POJ2828 Buy Tickets [树状数组,二分答案]
Buy Tickets
| Time Limit: 4000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 22611 | Accepted: 11045 |
Description
Railway tickets were difficult to buy around the Lunar New Year in China, so we must get up early and join a long queue…
The Lunar New Year was approaching, but unluckily the Little Cat still had schedules going here and there. Now, he had to travel by train to Mianyang, Sichuan Province for the winter camp selection of the national team of Olympiad in Informatics.
It was one o’clock a.m. and dark outside. Chill wind from the northwest did not scare off the people in the queue. The cold night gave the Little Cat a shiver. Why not find a problem to think about? That was none the less better than freezing to death!
People kept jumping the queue. Since it was too dark around, such moves would not be discovered even by the people adjacent to the queue-jumpers. “If every person in the queue is assigned an integral value and all the information about those who have jumped the queue and where they stand after queue-jumping is given, can I find out the final order of people in the queue?” Thought the Little Cat.
Input
There will be several test cases in the input. Each test case consists of N + 1 lines where N (1 ≤ N ≤ 200,000) is given in the first line of the test case. The next N lines contain the pairs of values Posi and Valiin the increasing order of i (1 ≤ i ≤ N). For each i, the ranges and meanings of Posi and Vali are as follows:
- Posi ∈ [0, i − 1] — The i-th person came to the queue and stood right behind the Posi-th person in the queue. The booking office was considered the 0th person and the person at the front of the queue was considered the first person in the queue.
- Vali ∈ [0, 32767] — The i-th person was assigned the value Vali.
There no blank lines between test cases. Proceed to the end of input.
Output
For each test cases, output a single line of space-separated integers which are the values of people in the order they stand in the queue.
Sample Input
4
0 77
1 51
1 33
2 69
4
0 20523
1 19243
1 3890
0 31492
Sample Output
77 33 69 51
31492 20523 3890 19243
Hint
The figure below shows how the Little Cat found out the final order of people in the queue described in the first test case of the sample input.
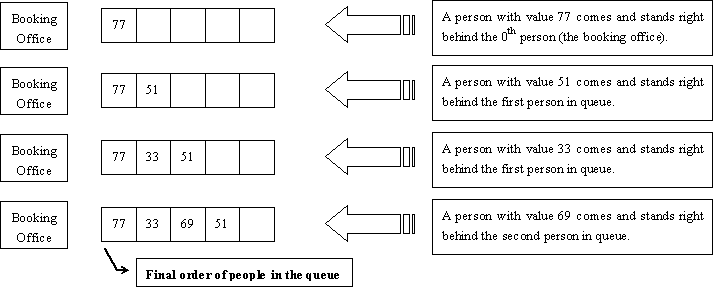
分析:
首先分析,直接暴力模拟是O(n^2)的复杂度,肯定不行,那么换一种思维,逆向进行。很明显,第n个人只要放在n个位置中的第p[n]的位置就行了,那么可以推出,第n-1个人应该放在剩下的n-1个位置中的第p[n-1]个位置就行了,依次类推,那么问题就转换成求i个位置中的第p[i]个位置在哪里。这里可以用线段树也可以用树状数组。蒟蒻用的是树状数组+二分,打的不好看将就下吧。
Code:
//It is made by HolseLee on 12th June 2018 //POJ 2828 #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<cstdlib> #include<cmath> #include<iostream> #include<iomanip> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; const int N=2e5+7; int n,c[N],ans[N]; struct Man{int pos,id,val;}a[N]; inline int read() { char ch=getchar();int num=0;bool flag=false; while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')flag=true;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){num=num*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();} return flag?-num:num; } inline int lowbit(int x) {return x&-x;} inline void add(int x,int y) { for(;x<=n;x+=lowbit(x))c[x]+=y; } inline int quary(int x) { int ret=0; for(;x>0;x-=lowbit(x))ret+=c[x]; return ret; } inline int get(int x) { int l=1,r=n,mid; while(l<=r){ mid=(l+r)>>1; if(quary(mid)>=x)r=mid-1; else l=mid+1;} return l; } int main() { while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF){ memset(c,0,sizeof(c)); memset(ans,0,sizeof(ans)); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)add(i,1); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ a[i].pos=read()+1; a[i].val=read();} for(int i=n;i>=1;i--){ int ka=get(a[i].pos); ans[ka]=a[i].val; add(ka,-1);} for(int i=1;i<n;i++) printf("%d ",ans[i]); printf("%d\n",ans[n]); } return 0; }
如需转载,请署名作者并附上原文链接,蒟蒻非常感激
名称:HolseLee
博客地址:www.cnblogs.com/cytus
个人邮箱:1073133650@qq.com


