【测试in 与exists 查询效率】
测试1w条数据和100w条数据下 in 和 exists的区别:
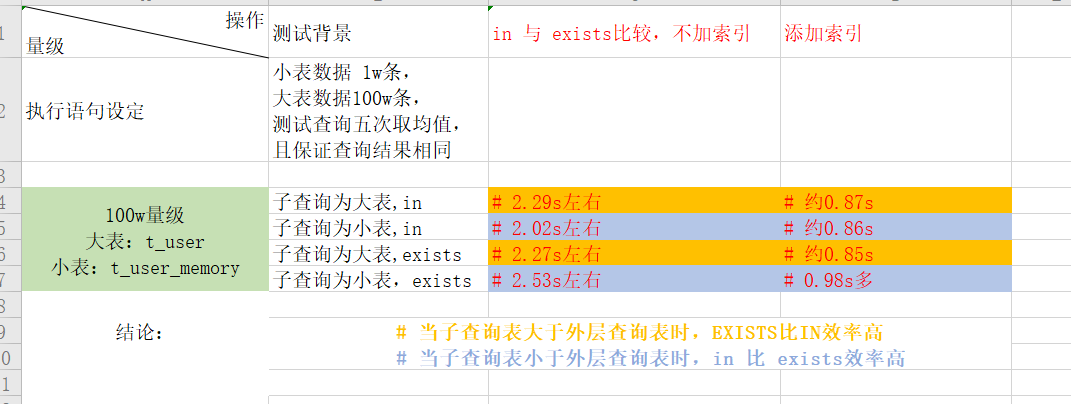
#t_user 为100w条,t_user_memory 为1w条 #1、in的原理: #在select * from A where id in(select id from B); 中,in()中的子查询只执行一次,它查询出B表中的所有ID值并缓存起来;之后,在内存中检查A表的id是否与B表中的id值相等,如果相等则则将A表的记录加入到结果集中,直到遍历完A表中的所有记录。 #所以B表的条数多少对查询影响很大 #2、exists的应用原理 #在select * from A where exists (select from B where A.id=B.id);之中 #exists()会执行A.length次,它并不缓存exists()结果集,因为exists()结果集的内容并不重要,重要的是其内查询语句的结果集空或者非空,空则返回false,非空则返回true,true的时候才会去查询,这样从执行次数上来说是少于in #3、 二者相比,在相同表下虽然exists执行次数普遍小于in,但是in 是在内存中做遍历比较的,exists则是在数据库中查询,这两个相比肯定是内存快一些。 #4、测试: t_user 比 t_user_memory表大,预测应当用in效率更高 #t_user数据 大于 t_user_memory数据 # 加索引 # 0.98s多 select * from t_user where exists(select c_name from t_user_memory where c_name=t_user.c_name); # 0.86s左右 select * from t_user where c_name in(select c_name from t_user_memory); # 当子查询小于外层查询时, IN EXISTS 效率高 # 约0.85s select * from t_user_memory where exists(select c_name from t_user where c_name=t_user_memory.c_name); # 约0.87s select * from t_user_memory where c_name in(select c_name from t_user); # 当子查询大于外层查询时,exists 比 in 效率高 # 不加索引 #五次取均值 # 2.53s左右 select * from t_user where exists(select c_user_id from t_user_memory where c_user_id=t_user.c_user_id); # 2.02s左右 select * from t_user where c_user_id in(select c_user_id from t_user_memory); # 当子查询小于外层查询时,in 比 exists效率高 # 2.27s左右 select * from t_user_memory where exists(select c_user_id from t_user where c_user_id=t_user_memory.c_user_id); # 2.29s左右 select * from t_user_memory where c_user_id in(select c_user_id from t_user); # 当子查询大于外层查询时,EXISTS比IN效率高


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号