使用c++调用python(一)
c调用python的原理大概是将python当做一个c++库来调用
window
导入头文件
将python的头文件复制到项目中,头文件在python安装目录中
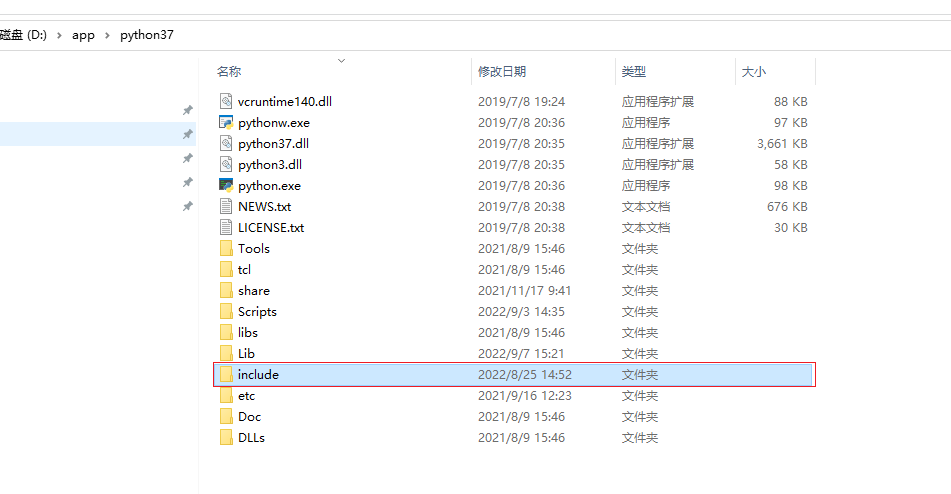
在vs项目属性中的vc++目录的包含目录添加头文件路径
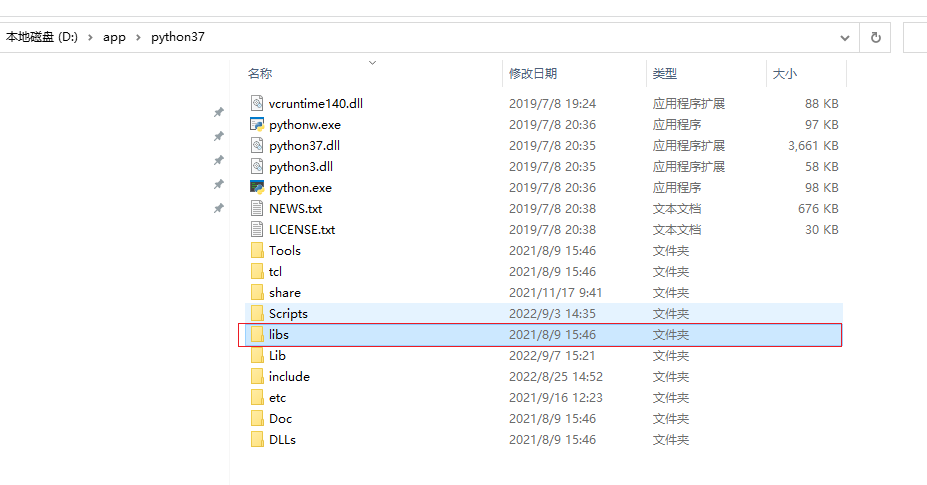
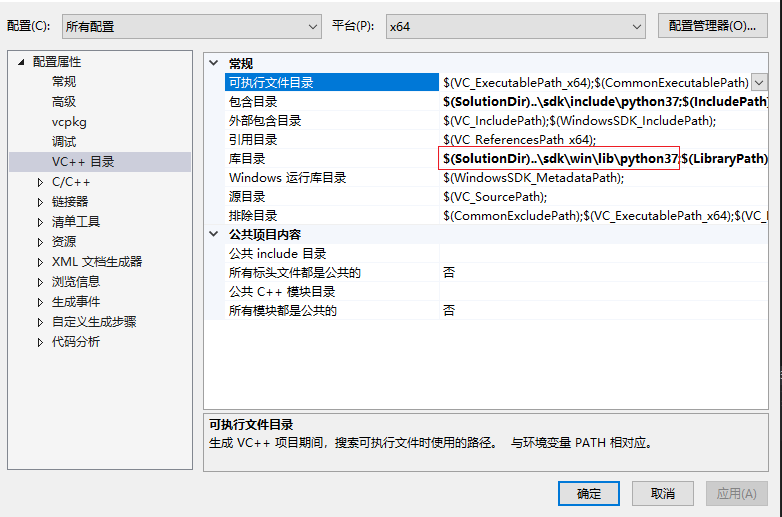
导入库文件(x64就导入64位的python,x86就导入32位的python,不能混在一起)
库文件在python安装目录的libs文件夹中
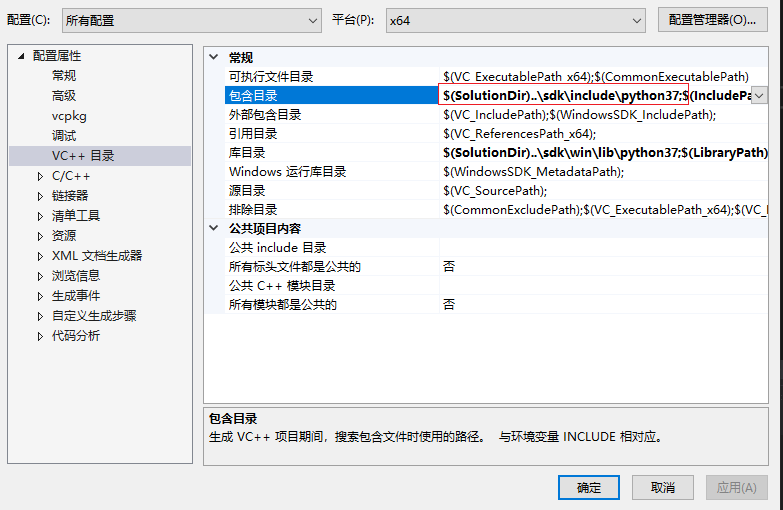
在vs项目属性中的vc++目录的库目录添加库文件所在文件路径
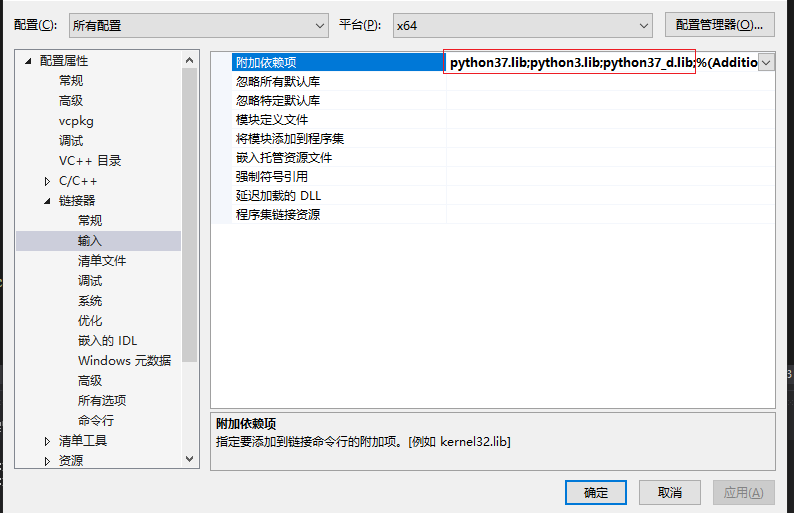
添加附加依赖项,没有python37_d.lib的把python37.lib复制一份重命名为python37_d.lib就行了
python37.lib
python3.lib
python37_d.lib
添加二进制文件
第一种方案
需要的二进制文件有 python3*.dll、python3.dll、DLLs、Lib文件夹(注意Lib中的site-packages文件的第三方python库按实际需要增减)
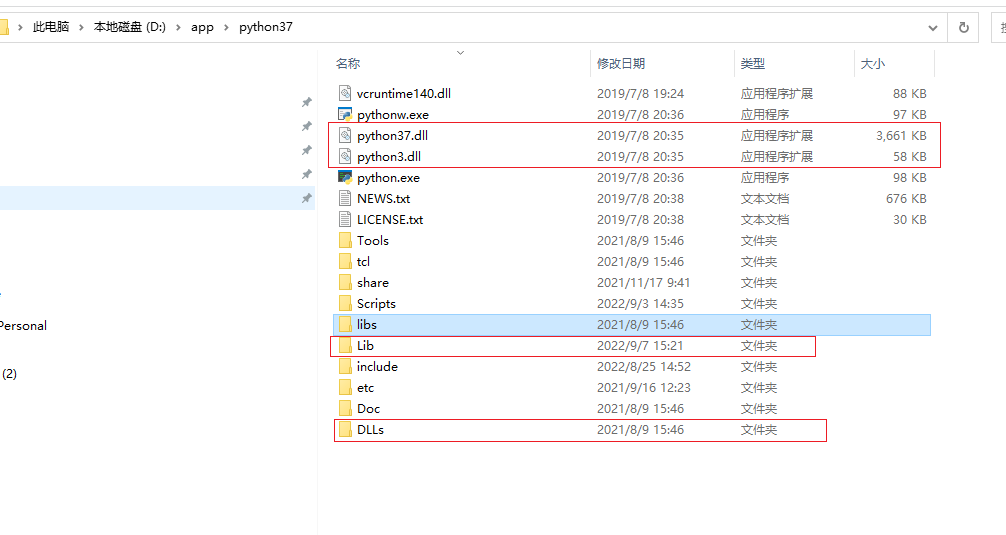
第二种方案
去python 官网下载内嵌包
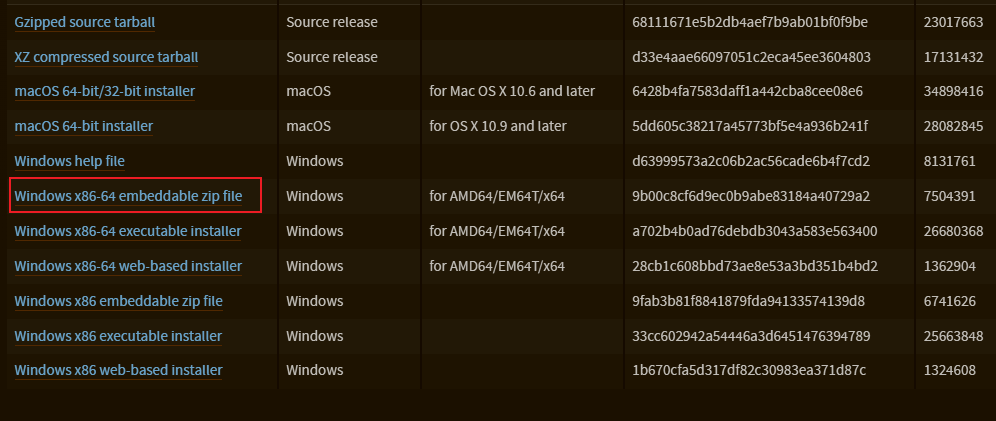
解压后,里面所有文件都需要,然后同样的site-packages按实际需要增减
使用api调用python代码
initializer.h
#pragma once
class initializer {
public:
initializer();
~initializer();
private:
static initializer initer;
};
initializer.cpp
#include "initializer.h"
#include <Python.h>
#ifdef _WIN32
#include <Windows.h>
#elif defined __APPLE__
#endif
#include "utils.h"
#include <vector>
initializer::initializer()
{
#ifdef _WIN32
#include <Windows.h>
SetDllDirectory(TEXT("python37\\"));
#elif defined __APPLE__
#endif
auto combinePaths = [](std::vector<std::string> paths,std::string sep=";") {
std::string preparedPath = "";
for (int i = 0; i < paths.size(); i++) {
preparedPath += get_executable_dir()+paths[i];
if (i != paths.size() - 1) {
preparedPath += sep;
}
}
return string2wstring(preparedPath);
};
Py_SetPythonHome(string2wstring(get_executable_dir()).c_str());
#ifdef _WIN32
Py_SetPath(combinePaths({"","\\python37.zip","\\site-packages"}).c_str());
#elif defined __APPLE__
Py_SetPath(combinePaths({"","/python37.zip","/site-packages","/lib-dynload"},":").c_str());
#endif
Py_Initialize();
PyRun_SimpleString("import sys");
PyRun_SimpleString("print(sys.path)");
}
initializer::~initializer()
{
Py_Finalize();
}
utils.h
#include <iostream>
std::string get_executable_dir();
std::string wstring2string(const std::wstring& ws);
std::wstring string2wstring(const std::string& s);
utils_win.cpp
#include "utils.h"
#include <Windows.h>
#include <comutil.h>
using namespace std;
#pragma comment(lib , "comsupp.lib")
#pragma comment(lib , "comsuppw.lib")
std::string get_executable_dir() {
std::string exeDir = "";
char szExeName[MAX_PATH] = {0,};
volatile int lastIndex = 0;
::GetModuleFileNameA(NULL, szExeName, MAX_PATH);
exeDir = szExeName;
lastIndex = exeDir.find_last_of("\\");
exeDir = exeDir.substr(0, lastIndex);
return exeDir;
}
std::string wstring2string(const wstring& ws)
{
_bstr_t t = ws.c_str();
char* pchar = (char*)t;
string result = pchar;
return result;
}
std::wstring string2wstring(const string& s)
{
_bstr_t t = s.c_str();
wchar_t* pwchar = (wchar_t*)t;
wstring result = pwchar;
return result;
}
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <Python.h>
#include "initializer.h"
using namespace std;
initializer initer;
void call_main() {
char* result;
PyObject* pModule = PyImport_ImportModule("test");
if (pModule == NULL) {
PyErr_Print();
cout << "module not found" << endl;
return;
}
PyObject* pFunc = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "main");
if (!pFunc || !PyCallable_Check(pFunc)) {
PyErr_Print();
cout << "not found function init" << endl;
return;
}
PyObject* pReturn = PyObject_CallObject(pFunc, NULL);
PyErr_Print();
}
void inputArgs(int argc, char** argv) {
if (argc > 0)
for (int i = 0; i < argc; i++)
PyRun_SimpleString((string("sys.argv.append(r'") + argv[i] + "')").c_str());
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
inputArgs(argc, argv);
call_main();
return 0;
}
编译出exe后在当前目录建立test.py
test.py
def main():
print("hello world!")
将依赖的二进制放入exe当前目录即可执行成功
Macos
导入头文件
头文件在python安装目录中include/python3.7m中(以python3.7为例)
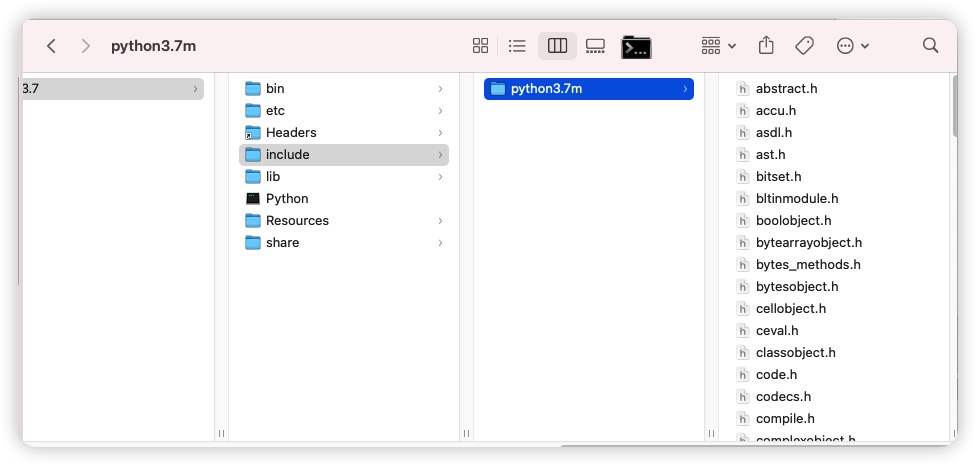
在Header Search Paths中添加头文件路径
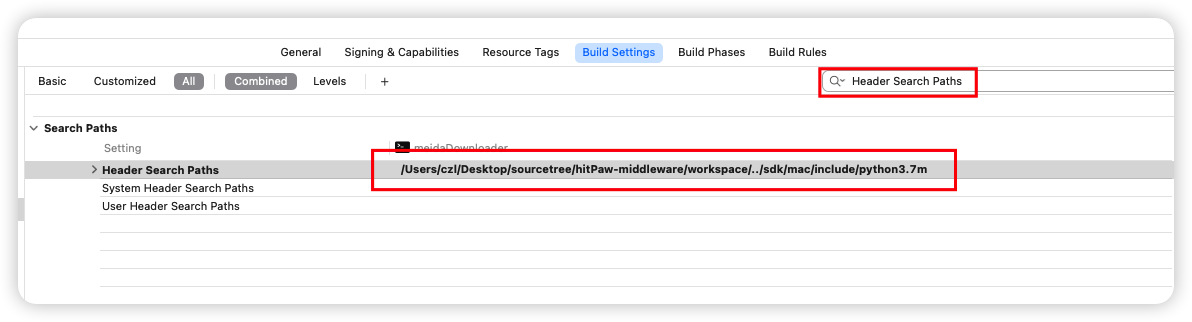
导入库文件
库文件Python
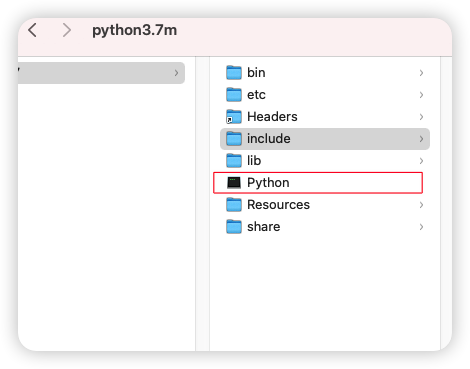
修改install_name
由于Python的install name是固定的路径,我们程序加载的时候会去这个绝对路径找Python,还好install_name_tool可以修改
有两种方式,一是修改Python的 install name,二是修改可执行文件的库加载路径
修改Python的 install name
install_name_tool -id @rpath/Python Python
修改可执行文件的库加载路径
install_name_tool -change /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.7/Python @loader_path/Python meidaDownloader
推荐使用第二种,最好不要修改Python库自带的Python文件
xcode将库文件导入进来
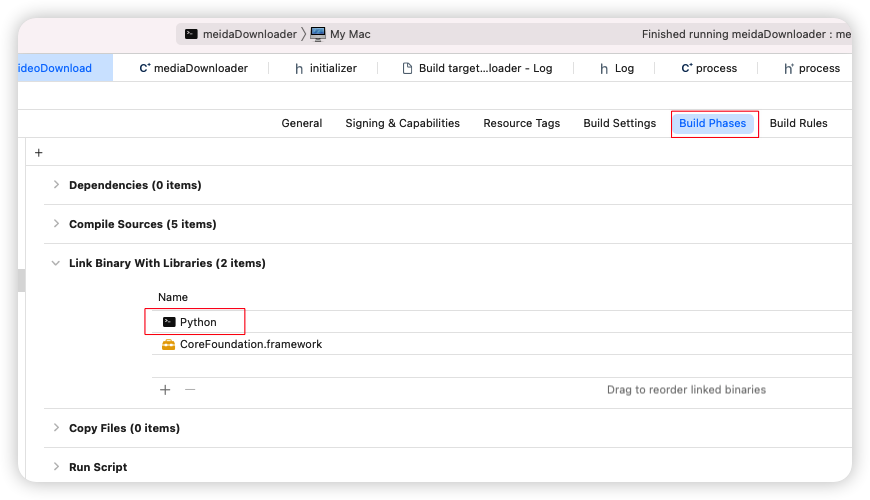
添加二进制文件
添加基础动态库
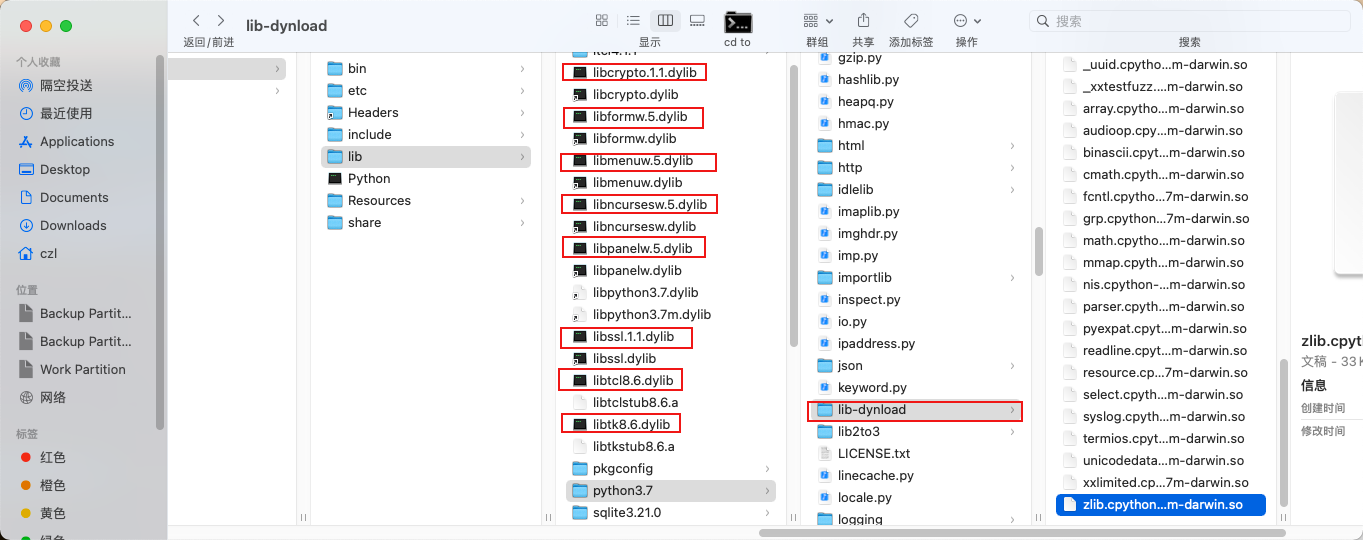
将上图使用红线标出的库和lib-dynload都复制出来,并且把那些库都放在lib-dynload里
这些动态库并不能用,因为它们和Python一样install_name是绝对路径,需要修改
czl@chenzhouliang lib % otool -L libssl.1.1.dylib
libssl.1.1.dylib:
/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.7/lib/libssl.1.1.dylib (compatibility version 1.1.0, current version 1.1.0)
/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.7/lib/libcrypto.1.1.dylib (compatibility version 1.1.0, current version 1.1.0)
/usr/lib/libSystem.B.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 1197.1.1)
比如上面这个,libssl.1.1.dylib自己的install name 不需要改 ,但是第二条依赖的libcrypto.1.1.dylib路径要改成相对路径
czl@chenzhouliang lib % otool -L libssl.1.1.dylib
libssl.1.1.dylib:
@rpath/libssl.1.1.dylib (compatibility version 1.1.0, current version 1.1.0)
@loader_path/libcrypto.1.1.dylib (compatibility version 1.1.0, current version 1.1.0)
/usr/lib/libSystem.B.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 1197.1.1)
改成这样即可
可是动态库太多了怎么办,可以使用脚本批量替换
import os,json,sys,re
def execCmd(cmd):
r = os.popen(cmd)
text = r.readlines()
r.close()
return text
def adjust_installName(filename,old,new):
GET_LIB_INFO = "otool -L %s"
REGEX = "\t/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.7/lib/(.+?) \(compatibility "
CMD = "install_name_tool -change %s%s %s%s %s"
# 获取信息
text = execCmd(GET_LIB_INFO % filename)
# 获取名称
names = []
for t in text:
m_obj = re.search(REGEX,t)
if m_obj is not None:
LibName = m_obj.group(1)
names.append(LibName)
# 构造命令字符串
for name in names:
cmd = CMD % (old,name,new,name,filename)
print("修改%s的install name %s" % (filename,cmd))
execCmd(cmd)
if __name__ == "__main__":
target_dir="/Users/czl/Desktop/st/cPythonDemo/sdk/mac/bin/lib-dynload"
old = "/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.7/lib/"
new = "@loader_path/"
# 通过文件夹获取文件名
g = os.walk(target_dir)
filenames = []
for path,dir_list,file_list in g:
for file_name in file_list:
filenames.append(os.path.join(path, file_name))
for filename in filenames:
try:
adjust_installName(filename,old,new)
except Exception:
pass
target_dir是动态库所在文件夹,old是原来的install name(不要带文件名),new 是新的intall name
添加内置python库
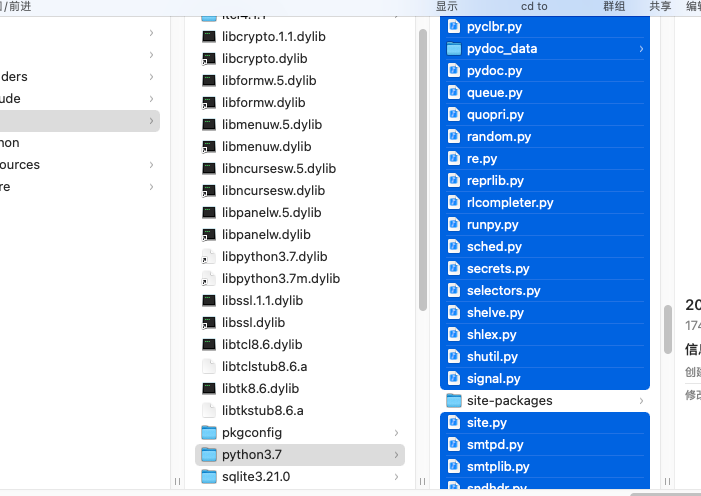
上图中所显示的文件夹中除了lib-dynload、site-packages都压缩起来,并命名为python37.zip
添加第三方库
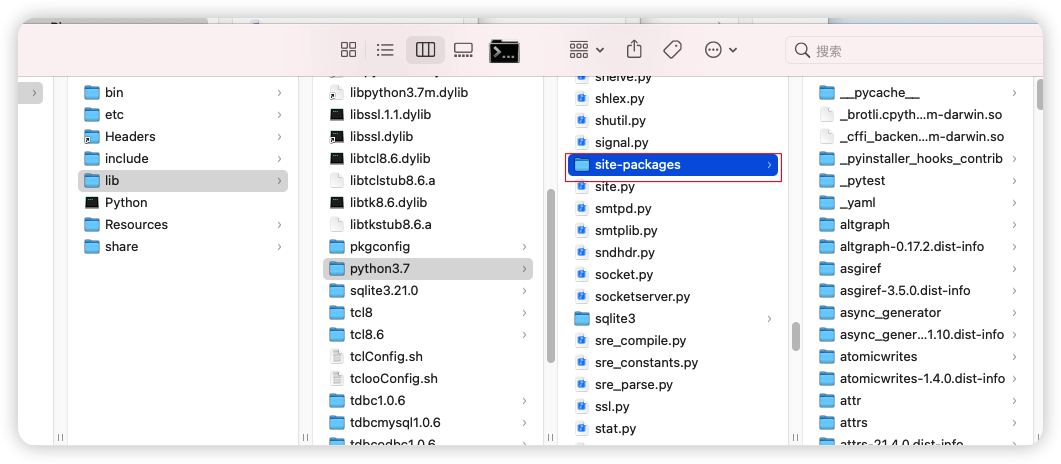
将site-packages复制出来,里面的包按实际情况删减
最后大概所有的二进制如下图所示:
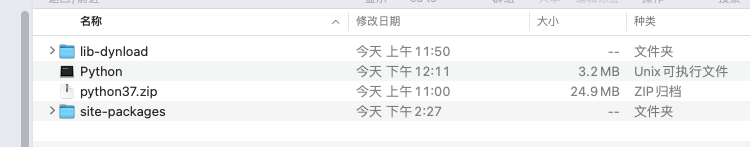
使用api调用python代码
代码和上面差不多,但是要把utils_win.cpp 改成 utils_mac.cpp
utils_mac.cpp
#include <string>
#include <locale>
#include <codecvt>
#include "utils.h"
#include <CoreFoundation/CFBundle.h>
std::string get_executable_dir()
{
CFURLRef resourceURL = CFBundleCopyExecutableURL(CFBundleGetMainBundle());
std::string bunddlePath;
char resourcePath[PATH_MAX];
if (CFURLGetFileSystemRepresentation(resourceURL, true,
(UInt8 *)resourcePath,
PATH_MAX))
{
if (resourceURL != NULL)
{
CFRelease(resourceURL);
}
bunddlePath = resourcePath;
bunddlePath = bunddlePath.substr(0,bunddlePath.find_last_of("/"));
return std::string(bunddlePath);
}
return "";
}
// convert wstring to string
std::string wstring2string(const std::wstring& input)
{
//std::wstring_convert<std::codecvt_utf8_utf16<wchar_t>> converter;
std::wstring_convert<std::codecvt_utf8<wchar_t>> converter;
return converter.to_bytes(input);
}
// convert string to wstring
std::wstring string2wstring(const std::string& input)
{
std::wstring_convert<std::codecvt_utf8<wchar_t>> converter;
return converter.from_bytes(input);
}
本文作者:乘舟凉
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/czlnb/p/16661937.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步