Java语言的词法分析器的Java实现
一.实验目的
1、 学会针对DFA转换图实现相应的高级语言源程序。
2、 深刻领会状态转换图的含义,逐步理解有限自动机。
3、 掌握手工生成词法分析器的方法,了解词法分析器的内部工作原理。
二.实验内容
Java语言的编译程序的词法分析部分实现。
从左到右扫描每行该语言源程序的符号,拼成单词,换成统一的内部表示送给语法分析程序。
具体的要求如下:
(1) 区分保留字、运算符、常数、界符和标识符
(2) 常数包含整型(正/负)、浮点型(正/负)、字符串和字符。
(3) 空白符是空格、回车符、制表符。
(4) 代码是自由格式。
(5) 注释包含单行注释和多行注释,并且不允许嵌套
程序的记号定义:
表2-1 Java语言记号
| 保留字 | 运算符 | 常数 | 界符 | 标识符 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| abstract | assert | + | 整数 | 字符串 | , | 以字母开头,由字母数字和下划线组成 |
| case | catch | - | 浮点数 | 字符 | ( | |
| continue | default | * | { | |||
| enum | extends | = | [ | |||
| for | goto | < | ; | |||
| instanceof | int | > | ) | |||
| new | package | += | } | |||
| return | strictfp | -= | ] | |||
| switch | synchronized | *= | ||||
| transient | try | == | ||||
| boolean | break | >= | ||||
| char | class | <= | ||||
| do | double | ? | ||||
| final | finally | . | ||||
| if | implements | : | ||||
| interface | long | != | ||||
| private | protected | |||||
| short | static | |||||
| this | throw | |||||
| void | volatile | |||||
| byte | native | |||||
| constant | public | |||||
| else | super | |||||
| float | throws |
三.实验要求
编译器实现的功能:
(1) 按语法规则将字符识别、分类,并转换成二元式形式打印
(2) 删除注释行(单行、多行)
(3) 删除空白符(空格、回车符、制表符)
(4) 列表打印源程序,按照源程序的行打印,在每行的前面加上行号,并且打印出每行包含的记号的二元形式
(5) 能识别词法错误并定位
Java词法分析进行具体的要求:
- 词法分析器每分析出一个完整的词法成分,就将该词法成分的行号和二元式添加到结果字符串info中:。
- 在所有代码分析完毕后,将info中的内容写入result.txt中;
- 若分析的过程中出现错误,则将错误信息和错误定位写入result.txt。
- 单词符号分种如下:
-
运算符:运算符分为由单个字符和两个字符组成的运算符。所以对于有可能组成两个运算符的字符,在分析完第一个字符后还要继续分析第二个字符才能分析出完整的运算符。
-
常量:常量又分为数字、字符串、字符。
- 数字:分为整数,浮点数,且都有正/负两种情况。其中,“正”用数字开头的“+”标识(可省略),“负”用数字开头的“-”标识;
- 字符串:字符串中允许有转义字符;
- 字符:合法的字符有:1.单个字符;2.“\”加“b”、“n”、“r”、“t”、“\”;3.“\”加1到3位数字。
-
标识符
-
保留字:标示符和保留字的词法构成相同。识别出字符串后,再根据保留字数组判断该字符串是否为保留字;
-
界符
- 词法分析器的具体功能实现是用函数analyze()。每次都根据当前的状态和当前的字符来判断下一步操作,下一步操作有:
- 转换系统状态;
- 读取下一个字符;
- 将当前字符存入字符串中,待该完成词法成分都在字符串中时再生成对应的二元式,并清空字符串。
根据具体情况,下一步操作可同时执行以上三个动作或只执行其中一个或两个。
DFA:
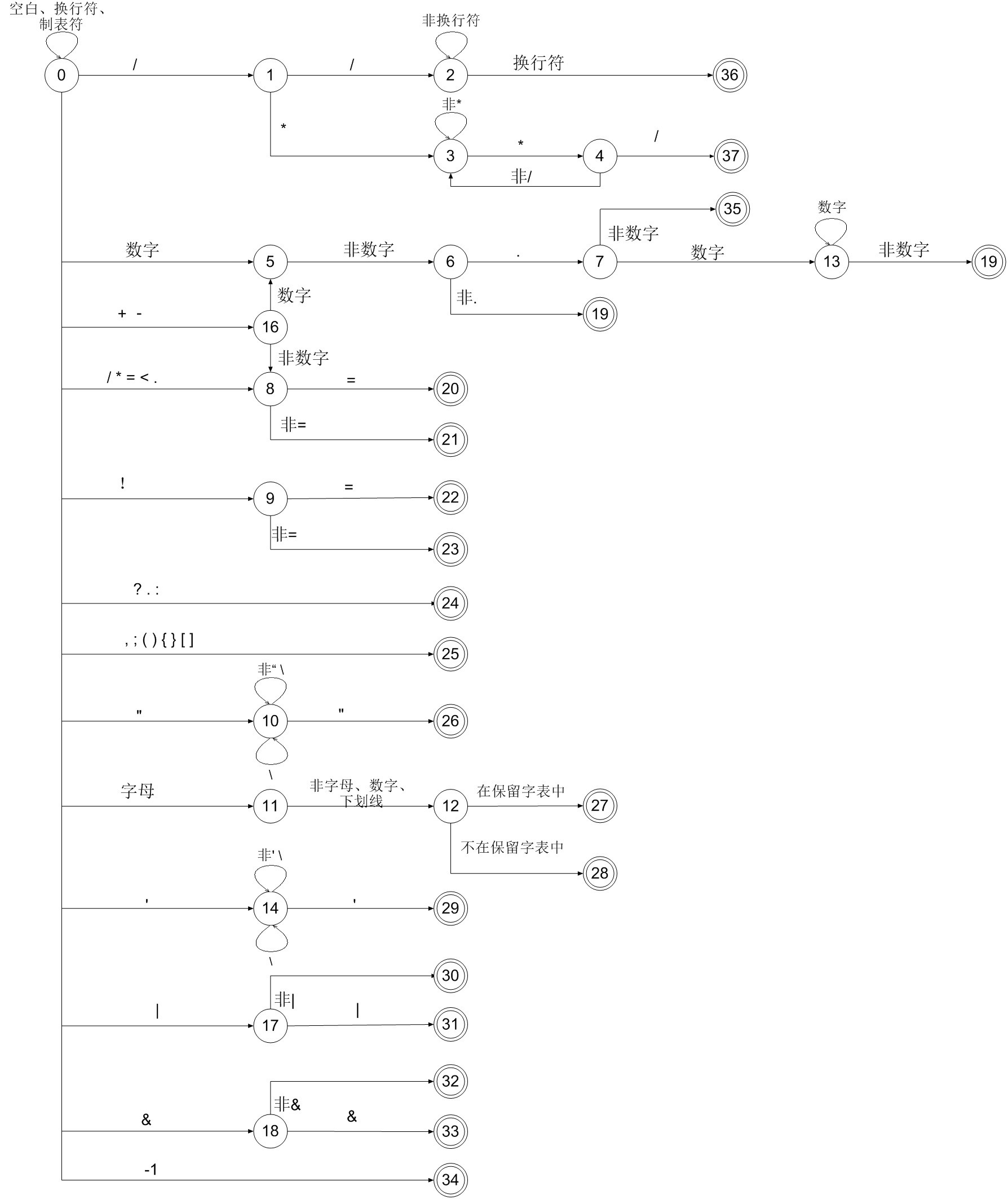
四.代码
package newp2;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Lexical {
private static final String reserveWords[] = { "abstract", "boolean", "break", "byte", "case", "catch", "char",
"class", "continue", "default", "do", "double", "else", "extends", "final", "finally", "float", "for", "if",
"implements", "import", "instanceof", "int", "interface", "long", "native", "new", "package", "private",
"protected", "public", "return", "short", "static", "super", "switch", "synchronized", "this", "throw",
"throws", "transient", "try", "void", "volatile", "while", "strictfp", "enum", "goto", "const", "assert" }; // 50
private FileReader fd;
private int state;
private char ch;
private String info; // 结果串
private String temp; // 临时存储
int lineNum;
public Lexical() {
info = "";
temp = "";
lineNum = 1;
getChar();
analyze();
write(info);
}
private void analyze() {
if (ch == (char) -1 && temp.equals(""))
return; // 已经读取到最后一个字符,且没有待处理字符
if (ch == '\n')
lineNum++;
switch (state) {
case 0:
temp = "";
if (ch == ' ' || ch == '\r' || ch == '\t' || ch == '\n') {
toNextCharAndChangeState(0);
} else if (ch == '/') {
toNextCharAndStoreTempAndChangeState(1);
} else if (isDigital(ch)) {
toNextCharAndStoreTempAndChangeState(5);
} else if (isOperator1(ch)) {
toNextCharAndStoreTempAndChangeState(8);
} else if (ch == '!') {
toNextCharAndStoreTempAndChangeState(9);
} else if (isOperator2(ch)) {
writeInfo((ch + ""), "运算符");
getChar();
} else if (isBoundary(ch)) {
writeInfo((ch + ""), "界符");
getChar();
} else if (ch == '"') {
toNextCharAndStoreTempAndChangeState(10);
} else if (isLetter(ch)) {
toNextCharAndStoreTempAndChangeState(11);
} else if (ch == '\'') {
toNextCharAndStoreTempAndChangeState(14);
} else if (ch == '-' || ch == '+') {
toNextCharAndStoreTempAndChangeState(16);
} else if (ch == '|') {
toNextCharAndStoreTempAndChangeState(17);
} else if (ch == '&') {
toNextCharAndStoreTempAndChangeState(18);
} else if (ch == (char) -1) {
// 程序应该结束
} else { // 非法字符
error(1);
return;
}
break;
case 1:
if (ch == '/') {
toNextCharAndChangeState(2);
} else if (ch == '*') {
toNextCharAndChangeState(3);
} else {
state = 8;
}
break;
case 2: // 处理注释
if (ch == '\n') {
state = 0;
getChar();
} else {
getChar();
}
break;
case 3: // 处理注释
if (ch == '*') {
toNextCharAndChangeState(4);
} else {
getChar();
}
break;
case 4: // 处理注释
if (ch == '/') {
toNextCharAndChangeState(0);
} else {
toNextCharAndChangeState(3);
}
break;
case 5:
if (isDigital(ch)) {
temp += ch;
getChar();
} else {
state = 6;
}
break;
case 6:
if (ch == '.') {
toNextCharAndStoreTempAndChangeState(7);
} else {
writeInfo(temp, "常数");
}
break;
case 7:
if (isDigital(ch)) {
toNextCharAndStoreTempAndChangeState(13);
} else {
error(4);
return;
}
break;
case 8:
if (ch == '=') {
temp += ch;
writeInfo(temp, "运算符");
getChar();
} else {
writeInfo(temp, "运算符");
}
break;
case 9:
if (ch == '=') {
temp += ch;
writeInfo(temp, "运算符");
getChar();
} else {
error(2);
return;
}
break;
case 10:
if (ch == '"') {
temp += ch;
writeInfo(temp, "常量");
getChar();
} else if (ch == '\\') {
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
temp += ch;
getChar();
}
state = 10;
} else {
toNextCharAndStoreTempAndChangeState(10);
}
break;
case 11:
if (isDigital(ch) || isLetter(ch) || ch == '_') {
toNextCharAndStoreTempAndChangeState(11);
} else {
state = 12;
}
break;
case 12:
if (isReserve(temp)) {
writeInfo(temp, "保留字");
getChar();
} else {
writeInfo(temp, "标识符");
getChar();
}
break;
case 13:
if (isDigital(ch)) {
toNextCharAndStoreTempAndChangeState(13);
} else {
writeInfo(temp, "常数");
}
break;
case 14:
if (ch == '\'') {
temp += ch;
if (isLegalChar(temp)) {
writeInfo(temp, "常量");
} else {
error(9);
return;
}
getChar();
} else if (ch == '\\') {
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
temp += ch;
getChar();
}
state = 14;
} else {
toNextCharAndStoreTempAndChangeState(14);
}
break;
case 16:
if (isDigital(ch)) {
toNextCharAndStoreTempAndChangeState(5);
} else {
state = 8;
}
break;
case 17:
if (ch == '|') {
temp += ch;
writeInfo(temp, "运算符");
getChar();
} else {
writeInfo(temp, "运算符");
}
break;
case 18:
if (ch == '&') {
temp += ch;
writeInfo(temp, "运算符");
getChar();
} else {
writeInfo(temp, "运算符");
}
break;
default:
error(3);
return;
}
analyze();
}
private boolean isLegalChar(String temp) {
char[] ch = temp.toCharArray();
int length = ch.length;
boolean isLegalChar = false;
/*
* Char a = '';// error char b = ' ';// length = 3; char c = '\n';//length = 4;
* b n r t " ' \ char d = '\122'; // length <= 6;
*/
if (length == 2) { // ''
isLegalChar = false;
} else if (length == 3) {
isLegalChar = true;
} else if (length == 4) {
if ((ch[1] == '\\') && (ch[2] == 'b' || ch[2] == 'n' || ch[2] == 'r' || ch[2] == 't' || ch[2] == '\"'
|| ch[2] == '\'' || ch[2] == '\\' || isDigital(ch[2]))) {
isLegalChar = true;
}
} else if (length <= 6) {
if (ch[1] == '\\') {
for (int i = 2; i < (length - 1); i++) {
if (!isDigital(ch[i])) {
isLegalChar = false;
break;
}
isLegalChar = true;
}
} else {
System.out.println('*');
isLegalChar = false;
}
} else {
isLegalChar = false;
}
return isLegalChar;
}
private void toNextCharAndChangeState(int state) {
this.state = state;
getChar();
}
private void toNextCharAndStoreTempAndChangeState(int state) {
temp += ch;
this.state = state;
getChar();
}
private boolean isReserve(String temp2) {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
if (temp.equals(reserveWords[i])) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private void writeInfo(String value, String type) {
info += lineNum + ": < " + type + " , " + value + " >\r\n";
state = 0;
}
private boolean isLetter(char ch) {
if ((ch >= 65 && ch <= 90) || (ch >= 97 && ch <= 122))
return true;
else
return false;
}
private boolean isBoundary(char ch) {
if (ch == ',' || ch == ';' || ch == '(' || ch == ')' || ch == '[' || ch == ']' || ch == '{' || ch == '}')
return true;
return false;
}
private boolean isOperator1(char ch) { // / * = < >
if (ch == '/' || ch == '*' || ch == '=' || ch == '<' || ch == '>')
return true;
return false;
}
private boolean isOperator2(char ch) { // ? . :
if (ch == '?' || ch == '.' || ch == ':')
return true;
return false;
}
private boolean isDigital(char ch) {
if (ch >= 48 && ch <= 57)
return true;
else
return false;
}
private void error(int i) {
info = "词法分析出错\r\n错误定位:" + i;
}
private void getChar() {
try {
if (fd == null) {
fd = new FileReader("D:/MyEclipse 10 Workspaces/Lexical analyzer/io file/test.txt");
}
ch = (char) fd.read();
if (ch == -1) { // 当从一个文件中读取数据时,在数据最后会返回一个int型-1来表示结束
fd.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
private void write(String info) {
try {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("D:/MyEclipse 10 Workspaces/Lexical analyzer/io file/result.txt");
fw.write(info);
fw.flush(); // 刷新数据,将数据写入文件中
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
new Lexical();
}
}

