Java中堆操作
堆
(1)基本介绍
本质上就是一个特殊的二叉树
1、是完全二叉树
2、要求对于树的中的任意节点来说,
当前节点的值必须是大于左右孩子的值=>大堆/大根堆/大顶堆
当前节点的值必须是小于左右孩子的值=>小堆/小根堆/小顶堆
注意:
1、不能是有些节点满足当前节点大于左右孩子节点,有些节点满足当前节点小于孩子节点
2、堆中规则只是父节点和子节点的关系,左右子树之间没有约束
给定一个节点,如何找到该节点的子节点?根据下标找规律
A下标0,左子树1,右子树2
B下标1,左子树3,右子树4,
C下标2,左子树5,右子树6,
D下标3,左子树7,右子树8.
如果当前下标为i,左子树下标就是2*i+1,右字数下标就是2*i+2
如果当前节点下标为i,父节点下标为(i-1)/2
(2)常用操作
import java.util.Collections; import java.util.PriorityQueue; public class HeapTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建一个小堆,默认是小堆 PriorityQueue<Integer> minheap = new PriorityQueue<>(); // 创建一个大堆 PriorityQueue<Integer> maxheap = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder()); // 添加元素 minheap.add(10); maxheap.add(10); // 获取元素 minheap.peek(); maxheap.peek(); // 删除顶部元素 minheap.poll(); maxheap.poll(); // 堆大小 minheap.size(); maxheap.size(); // 迭代器 while (!minheap.isEmpty()){ System.out.println(minheap.poll()); } } }
其他操作:
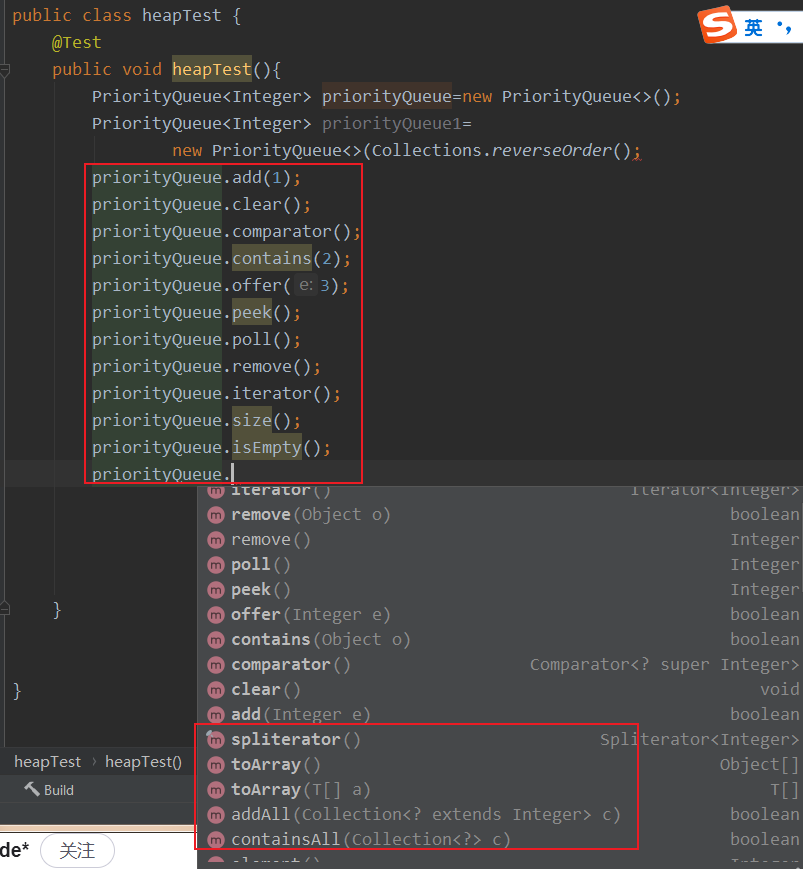
部分方法源码如下:
add()源码:
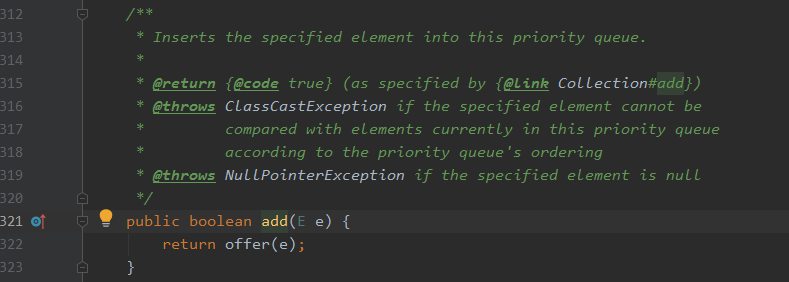
public boolean add(E e) { return offer(e); }
add(E e) 和 offer(E e) 方法都是向PriorityQueue中加入一个元素,其中add()其实调用了offer()方法如下:
offer()源码:
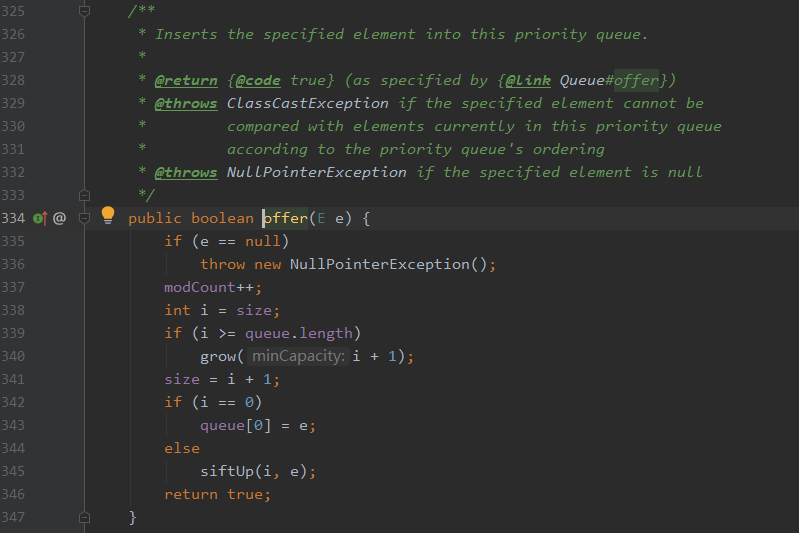
public boolean offer(E e) { if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException(); //如果压入的元素为null 抛出空指针异常 int i = size; if (i >= queue.length) grow(i + 1); //如果数组的大小不够,扩充 size = i + 1; if (i == 0) queue[0] = e; //如果只有一个元素之间放在堆顶 else siftUp(i, e); //否则调用siftUp函数从下往上调整堆。 return true; }
对上面代码做几点说明:
①优先队列中不能存放空元素。
②压入元素后如果数组的大小不够会进行扩充,上面的queue其实就是一个默认初始值为11的数组(也可以赋初始值)。
扩充源码如下:
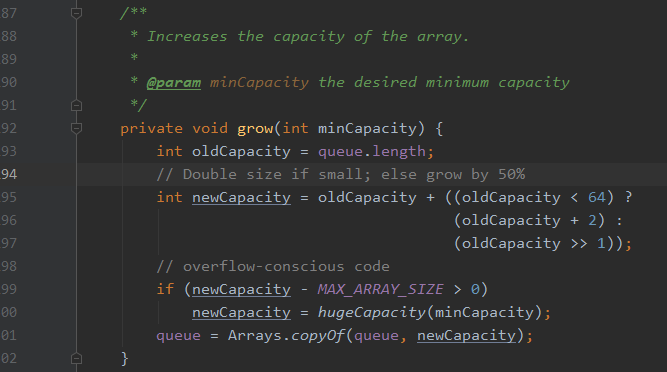
private void grow(int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = queue.length; // Double size if small; else grow by 50% 默认两倍,否则扩50% int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((oldCapacity < 64) ? (oldCapacity + 2) : (oldCapacity >> 1)); // overflow-conscious code if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, newCapacity); }
③offer元素的主要调整逻辑在 siftUp ( i, e )函数中。下面看看 siftUp(i, e) 函数到底是怎样实现的。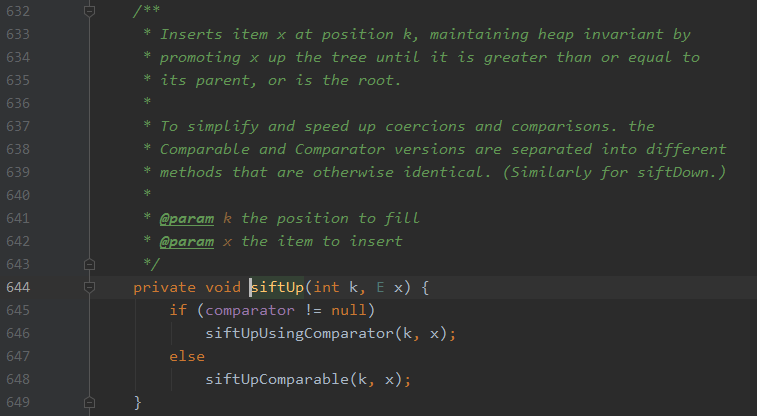
private void siftUp(int k, E x) { if (comparator != null) siftUpUsingComparator(k, x); else }
进入siftUpUsingComparator(k, x)和siftUpComparable(k, x)
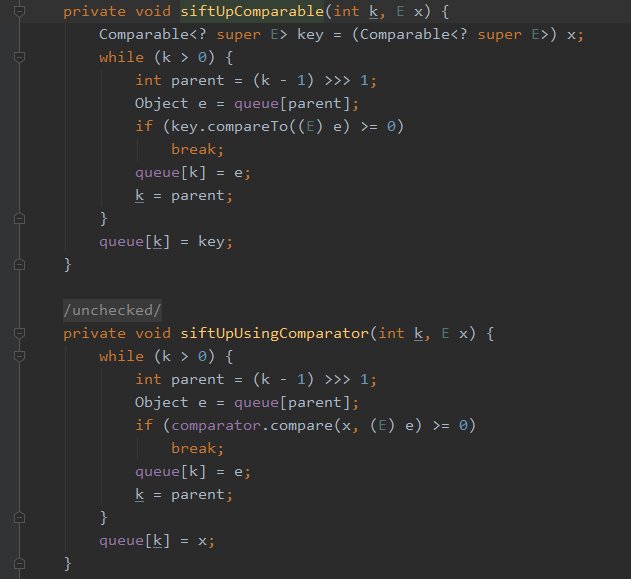
private void siftUpComparable(int k, E x) { Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>) x; while (k > 0) { int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1; Object e = queue[parent]; if (key.compareTo((E) e) >= 0) break; queue[k] = e; k = parent; } queue[k] = key; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private void siftUpUsingComparator(int k, E x) { while (k > 0) { int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1; Object e = queue[parent]; if (comparator.compare(x, (E) e) >= 0) break; queue[k] = e; k = parent; } queue[k] = x; }
代码还是比较简明的,就是当前元素与父节点不断比较如果比父节点小就交换然后继续向上比较,否则停止比较的过程
poll() 方法
poll 方法每次从 PriorityQueue 的头部删除一个节点,也就是从小顶堆的堆顶删除一个节点,注意和remove区别:remove()不仅可以删除头节点而且还可以用 remove(Object o) 来删除堆中的与给定对象相同的最先出现的对象。先看看poll()方法。
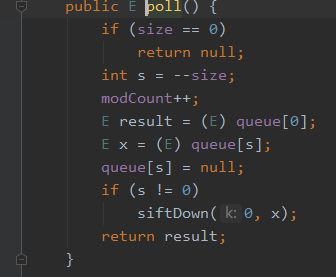
public E poll() { if (size == 0) return null; //如果堆大小为0则返回null int s = --size; modCount++; E result = (E) queue[0]; E x = (E) queue[s]; queue[s] = null; //如果堆中只有一个元素直接删除 if (s != 0) siftDown(0, x); //否则删除元素后对堆进行调整 return result; }
进入 siftDown(0, x) 方法的源码:
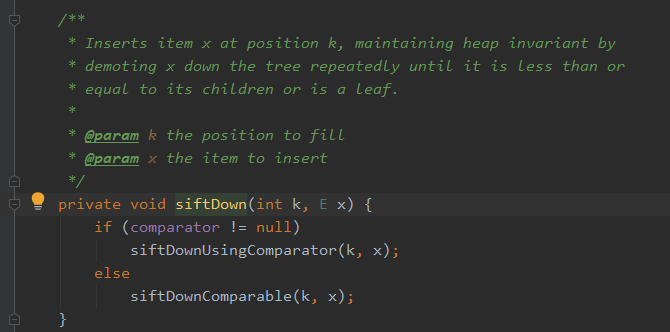
private void siftDown(int k, E x) { if (comparator != null) siftDownUsingComparator(k, x); else siftDownComparable(k, x); }
查看siftDownUsingComparator(k, x)和siftDownComparable(k, x)
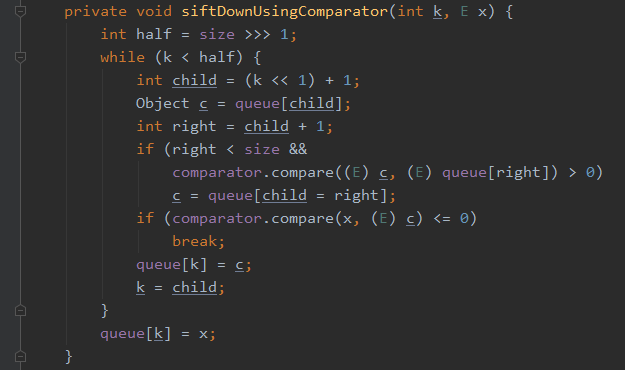
private void siftDownUsingComparator(int k, E x) { int half = size >>> 1; while (k < half) { int child = (k << 1) + 1; Object c = queue[child]; int right = child + 1; if (right < size && comparator.compare((E) c, (E) queue[right]) > 0) c = queue[child = right]; if (comparator.compare(x, (E) c) <= 0) break; queue[k] = c; k = child; } queue[k] = x; }
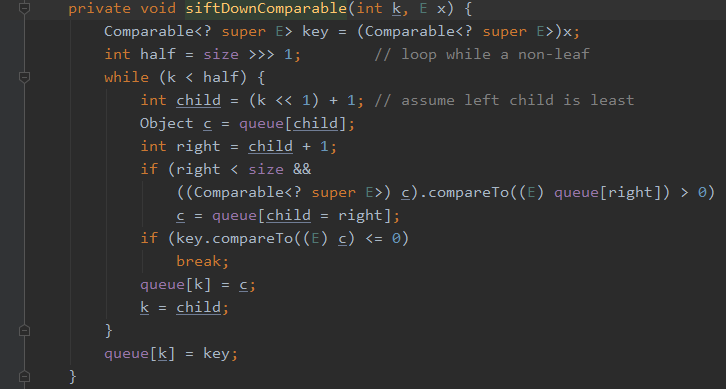
private void siftDownComparable(int k, E x) { Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>)x; int half = size >>> 1; // loop while a non-leaf while (k < half) { int child = (k << 1) + 1; // assume left child is least Object c = queue[child]; int right = child + 1; if (right < size && ((Comparable<? super E>) c).compareTo((E) queue[right]) > 0) c = queue[child = right]; if (key.compareTo((E) c) <= 0) break; queue[k] = c; k = child; } queue[k] = key; }
siftDown()方法就是从堆的第一个元素往下比较,如果比左右孩子节点的最小值小则与最小值交换,交换后继续向下比较,否则停止比较。
remove() 方法
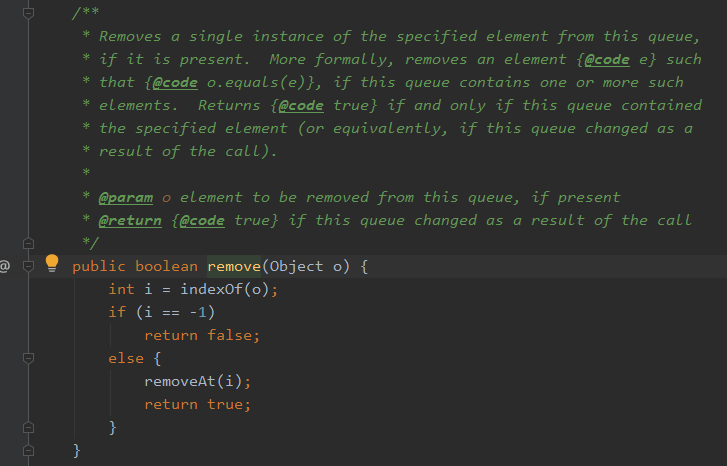
public boolean remove(Object o) { int i = indexOf(o); //先在堆中找到o的位置 if (i == -1) return false; //如果不存在则返回false。 else { removeAt(i); //否则删除数组中第i个位置的值,调整堆。 return true; } }
进入removeAt(int i)
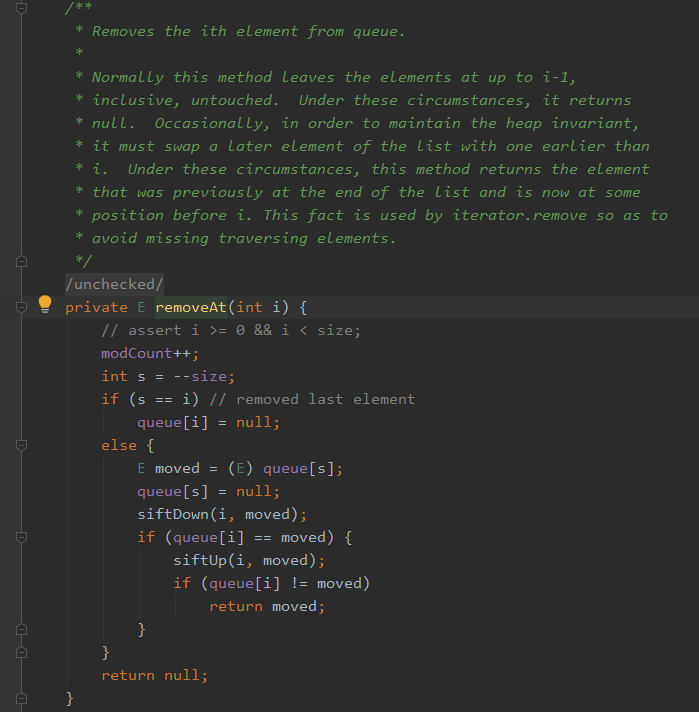
private E removeAt(int i) { assert i >= 0 && i < size; modCount++; int s = --size; if (s == i) // removed last element queue[i] = null; else { E moved = (E) queue[s]; queue[s] = null; siftDown(i, moved); //siftDown向下调整 if (queue[i] == moved) { siftUp(i, moved); if (queue[i] != moved) return moved; } } return null; }
(3)堆的创建
堆的创建:给定一个数组,整理成堆这样的结构(转换完全二叉树并且使用数组来存储,满足下标条件,满足下标关系,还满足堆的条件)
3.1向下调整
向下调整的思路(以大堆为例):
从待调整的位置出发作为父节点,然后根据下标关系得到他的子树,然后找到他的子树的最大值,然后他的孩子结点指向左右子树的最大值,然后拿他的最大值与父节点的值做比较,若不满足堆的大小,则交换两个元素。
比如:
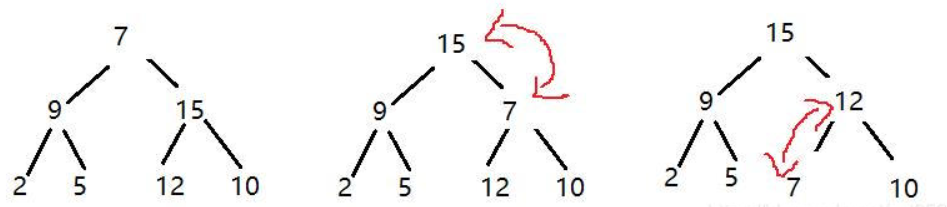
除了根节点之外,其他节点都已经符合 大堆 的要求了,此时要想让这个结构变成堆,就需要从根节点出发,进行向下调整
以大堆为例。从当前节点出发,先找到左右子树根节点,比较大的值,把当前节点和比较大的这个子节点进行交换
交换一次,不能完成调整,此时数组仍不是一个堆就从左右子树中找到一个最大的数进行交换。
public class Heap { //向下调整是创建堆的一个核心操作 //前提条件是当前被调整的左右子树都是堆 //方法参数中给出堆表示当前元素有效位置的大小 //可以通过arr.length,这个大小是整个大小 //index是表示从这个位置开始向下进项调整 private void shiftDown(int [] arr ,int size,int index){ //调整过程中,从待调整的位置出发 //取出该结点的左右子树(通过下标换算的方式) //若当前是大堆,找出左右孩子中较大的值 int parent=index; int child=2*parent+1; while(child<size){ //需要找到左右子树中较大的值 //左右子树下标差1 if(child+1<size&&arr[child+1]>arr[child]) { child=child+1; } //当左右子树遍历执行完之后,child就指向左右子树中较大的值 //拿父节点和当前较大的结点去比较,看是否满足大堆的要求 if(arr[parent]<arr[child]){ //不满足大堆的要求,交换两个元素 int tmp=arr[parent]; arr[parent]=arr[child]; arr[child]=tmp; }else{ break; } parent=child; child=2*index+1; } } //建堆操作 public void createHeap(int [] arr){ //基于向下建堆的操作; //从最后一个结点的父节点往前,对于每个下标从后往前向下调整即可 //或者最后一个非叶子结点 for(int i=(arr.length-1-1)/2;i>=0;i--){ shiftDown(arr,arr.length,i); } } }
3.2向上调整
向上调整的基本思路(大堆为例):
首先从当前结点出发作为子节点,然后根据下标的关系表达找到他的父节点,如果双亲比孩子大,则满足堆的性质,调整结束,反之,将两个结点进行交换。然后将结点向上移动。
public static void shiftUp(int [] arr,int size,int index){ int child=index; int parent=(child-1)/2; //如果child为0,已经调整到最上面了 while(child>0){ if(arr[parent]<arr[child]){ //不符合大堆要求 //交换两个元素 int tmp=arr[parent]; arr[parent]=arr[child]; arr[child]=tmp; }else{ break; } child=parent; parent=(child-1)/2; } }
其他博主写的:(挺好)
(69条消息) java详解数据结构-----堆-----Heap_梦の澜的博客-CSDN博客_java堆数据结构
(69条消息) Java堆结构PriorityQueue完全解析_HankingHu的博客-CSDN博客_priorityqueue 堆






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY