文本挖掘(四)python电影评论情感分类模型 -- 基于keras的全连接神经网络
简介:以keras书中案例,讲述构建电影评论情感分类模型。
1.定义问题,收集数据
使用消极、积极两类电影评论集,构建对情感分类模型,并后续用于预测。由于只有两类,因此是一个二分类模型。
原始数据采用keras库中的imdb数据集,它包含来自互联网电影数据库(IMDB)的50 000 条严重两极分化的评论。数据集被分为用于训练的25 000 条评论与用于测试的25 000 条评论,训练集和测试集都包含50% 的正面评论和50% 的负面评论。
from keras.datasets import imdb # 为什么限定为使用常见的前10000个词汇呢 # 防止词向量过大 (train_data, train_labels), (test_data, test_labels) = imdb.load_data(num_words=10000)
通过内置字典,还原回评论。
# word_index is a dictionary mapping words to an integer index word_index = imdb.get_word_index() # We reverse it, mapping integer indices to words reverse_word_index = dict([(value, key) for (key, value) in word_index.items()]) # We decode the review; note that our indices were offset by 3 # because 0, 1 and 2 are reserved indices for "padding", "start of sequence", and "unknown". decoded_review = ' '.join([reverse_word_index.get(i-3, '?') for i in train_data[0]])
原始数据集为整数序列,需要将列表转换为张量。将整数序列进行One-hot编码。
import numpy as np def vectorize_sequences(sequences, dimension=10000): # Create an all-zero matrix of shape (len(sequences), dimension) results = np.zeros((len(sequences), dimension)) for i, sequence in enumerate(sequences): # 切片赋值,传入数值列 results[i, sequence] = 1. # set specific indices of results[i] to 1s return results # Our vectorized training data x_train = vectorize_sequences(train_data) # Our vectorized test data x_test = vectorize_sequences(test_data)
x_test.shape #(25000, 10000)
转换标签数据类型
# Our vectorized labels y_train = np.asarray(train_labels).astype('float32') y_test = np.asarray(test_labels).astype('float32')
2.构建网络
使用全连接神经网络,中间层一般使用relu作为激活函数,二元分类末端使用sigmoid激活函数,最终输出为一个概率值。
from keras import models from keras import layers model = models.Sequential() model.add(layers.Dense(16, activation='relu', input_shape=(10000,))) model.add(layers.Dense(16, activation='relu')) model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
3.定义优化器和损失函数
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['binary_accuracy'])
4.构建训练集和验证集
x_val = x_train[:10000] partial_x_train = x_train[10000:] y_val = y_train[:10000] partial_y_train = y_train[10000:]
5.开始训练,设置提前中断。在第8个回合停止了训练。
path_checkpoint = "model_checkpoint.h5" es_callback = keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(monitor="val_loss", min_delta=0, patience=5) # 使用ModelCheckpoint回调EarlyStopping函数定期保存检查点,并使用该回调函数在验证损失不再改善时中断训练。 modelckpt_callback = keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint( monitor="val_loss", filepath=path_checkpoint, verbose=1, save_weights_only=True, save_best_only=True, ) history = model.fit(partial_x_train, partial_y_train, epochs=20, batch_size=512, validation_data=(x_val, y_val), callbacks=[es_callback, modelckpt_callback])
6.可视化输出模型训练效果
history_dict = history.history history_dict.keys() import matplotlib.pyplot as plt acc = history.history['binary_accuracy'] val_acc = history.history['val_binary_accuracy'] loss = history.history['loss'] val_loss = history.history['val_loss'] epochs = range(1, len(acc) + 1) # "bo" is for "blue dot" plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'bo', label='Training loss') # b is for "solid blue line" plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'b', label='Validation loss') plt.title('Training and validation loss') plt.xlabel('Epochs') plt.ylabel('Loss') plt.legend() plt.show()
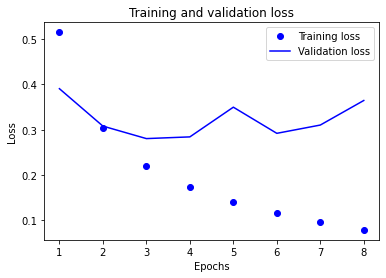
plt.clf() # clear figure acc_values = history_dict['binary_accuracy'] val_acc_values = history_dict['val_binary_accuracy'] plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label='Training acc') plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'b', label='Validation acc') plt.title('Training and validation accuracy') plt.xlabel('Epochs') plt.ylabel('Loss') plt.legend() plt.show()
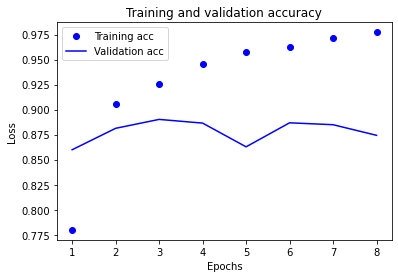
7.对测试集进行测试,最终效果精确度约为86%。
# 评分 [0.38946253061294556, 0.8613200187683105] results = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test)
小结:
使用keras构建了简单的全连接神经网络情感分论模型。
下一步,构建更复杂的网络使模型更复杂已找到恰到拟合的界限。如,增加网络节点,层数(开头增加embedding层,中间增加隐藏层)。如用其他网络模型如LSTM适合处理序列问题。




