省选测试5
省选测试5
T1
一开始,你拥有一个饼干
现在有三种操作
-
一种是将手里的饼干数量 +1
-
一种是将手里的 \(A\) 个饼干换成 1¥
-
一种是将 1¥换成 \(B\) 个饼干
求出在\(K\)次操作后最多有多少饼干
\(A, B, K <= 1e9\);
模拟分情况讨论就好了.
上面的操作可以归为两种 : 一种是花费1来使饼干数量+1; 另一种是花费2使饼干数量+(\(B-A\)), 前提是当前有\(A\)个饼干.
我们分这两种情况 :
\(B <= A + 2\), 这样的话第二种操作没有第一种操作优, 直接用\(K\)次第一种操作就好了;
\(B> A+2\), 看一下可以执行多少次第二种操作, 剩下的操作次数执行操作一就好了.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline long long read() {
long long s = 0, f = 1; char ch;
while(!isdigit(ch = getchar())) (ch == '-') && (f = -f);
for(s = ch ^ 48;isdigit(ch = getchar()); s = (s << 1) + (s << 3) + (ch ^ 48));
return s * f;
}
int k, a, b;
int main() {
freopen("a.in","r",stdin); freopen("a.out","w",stdout);
k = read(); a = read(); b = read();
if(b - a <= 2) printf("%lld\n", 1ll + k);
else {
if(1 + k <= a + 1) printf("%lld\n", 1ll + k);
else {
int t = k - (a - 1);
int d = t / 2, mo = t % 2;
long long ans1 = 1ll * d * (b - a) + a + mo;
long long ans2 = 1ll + k;
printf("%lld\n", max(ans1, ans2));
}
}
fclose(stdin); fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
/*
4 2 6
*/
T2
有 \(n\) 座城市,一些民族。这些城市之间由 \(n-1\) 条有边权道路连接形成了以城市 1 为根的有根树。
每个城市都是某一民族的聚居地,已知第 \(i\) 个城市的民族是 \(A_i\),人数是 1。
我们定义一个民族 \(x\) 的来往程度 \(f(x)\)为民族为 \(x\) 的点两两之间的距离之和,距离定义为树上两点间最短路距离。
他想知道以 \(i\) 为根的子树内来往程度最大的民族 \(x\) 是多少,如果有多个,求编号最小。
以及对于给定的 \(k_i\),求 \(i\) 子树内编号的 \(k_i\)小民族 \(y\) 的 \(f(y)\)。
\(n <= 10 ^ 5\)
线段树合并.
对于原树上的每一个节点都维护一颗权值线段树, 然后从下往上合并子树, 统计答案.
定义一些数组 :
\(len[x]\) 代表原树上从1到\(x\)的路径权值.
当前\(o\)为权值线段树上的叶子节点, 所在的权值为\(l\) :
\(siz[o]\) 表示以\(x\)为根的子树内, 民族为\(l\)的节点个数.
\(sumlen[o]\) 表示以\(x\)为根的子树内, 民族为\(l\)的节点的\(len\)之和.
\(f[o]\) 表示以\(x\)为根的子树内, 所有民族为\(l\)的节点的来往度\(f(l)\).
当前\(o\)为权值线段树上的非叶子节点 :
\(Max[o]\) 表示以\(x\)为根的子树内所有民族的最大的来往度.
\(id[o]\) 表示这个最大的来往度的民族的编号.
\(tag[o]\)表示以\(x\)为根的子树内所有民族的种数.
对于询问1, 我们直接维护出\(id[rt[x]]\)就好了, 询问2的话用维护出的\(tag\)数组在线段树二分就可以了.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ls(o) t[o].ls
#define rs(o) t[o].rs
#define mid ((l + r) >> 1)
using namespace std;
inline long long read() {
long long s = 0, f = 1; char ch;
while(!isdigit(ch = getchar())) (ch == '-') && (f = -f);
for(s = ch ^ 48;isdigit(ch = getchar()); s = (s << 1) + (s << 3) + (ch ^ 48));
return s * f;
}
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int n, cnt, tot, cnt_b;
int a[N], b[N], k[N], rt[N], ans1[N], head[N];
long long len[N], ans2[N];
struct edge { int to, nxt, val; } e[N << 1];
struct tree { int ls, rs, id, siz, tag; long long f, Max, sumlen; } t[N * 100];
void add(int x, int y, int z) {
e[++ cnt].nxt = head[x]; head[x] = cnt; e[cnt].to = y; e[cnt].val = z;
}
void get_tree(int x, int Fa) {
for(int i = head[x]; i ; i = e[i].nxt) {
int y = e[i].to; if(y == Fa) continue ;
len[y] = len[x] + e[i].val; get_tree(y, x);
}
}
void up(int o) {
t[o].tag = t[ls(o)].tag + t[rs(o)].tag;
t[o].Max = max(t[ls(o)].Max, t[rs(o)].Max);
if(t[o].Max == t[ls(o)].Max && ls(o)) t[o].id = t[ls(o)].id;
else t[o].id = t[rs(o)].id;
}
void insert(int &o, int l, int r, int x, int i) {
if(!o) o = ++ tot;
if(l == r) {
t[o].siz = t[o].tag = 1; t[o].id = l;
t[o].sumlen = len[i];
return ;
}
if(x <= mid) insert(ls(o), l, mid, x, i);
if(x > mid) insert(rs(o), mid + 1, r, x, i);
up(o);
}
int merge(int x, int y, int l, int r, int lca) {
if(!x || !y) return x + y;
if(l == r) {
t[x].f = t[x].f + t[y].f + t[x].sumlen * t[y].siz + t[y].sumlen * t[x].siz - 2ll * t[x].siz * t[y].siz * len[lca];
t[x].siz += t[y].siz; t[x].tag = 1; t[x].sumlen += t[y].sumlen; t[x].Max = t[x].f; t[x].id = l;
return x;
}
ls(x) = merge(ls(x), ls(y), l, mid, lca);
rs(x) = merge(rs(x), rs(y), mid + 1, r, lca);
up(x); return x;
}
long long query(int o, int l, int r, int k) {
if(l == r) return t[o].Max;
int res = t[ls(o)].tag;
if(res >= k) return query(ls(o), l, mid, k);
else return query(rs(o), mid + 1, r, k - res);
}
void get_ans(int x, int Fa) {
for(int i = head[x]; i ; i = e[i].nxt) {
int y = e[i].to; if(y == Fa) continue ;
get_ans(y, x);
// cout << x << " " << y << "----------->\n";
rt[x] = merge(rt[x], rt[y], 1, cnt_b, x);
// cout << x << ":" << t[rt[x]].id << " " << t[rt[x]].Max << "\n";
}
// cout << x <<":" << t[rt[x]].id << "\n";
ans1[x] = b[t[rt[x]].id];
if(k[x] > t[rt[x]].tag) ans2[x] = -1;
else ans2[x] = query(rt[x], 1, cnt_b, k[x]);
}
int main() {
freopen("b.in","r",stdin); freopen("b.out","w",stdout);
n = read();
for(int i = 1, x, y, z;i < n; i++) {
x = read(); y = read(); z = read();
add(x, y, z); add(y, x, z);
}
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++) a[i] = b[i] = read();
sort(b + 1, b + n + 1);
cnt_b = unique(b + 1, b + n + 1) - b - 1;
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++) a[i] = lower_bound(b + 1, b + cnt_b + 1, a[i]) - b;
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++) k[i] = read();
get_tree(1, 0);
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++) insert(rt[i], 1, cnt_b, a[i], i);
get_ans(1, 0);
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++) printf("%d %lld\n", ans1[i], ans2[i]);
fclose(stdin); fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
/*
10
1 3 5
1 2 5
3 6 2
3 9 1
2 4 9
4 5 2
5 10 1
6 7 4
6 8 9
1 3 2 2 1 1 2 3 1 2
2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 2
*/
T3
给出\(a,b,K\), 满足\((a,b) = 1\), 求解不能被\(a*x+b*y,x >= 0, y >= 0\)表示出来的第\(K\)大的数字, 数据保证存在合法解.
\(a,b<=5e7, K <= 1e18\).
乱搞.
首先我们要知道两个定理 :
1.不可以被表示出来的数字最大是\(a*b - a - b\).
2.不可以被表示出来的数字的个数是\((a-1)*(b-1)/2\).
以上两个定理需要$a,b$互质.我不会证.
首先由第二个定理, 我么可以把问题转化成第\(K\)小, 这样比较好做.
我们考虑按\(a\)分块, \([1,a]\)是一块, \([a+1,2a]\)也是一块......
然后我们考虑每一块内可以被表示出来的数字有多少呢?
while(1ll * (d + 1) * b <= 1ll * i * a) d ++;
我们相当于枚举\(b\)的个数.\(d+1\)就是当前块内可以被表示出来的数字的个数, +1是因为端点上有一个\(a\)的倍数. 注意每一次枚举\(i*a\), 这个\(d\)是不会清空的, 因为上一块的\(d_1 * b\)到了这一块就变成了\(a+d_1*b\)了, 还是可以被表示出来.
画个图吧 :
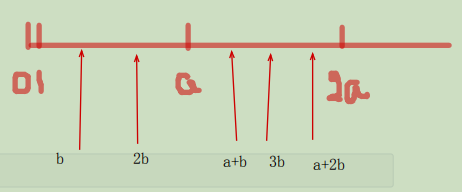
这样我们可以统计出这些块内有多少个可以被表示出来的数字(别忘了0). 然后我们可以确定出第\(K\)小的数字最终在那一块里避免, 我们\(O(a)\)的枚举这个块内的数字就好了.
如何判断这个块内那些数字不可以被表示出来呢?
设当前枚举的数字是\(c\), 那么如果有\(i*b \equiv c \bmod a\)并且\(i<=d\), 那么这个\(c\)就是可以被表示出来的.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline long long read() {
long long s = 0, f = 1; char ch;
while(!isdigit(ch = getchar())) (ch == '-') && (f = -f);
for(s = ch ^ 48;isdigit(ch = getchar()); s = (s << 1) + (s << 3) + (ch ^ 48));
return s * f;
}
const int N = 5e7 + 5;
int a, b, p, d;
long long k, sum;
bitset <N> vis;
int main() {
freopen("c.in","r",stdin); freopen("c.out","w",stdout);
a = read(); b = read(); k = read();
k = 1ll * (a - 1) * (b - 1) / 2 - k + 1;
vis[0] = 1;
for(int i = 0;i <= b; i++) {
while(1ll * (d + 1) * b <= 1ll * i * a) d ++, vis[1ll * d * b % a] = 1;
if(1ll * i * a - sum - d >= k) break ;
p = i; sum += d + 1;
}
// cout << sum << "\n";
k -= 1ll * p * a + 1 - sum;
// cout << k << " " << p << "\n";
// for(int i = 0;i < a; i++) cout << i << ":" << vis[i] << "\n";
for(int i = 0;i < a; i++)
if(!vis[i]) {
k --;
if(!k) printf("%lld\n", 1ll * a * p + i);
}
fclose(stdin); fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
/*
6 7 1
*/


