浅析ThreadLocal源码
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
// We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at
// least as common to use set() to create new entries as
// it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast
// path would fail more often than not.
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); // 位运算计算 下标位置
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) { // 循环遍历数组中的每个位置,直到找到一个空闲的位置或者找到了指定键
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
// 1.找空闲位置的过程中查看这个key是不是已经存在,存在 覆盖其value 结束
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
// 2.找空闲位置的过程中遇到key已经被GC的话,替换掉这个entry 然后结束
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
// 执行到这个位置,说明:i是空位置且从最开始的下标i当前的下标i,这之间没有相同的key,也没有被GC的key
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
// i是当前插入的下标
// cleanSomeSlots 是试探性的从i位置开始扫描过期被GC的key,扫描的元素个数是log2(sz)次
// rehash的条件是试探性扫描没有扫描出来需要回收的entry且元素个数已经达到阈值
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i /*当前插入的位置*/, sz /*当前一共有多少元素*/) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
private boolean cleanSomeSlots(int i, int n) {
boolean removed = false;
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// 循环执行log2(n)次
do {
i = nextIndex(i, len);
Entry e = tab[i];
// 如果当前位置的 Entry 对象不为空且其关联的键为 null(即已过期),则执行下面的操作
if (e != null && e.get() == null) {
n = len;
removed = true;
i = expungeStaleEntry(i);
}
} while ( (n >>>= 1) != 0);
return removed;
}
private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// expunge entry at staleSlot
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = null;
size--;
// Rehash until we encounter null
Entry e;
int i;
// 使用循环从下一个槽位开始,遍历直到遇到 null 条目。这个循环主要用于重新哈希(ThreadLocalMap 使用的是 线性探测解决哈希冲突 )。
for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
// 检查ThreadLocal是否为null 如果为null需要移除
e.value = null;
tab[i] = null;
size--;
} else /* key!=null */ {
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
if (h != i) { // ThreadLocalMap 使用的是 线性探测解决哈希冲突 因此是有可能 h!=i的
tab[i] = null;
// Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until
// null because multiple entries could have been stale.
// 说明之前出现冲突 将原来i位置的搬到h位置
while (tab[h] != null/*h位置已经有元素了,说明现在任然冲突,将其放到h后面第一个空位置*/)
h = nextIndex(h, len);
tab[h] = e;
}
}
}
return i;
}
对于expungeStaleEntry,参考下图:
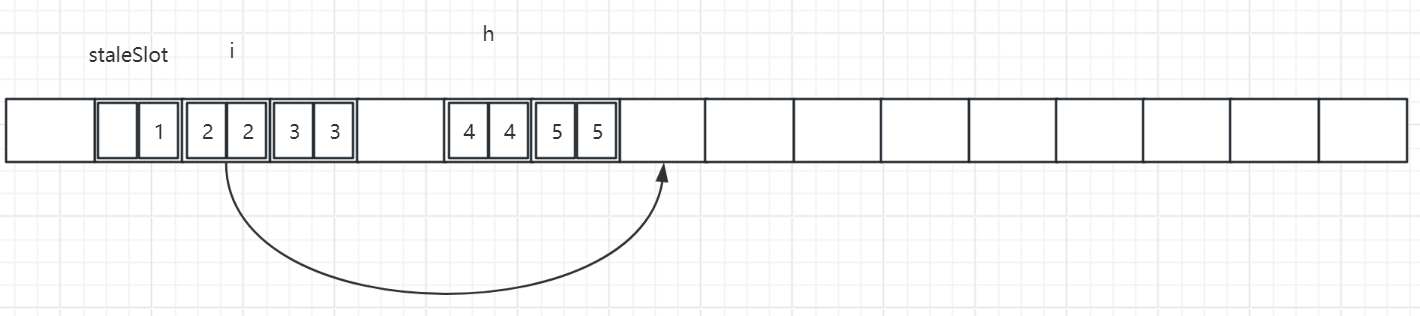
如图,staleSlot位置需要清掉,后面的元素需要重新哈希,直到遇到entry还是null的为止,也就是会遍历到staleSlot+3位置会停下来,对i位置重新哈希计算的位置h已经存在元素,从h往后遍历,遇到空位置就将i位置的entry移过去。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)