Windows是基于GUI的(gdi32\user32),我们所看到并频繁与之交互的按钮、菜单、文本编辑器等(包括其中的文本)都是画出来的。
他们本来都只是看得见却摸不着的东西,经过一些处理,我们让他们变得看得见也摸得着。这是计算机可交互图形学的概念,也是设计图形化操作系统的重要基础。
下面我通过基于.NET的一个例子来说明可交互图形在2D场景下的基础概念。
我定义了表示一个2D场景的抽象基类:
Public MustInherit Class Shape
Public Property Position As Point '形状的位置
Friend MustOverride Function IsMouseOver(ByVal mousePoint As Point) As Boolean'鼠标指针是否进入区域
End Class
接下来用一个表示2D三角形的类来说明
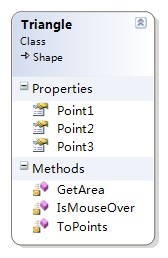
Point1 、2、3是System.Drawing.Point类型,用于表示三角形三个定点与形状位置的相对位置。
GetArea()是一个静态方法,接收三个System.Drawing.Point类型的参数。用于计算三个点所围成的三角形区域的面积。
ToPoints()方法计算三个顶点与Position的相对距离,返回Point的数组,为的是给调用GDI方法时传递参数
Friend Shared Function GetArea(ByVal p1 As Point, ByVal p2 As Point, ByVal p3 As Point) As Double
Dim a, b, c As Double
a = Math.Sqrt((p1.X - p2.X) ^ 2 + (p1.Y - p2.Y) ^ 2)
b = Math.Sqrt((p2.X - p3.X) ^ 2 + (p2.Y - p3.Y) ^ 2)
c = Math.Sqrt((p1.X - p3.X) ^ 2 + (p1.Y - p3.Y) ^ 2)
Dim p As Double = (a + b + c) / 2
Return Math.Sqrt(p * (p - a) * (p - b) * (p - c))
End Function
判断鼠标指针是否在三角形区域内,这里有一个比较好的思路:
分别计算鼠标指针的位置与三角形中两个顶点的面积,共得到三个三角形面积,它们的面积之和如果大于我们要检测的三角形面积,就是不在它区域内。如果小于则就是在了。
于是,IsMouseOver()就可以这样写:
Friend Overrides Function IsMouseOver(ByVal mousePoint As System.Drawing.Point) As Boolean
Dim p1 As New Point(Position.X + Point1.X, Position.Y + Point1.Y)
Dim p2 As New Point(Position.X + Point2.X, Position.Y + Point2.Y)
Dim p3 As New Point(Position.X + Point3.X, Position.Y + Point3.Y)
Dim aera1 As Double = GetArea(mousePoint, p1, p2)
Dim aera2 As Double = GetArea(mousePoint, p1, p3)
Dim aera3 As Double = GetArea(mousePoint, p2, p3)
Dim he As Double = aera1 + aera2 + aera3
Dim duibi As Double = GetArea(p1, p2, p3)
Return CInt(he) <= CInt(duibi)
End Function
由于涉及到精度问题所以用Cint()来转换
好了,形状的逻辑功能已经完成,现在要把它显示出来。
在Form中:
Dim shapes As New List(Of Shape)
Protected Overrides Sub OnPaint(ByVal e As System.Windows.Forms.PaintEventArgs)
MyBase.OnPaint(e)
e.Graphics.SmoothingMode = Drawing2D.SmoothingMode.AntiAlias
For Each s In shapes
If TypeOf s Is Triangle Then
e.Graphics.FillClosedCurve(Brushes.Black,
DirectCast(s, Triangle).ToPoints, Drawing2D.FillMode.Winding, 0.0!)
End If
Next
End Sub
Private Sub Form1_Load(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
shapes.Add(New Triangle _
With {.Position = New Point(100, 100),
.Point1 = New Point(0, 0),
.Point2 = New Point(0, 100),
.Point3 = New Point(100, 100)})
shapes.Add(New Triangle _
With {.Position = New Point(200, 100),
.Point1 = New Point(0, 0),
.Point2 = New Point(0, 100),
.Point3 = New Point(100, 100)})
End Sub
添加三角形并绘画,这里添加了两个三角形。
判断是否在区域内从而控制拖放:
Dim moving As Boolean = False
Dim downPos As Point
Dim shapeIndex As Integer
Private Sub Form1_MouseDown(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventArgs) Handles Me.MouseDown
If e.Button = Windows.Forms.MouseButtons.Left AndAlso DirectCast(shapes(0), Triangle).IsMouseOver(e.Location) Then
moving = True
downPos = e.Location
shapeIndex = 0
End If
If e.Button = Windows.Forms.MouseButtons.Left AndAlso DirectCast(shapes(1), Triangle).IsMouseOver(e.Location) Then
moving = True
downPos = e.Location
shapeIndex = 1
End If
End Sub
Private Sub Form1_MouseMove(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventArgs) Handles Me.MouseMove
If moving Then
shapes(shapeIndex).Position = e.Location
Me.Invalidate() '重画-
End If
End Sub
Private Sub Form1_MouseUp(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventArgs) Handles Me.MouseUp
moving = False
End Sub
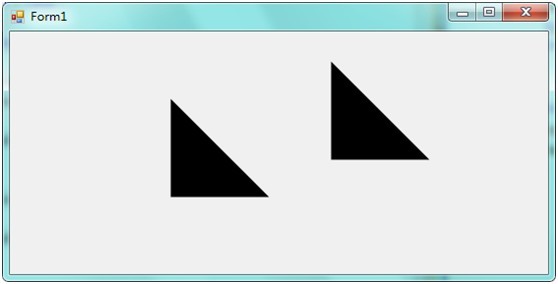
最终,两个可在 Form上拖放位置(交互)的三角形就出来了
代码下载:可交互的图形



【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步