String[]和List的区别及相互转换
Hello,everybody。好几天不见啦,我一直在想着怎么整场大戏,琢磨写个好点的文章。(其实是因为玩了一个星期,emmmm,因为懒)。
1.两者的区别
结构方面:
List< String >:泛型,非定长,可变。
String[]:数组,定长,不可变。

使用方面:
他们的作用一样,但是灵活性不一样。
List< String >是可以方便使用的,如果不能确定数组的长度,或者需要不断的像中间插入一个字符串,可以用List< String >。
String[]是定长的,如果能确定字符串数组的长度,可以使用String[]。
2.两者的相互转换
先看代码:
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { //定义一个字符长度为5的字符串 String[] strings = new String[5]; strings[0] = "a"; strings[1] = "b"; strings[2] = "c"; strings[3] = "d"; strings[4] = "e"; //调用Arrays中的asList方法将String[]转化为List<String> List<String> list = Arrays.asList(strings); System.out.println("list<String>:"+list.toString()); //调用toArray方法将List<String>转化为String[] String[] strs = list.toArray(new String[]{}); System.out.println("String[]:"+Arrays.toString(strs)); } }
输出的结果是:
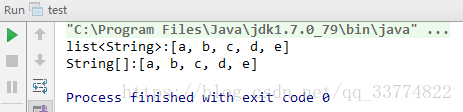
代码中已经写明了两者转换时,所采用的方法,大家好好看代码哦。
本来到这里就结束了,可是我在上面的过程又发现了一个好玩的(拿我丽颖镇楼,虽然已成人妇,哭唧唧)。

下面,如果我在刚才的代码中加入了添加方法,那么结果是什么样的呢,代码如下:
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { //定义一个字符长度为5的字符串 String[] strings = new String[5]; strings[0] = "a"; strings[1] = "b"; strings[2] = "c"; strings[3] = "d"; strings[4] = "e"; //调用Arrays中的asList方法将String[]转化为List<String> List<String> list = Arrays.asList(strings); System.out.println("list<String>:"+list.toString()); //为list添加一个元素 list.add("f"); System.out.println("list<String>:"+list.toString()); } }
大家猜猜看,这样出来的结果是啥,下篇说哈,传送门来了。UnsupportedOperationException异常

把每一件简单的事情做好,就是不简单;把每一件平凡的事情做好,就是不平凡!相信自己,创造奇迹~~





