Spring Security 知识点总结
Security部分
-
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
security 配置的核心类在这里配置权限等信息
-
authentication
authentication 是认证(登陆)
-
authorization
authorization 指的是授权(获取权限)
-
所有post请求都403异常的原因
据说是因为跨域欺骗问题http.csrf().disable()可以解决
但是为什么会有跨域?或者说跨站点请求欺骗 -
security整体架构图

-
认证流程图

关键逻辑在 AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider 类的authenticate方法中
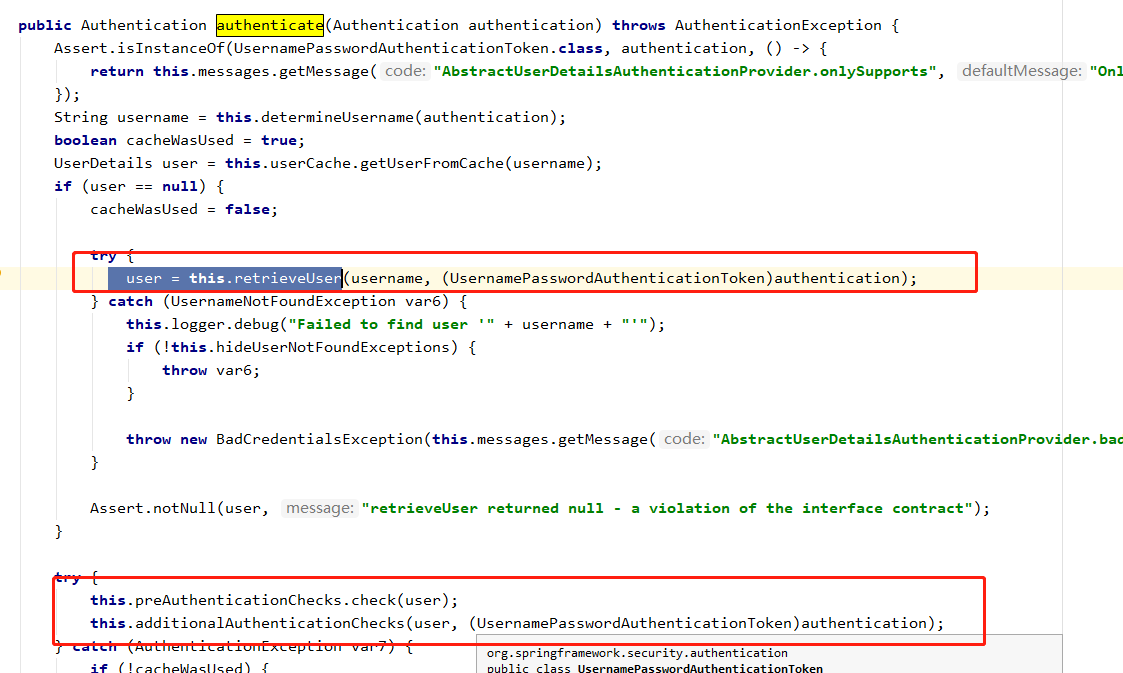
-
idea 泛型不提示警告问题怎解决?
-
怎么获取登陆异常信息?
-
配置多个UserDetailsService的情况
结果都不生效?还是说没用对? -
BCryptPasswordEncoder
一种不可逆的摘要算法,不同盐生成的摘要不同,验证不需要传入盐,盐就在密文中,一般加密的时候都是生成随机盐
String p1 = BCrypt.hashpw("root", BCrypt.gensalt());
String p2 = BCrypt.hashpw("root",BCrypt.gensalt());
System.out.println(p1);
System.out.println(p2);
System.out.println(BCrypt.checkpw("root", p1));
System.out.println(BCrypt.checkpw("root", p2));
输出结果:
$2a$10$6Q6STleeJc0e49C98ur.7OHEvzpbrfxLedv908Qz8Sfi3DtUfhLKK
$2a$10$w8zEZLf6LLYG4KksSLTek.LAuzOJX.Eeb1MntUHksFhXY1J48PuTC
true
true
-
授权流程图

-
用户传入的密码应该是明文还是密文?
-
传入明文,然后加密后和数据库的密文对比,缺点明文密码可能被获取。
-
传入密文,然后直接和数据密文对比,即便被获取也是密文,但是直接那密文也能登陆和明文密码没区别。
那种好?有没有一种数据库存密文,前端传入不同密文,然后还能严重这两个密文是同一个密码的加密方式?
-
-
AccessDecisionManager 投票决策管理者(什么情况需要投票?)
AccessDecisionManager 通过投票决定是否有范围权限,有三种实现
-
AffirmativeBased:只要有一票通过就通过,全都弃权也算通过(默认是这种策略)
-
ConsensusBased:投票通过的多余不通过的就通过,等于情况需要单独指定
-
UnanimousBased:只要有一票反对就不通过
-
-
spring boot 集成 securit
1. 导入maven 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
<version>2.5.5</version>
</dependency>
2. 集成WebSecurityConfigurer并且重写configure(HttpSecurity http)方法
/**
* security 的主要配置
*
*
* @Author ZHANGYUKUN
* @Date 2022/11/9
*/
@Configuration
public class MyWebSecurityConfigurer extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable();
ExpressionUrlAuthorizationConfigurer<HttpSecurity>.ExpressionInterceptUrlRegistry requestMatcherRegistry = http.authorizeRequests();
requestMatcherRegistry.antMatchers("/security/p1").hasAuthority("/security/p1"); // /security/p1 需要指定权限 /security/p1
requestMatcherRegistry.antMatchers("/security/p2").hasAuthority("/security/p2"); // /security/p2 需要指定权限 /security/p2
requestMatcherRegistry.antMatchers("/security/**").authenticated(); // /security/** 需要登陆
requestMatcherRegistry.anyRequest().permitAll(); //其他接口都不拦截
requestMatcherRegistry.and()
.formLogin()
//.loginPage("/login.jsp") //指定登陆页面
.loginProcessingUrl("/login/post") //指定登陆接口,默认是/login
.successForwardUrl("/security/login_success") //登陆成功重定向页面(默认首页)
.failureForwardUrl("/security/login_fail")//登陆失败页面,默认登陆页,并且提示登陆失败
;
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
3. 配置UserDetailsService
/**
* security 查询用户的服务
*
* @Author ZHANGYUKUN
* @Date 2022/11/9
*/
@Component
public class MyUserDetailsManager implements UserDetailsService {
private Map<String, User> userMap = new HashMap<>();
{
userMap.put("root",new User("root",BCrypt.hashpw("root",BCrypt.gensalt()), Arrays.asList("/security/p1")));
userMap.put("zhangsan",new User("zhangsan", BCrypt.hashpw( "zhangsan",BCrypt.gensalt()),Arrays.asList("/security/p2")));
}
/**
* 获取用户信息
* @param userName
* @return
* @throws UsernameNotFoundException
*/
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String userName) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
User user = userMap.get(userName);
if( user == null ){
throw new UsernameNotFoundException(userName);
}
return org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User
.withUsername( user.getUserName() )
.password( user.getPassword() )
.authorities( ArrayUtil.toArray( user.getPermissions(),String.class )
).build() ;
}
}
4. 配置PasswordEncoder
在第二步中的代码中已经写了
这时候就可以访问 security默认提供的登陆页面/login了
- 获取登陆用户信息
String userName = "";
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if(Objects.nonNull( authentication )){
System.out.println( authentication.getPrincipal().getClass() );
if( authentication.getPrincipal() instanceof UserDetails){
userName = ((UserDetails) authentication.getPrincipal()).getUsername();
}
}
-
session创建政策(token方式使用无状态,session方式需要创建session)
http.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.IF_REQUIRED); -
安全回话cookie(在spring boot配置文件中配置)
server.servlet.session.cookie.http-only=true,设置禁用浏览器脚本访问cookie
server.servlet.session.cookie.secute=true,设置cookie只能通过https连接发送 -
退出登陆和退出登陆事件
requestMatcherRegistry.and() .logout() //.logoutUrl("logout")//退出接口地址(默认就是/logout),成功退出以后会清理清除session和SecurityContent上下文,并跳转到退出成功页面 .addLogoutHandler((a,b,c)->{ System.out.println("退出了手动清理数据,或者做点别的事"); }) .logoutSuccessUrl("/logout_OK")//退出成功后重定向的地址(默认退出成功到登陆页) ; -
配置授权
方法1:在配置方法里面配置
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/security/p1").hasAuthority("/security/p1");
方法2:在方法上面使用注解 在任何配置类上开启全局方法授权@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled=true,securedEnabled=true)然后再controller方法上面写入任意权限注解
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('security/p1')")
@PostAuthorize("hasPermission('','security/p2')")
@Secured("表达式")
-
@PreAuthorize 和 @PostAuthorize区别 在在方法调用前还是后验证权限,正常在之前验证
并且他们默认提示的异常不同,前者实体不允许访问,后者提示Access is denied,而且被调用方法也会被执行,只是拿不到返回值
-
表达式 hasAuthority 和 hasPermission 的区别是什么
hasAuthority使用spring自带的语法检查角色和权限,正常用它就够了。
hasPermission需要自定义语法解析器实现PermissionEvaluator接口 -
@Secured 和 @PreAuthorize 区别
@Secured 不支持 SPEL表达式,有些功能不能实现,只能有 或,不支持 与类似这样,@Secured({"role1", "role2"})
@PreAuthorize 支持SPEL 表达式能实现 支持的语法更多,比如 条件与,类似这样,@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_role1') and hasRole('ROLE_role2')")
还有一种JSR标注的检查权限的语法入@RolesAllowed,@PermitAll,@DenyAll -
SpEL的基本用法总结?
-
hasRole和hasAuthority表达式的区别
sucurity 的权限和角色是通过都是通过权限字符串的方式闯入,以ROLE_开头的就是角色,比如权限 p1 直接穿入p1,如果是角色admin,那么穿入的就是Role_admin,security会把ROLE_开头的既当作权限又当作角色。
new SimpleGrantedAuthority("Role_admin"),表示有一个权限Rol_admin并且表示有一个角色admin(估计是怕真的有Role_开头的权限,所以才及识别成权限又识别成角色的)。
检查的时候,
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')") //允许
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')") //允许
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('ROLE_ADMIN')") //允许
hasRole和hasAuthority表达式的区别在于,hasRole是用来检查角色,如果没有ROLE_开头会默认给加上,hasAuthorty是检查权限。
能耍的时候就一定要耍,不能耍的时候一定要学。
--天道酬勤,贵在坚持posted on 2022-11-10 01:34 zhangyukun 阅读(283) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!