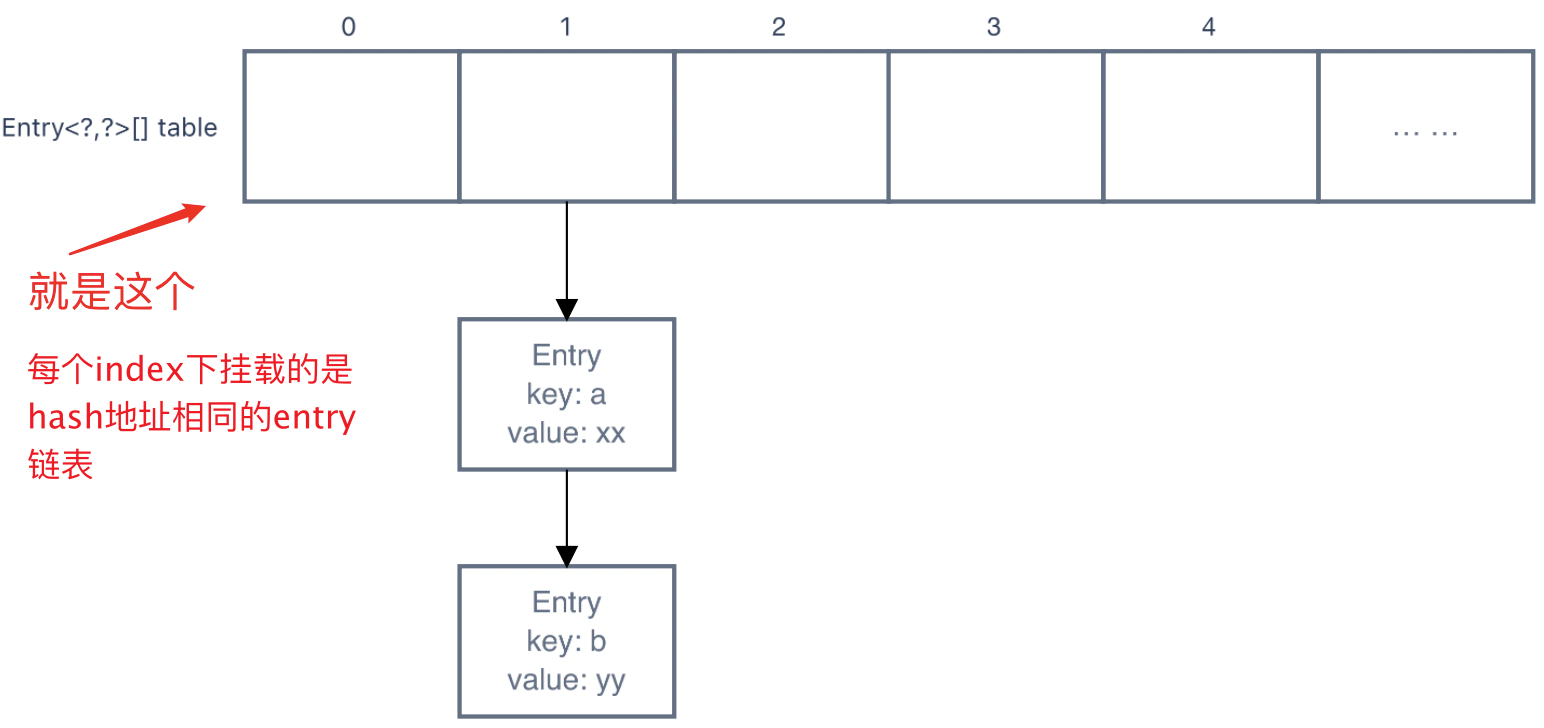
Ps.链地址法就是将所有hash地址相同的entry都挂在地址下,形如:
所以可以看出,查找hash地址相同的节点需要一个个遍历,时间复杂度为n,效率很低。 所以在1.8中该用了红黑树,红黑树是一个插入、查找时间复杂度都约为logn的数据结构,很大程度上提升了查找的性能。
代码讲解
属性
Entry<?,?>[] table
-
int size:map中键值对的数量 -
int threshold:table进行扩容的一个阈值,定义map中有多少元素时,map快满了。map size大于这个阈值,则有可能会对table进行扩容 -
float loadFactor:计算threshold的一个因子(threshold = table.length * loadFactor),默认值为0.75 -
int modCount:map中节点数的变更次数,一种类似乐观锁的机制。每次会影响map中的size的操作,都会使
modCount++。然后遍历map时,会先拿到此时的modCount,然后在遍历每个节点的时候去对比map的modCount和之前拿到的是否一致,如果不一致则说明有线程在你遍历的时候修改了map,所以就会抛出
ConcurrentModificationException。 -
int hashSeed:计算hash的一个参数key的hashcode会和hash seed做与运算,然后结果再进行一系列位运算,最终得到hash值。
然后再把hash值放进hash函数进行计算,得到hash地址
HashMap的空参构造方法
public HashMap() { // DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY -> 1 << 4,即为16 // DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR -> 0.75 this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); }
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { // initial capcity 不能小于0 if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity); // initial capacity 最大为:1 << 30,即2的30次方 if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; // 校验loadFactor if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); this.loadFactor = loadFactor; // 此时会让threshhold暂存initial capacity // 在第一次put时,会扩充table,扩充的值为:>=threshold的最小2次幂数,threshold值会变为 table.length*loadFactor // 所以虽然最初threshold是存的table的init capacity,但是在第一次put时就会让threshold回归其本来的作用(设置一个扩张table的阈值) threshold = initialCapacity; // 空的方法 init(); }
HashMap的put方法
put
public V put(K key, V value) { // 如果table为空,则扩充table if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) { inflateTable(threshold); } // 放null值 if (key == null) return putForNullKey(value); // 根据key计算得到hash值 int hash = hash(key); // 哈希函数:根据hash值计算得到在table中的下标(使用位运算) int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); // 得到下标所在的链表的表头 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)table[i]; // 遍历链表 for(; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; // 如果链表中的当前项和要插入的值相同,则使用新的值替换旧的值 // hash值同 && key同(引用的是同一个对象 或 equals) if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } // -------到此处说明table中原本没有节点的key和当前节点的key一样------- // 将map节点的修改次数++ modCount++; // 使用头插法添加一个节点 addEntry(hash, key, value, i); return null; }
inflateTable
private void inflateTable(int toSize) { // Find a power of 2 >= toSize // 找到最小的,大于2次幂的数。toSize为17,则capacity为32 int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize); // 为threshhold、table赋值 threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); table = new Entry<?,?>[capacity]; // 修改hashSeed initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity); }
initHashSeedAsNeeded
final boolean initHashSeedAsNeeded(int capacity) { // hashSeed初始为0,所以初始currentAltHashing为false boolean currentAltHashing = hashSeed != 0; // vm是否启动? // 如无特殊设置,Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD值为Integer.MAX_VALUE。一般capacity不会这么大 // 所以useAltHashing一般为false boolean useAltHashing = sun.misc.VM.isBooted() && (capacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD); // 如上面分析的,switching一般都为false,不会修改hashSeed boolean switching = currentAltHashing ^ useAltHashing; if (switching) { hashSeed = useAltHashing ? sun.misc.Hashing.randomHashSeed(this) : 0; } return switching; }
putForNullKey
private V putForNullKey(V value) { // 把null key放到table的第一个item下 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)table[0]; for(; e != null; e = e.next) { if (e.key == null) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } // -------到此处说明table中原本没有null key------- modCount++; // 把null key的hash值直接定义为0 // 所以它是放在table的第一个item下 addEntry(0, null, value, 0); return null; }
hash
final int hash(Object k) { int h = hashSeed; if (0 != h && k instanceof String) { return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k); } // key的hashcode会和hash seed做与运算 h ^= k.hashCode(); // This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by // constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded // number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor). h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12); return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4); }
indexFor
static int indexFor(int h, int length) { // hash()计算得到的hash值,和table的length做并运算 // 若table length为16,则: // // Case1. // h = 20 0001 0100 // length-1 = 15 0000 1111 // --------- // index = 8 0000 0100 // // Case2. // h = 78 0100 1110 // length-1 = 15 0000 1111 // --------- // index = 14 0000 1110 // // 这就是为什么table的capacity必须是2次幂的原因,因为hash函数需要用capacity-1的值做位运算 return h & (length-1); }
addEntry
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { // 如果当前table的length超过阈值,并且table[bucketIndex]上已有节点,则扩充table if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) { // 生成一个capacity是原来两倍的table,然后将原来的table拷贝过去(重新计算hash) resize(2 * table.length); // 重新计算hash(resize中可能会改变hashSeed的值) hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0; // 重新计算在hash在table中index bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length); } // 创建节点(使用头插法) createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex); }
resize
void resize(int newCapacity) { Entry<?,?>[] oldTable = table; int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; // 原来的table已经达到了最大值(2的30次方),不扩容了 if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return; } // 生成一个capacity为原来2倍的table Entry<?,?>[] newTable = new Entry<?,?>[newCapacity]; // 把原来table中的entry挪到新table中 transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity)); // 替换table table = newTable; // 更新threshhold threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); }
transfer
void transfer(Entry<?,?>[] newTable, boolean rehash) { Entry<?,?>[] src = table; int newCapacity = newTable.length; // 遍历原来table的每个节点 for (int j = 0; j < src.length; j++) { Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)src[j]; // 遍历table下链表的每个entry while(null != e) { Entry<K,V> next = e.next; // 是否重新计算hash值(如果hashSeed改变了,就需要重新计算hash值) if (rehash) { e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key); } // 计算在新table中的的下标 // 根据indexFor()中计算下标的公式"h & (length-1)"可知 // 新下标要么和原来一样,要么是原来的下标+原来table的size // 如: // Case1. // 原来table中的下标: // h = 20 0001 0100 // length-1 = 15 0000 1111 // --------- // index = 4 0000 0100 // // 新table中的下标. // h = 20 0001 0100 // length-1 = 31 0001 1111 // --------- // index = 20 0001 0100 // // Case2. // 原来table中的下标: // h = 78 0100 1110 // length-1 = 15 0000 1111 // --------- // index = 14 0000 1110 // // 新table中的下标: // h = 78 0100 1110 // length-1 = 31 0001 1111 // --------- // index = 14 0000 1110 // int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); e.next = (Entry<K,V>)newTable[i]; newTable[i] = e; e = next; } } }
复制的过程:

HashMap并发下,死循环的问题:HashMap头插法循环问题
createEntry
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { // 头插法,过程和resize类似(差别就在于,没有循环e) @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)table[bucketIndex]; table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e); size++; }
总结
JDK1.7中HashMap的hash算法:
- Hash函数:位运算计算公式:
h & (length-1) - Hash冲突解决办法:链地址法(插入方法:头插法)
JDK1.7中HashMap中的数据结构和算法还是很标准的基础数据结构,包括链表的头插法,也是链表的基础插入方法。将table的构建过程,和链表的插入方法模拟过一遍后,就能够理解这个对象的底层计算逻辑了。
HashMap为了增加运算的速度,用了很多位运算,主要用于hash值的计算,和hash地址的计算。
HashMap性能上的痛点在于:
- 链表的查找是简单的顺序查找,时间复杂度是n。这点在JDK1.8中改为了查找更快的树形数据结构——红黑树
- 扩容很耗费时间(需要遍历一遍将原来table中的所有entry,然后挪到另一个table中),所以开发时定义合适的初始大小能够提升性能



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~