图 floyd
You are given an array of variable pairs equations and an array of real numbers values, where equations[i] = [Ai, Bi] and values[i] represent the equation Ai / Bi = values[i]. Each Ai or Bi is a string that represents a single variable.
You are also given some queries, where queries[j] = [Cj, Dj] represents the jth query where you must find the answer for Cj / Dj = ?.
Return the answers to all queries. If a single answer cannot be determined, return -1.0.
Note: The input is always valid. You may assume that evaluating the queries will not result in division by zero and that there is no contradiction.
Example 1:
Input: equations = [["a","b"],["b","c"]], values = [2.0,3.0], queries = [["a","c"],["b","a"],["a","e"],["a","a"],["x","x"]] Output: [6.00000,0.50000,-1.00000,1.00000,-1.00000] Explanation: Given: a / b = 2.0, b / c = 3.0 queries are: a / c = ?, b / a = ?, a / e = ?, a / a = ?, x / x = ? return: [6.0, 0.5, -1.0, 1.0, -1.0 ]
Example 2:
Input: equations = [["a","b"],["b","c"],["bc","cd"]], values = [1.5,2.5,5.0], queries = [["a","c"],["c","b"],["bc","cd"],["cd","bc"]] Output: [3.75000,0.40000,5.00000,0.20000]
Example 3:
Input: equations = [["a","b"]], values = [0.5], queries = [["a","b"],["b","a"],["a","c"],["x","y"]] Output: [0.50000,2.00000,-1.00000,-1.00000]
Constraints:
1 <= equations.length <= 20equations[i].length == 21 <= Ai.length, Bi.length <= 5values.length == equations.length0.0 < values[i] <= 20.01 <= queries.length <= 20queries[i].length == 21 <= Cj.length, Dj.length <= 5Ai, Bi, Cj, Djconsist of lower case English letters and digits.
解法一:bfs
class Solution { public double[] calcEquation(List<List<String>> equations, double[] values, List<List<String>> queries) { Map<String,List<Pair>> graph = new HashMap(); //O(E) for(int i=0;i<values.length;i++){ String a = equations.get(i).get(0); String b = equations.get(i).get(1); List<Pair> list = graph.getOrDefault(a,new ArrayList()); list.add(new Pair(b,values[i])); graph.put(a, list); list = graph.getOrDefault(b,new ArrayList()); list.add(new Pair(a,1/values[i])); graph.put(b, list); } double[] result = new double[queries.size()]; //O(VN) for(int i=0;i<queries.size();i++){ result[i] = bfs(graph, queries.get(i).get(0), queries.get(i).get(1) ); } //summaray: O(E+EN) ?? return result; } //O(V) private double bfs(Map<String,List<Pair>> graph, String start, String end){ if(!graph.containsKey(start) || !graph.containsKey(end)) return -1.0; Queue<Pair> queue = new LinkedList(); Set<String> visited = new HashSet(); queue.offer(new Pair(start,1)); visited.add(start); while(!queue.isEmpty()){ Pair curr = queue.poll(); if(curr.key.equals(end)) return curr.val; for(Pair other:graph.getOrDefault(curr.key,List.of())){ if(visited.contains(other.key)) continue; visited.add(other.key); queue.offer(new Pair(other.key, curr.val*other.val)); } } return -1; } } class Pair{ String key; double val; Pair(String key, double val){ this.key = key; this.val = val; } }
解法二:floyd
class Solution { public double[] calcEquation(List<List<String>> equations, double[] values, List<List<String>> queries) { Map<String,Map<String,Double>> map = new HashMap(); for(int i=0;i<values.length;i++){ String first = equations.get(i).get(0),second = equations.get(i).get(1); map.put(first,map.getOrDefault(first,new HashMap())); map.put(second,map.getOrDefault(second,new HashMap())); Map<String,Double> firstMap = map.get(first); Map<String,Double> secondMap = map.get(second); firstMap.put(first,1d);//便于handle a/a的运算 secondMap.put(second,1d); firstMap.put(second,values[i]); secondMap.put(first,1/values[i]); } for(String key:map.keySet()){ Map<String,Double> currmap = map.get(key); for(String key1:currmap.keySet()){ for(String key2:currmap.keySet()){ if(key.equals(key1) || key.equals(key2) || key1.equals(key2)) continue; double value12 = map.get(key1).get(key)/map.get(key2).get(key); map.get(key1).put(key2,value12); map.get(key2).put(key1,1/value12); } } } double[] results = new double[queries.size()]; for(int i=0;i<queries.size();i++){ String first = queries.get(i).get(0),second = queries.get(i).get(1); if(map.get(first)!=null && map.get(first).get(second)!=null) //处理 a/b 但a,b 不存在关系的情况 results[i]=map.get(first).get(second); else results[i]=-1; } return results; } }
There are a total of numCourses courses you have to take, labeled from 0 to numCourses - 1. You are given an array prerequisites where prerequisites[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that you must take course ai first if you want to take course bi.
- For example, the pair
[0, 1]indicates that you have to take course0before you can take course1.
Prerequisites can also be indirect. If course a is a prerequisite of course b, and course b is a prerequisite of course c, then course a is a prerequisite of course c.
You are also given an array queries where queries[j] = [uj, vj]. For the jth query, you should answer whether course uj is a prerequisite of course vj or not.
Return a boolean array answer, where answer[j] is the answer to the jth query.
Example 1:

Input: numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0]], queries = [[0,1],[1,0]] Output: [false,true] Explanation: The pair [1, 0] indicates that you have to take course 1 before you can take course 0. Course 0 is not a prerequisite of course 1, but the opposite is true.
Example 2:
Input: numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [], queries = [[1,0],[0,1]] Output: [false,false] Explanation: There are no prerequisites, and each course is independent.
Example 3:
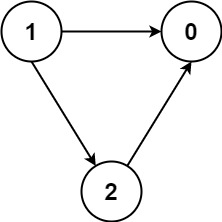
Input: numCourses = 3, prerequisites = [[1,2],[1,0],[2,0]], queries = [[1,0],[1,2]] Output: [true,true]
Constraints:
2 <= numCourses <= 1000 <= prerequisites.length <= (numCourses * (numCourses - 1) / 2)prerequisites[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi <= n - 1ai != bi- All the pairs
[ai, bi]are unique. - The prerequisites graph has no cycles.
1 <= queries.length <= 1040 <= ui, vi <= n - 1ui != vi
class Solution { public List<Boolean> checkIfPrerequisite(int numCourses, int[][] pre, int[][] queries) { //1.建图 Map<Integer,List<Integer>> graph = new HashMap(); int[] indegree = new int[numCourses]; for(int[] pair:pre){ List<Integer> list = graph.getOrDefault(pair[0],new ArrayList()); graph.put(pair[0],list); list.add(pair[1]); indegree[pair[1]]++; } //2.将入度为0的点加入队列 List<Integer> parents = new ArrayList(); boolean[][] mem = new boolean[numCourses][numCourses]; Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList(); for(int i=0;i<numCourses;i++){ if(indegree[i]==0) queue.offer(i); } //3.bfs 拓扑遍历 while(!queue.isEmpty()){ int curr = queue.poll(); //加入已遍历列表 parents.add(curr); for(int neighbor:graph.getOrDefault(curr,Arrays.asList())){ indegree[neighbor]--; if(indegree[neighbor]==0) queue.offer(neighbor); //设置当前点与其neighbor关系 mem[curr][neighbor]=true; //判断当前点与已遍历节点的关系,传递给已遍历点到neighbor for(int parent:parents){ if(mem[parent][curr]) mem[parent][neighbor]=true; } } } //4.query 得到结果集 List<Boolean> result = new ArrayList(); for(int[] pair:queries) result.add(mem[pair[0]][pair[1]]); return result; } }





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· .NET周刊【3月第1期 2025-03-02】