Java第09次实验(IO流)
0. 字节流与二进制文件
- 使用DataOutputStream与FileOutputStream将Student对象写入二进制文件student.data
- 二进制文件与文本文件的区别
- try...catch...finally注意事项
- 使用try..with...resouces关闭资源
- 使用DataInputStream与FileInputStream从student.data中读取学生信息并组装成对象
我的代码
1 class Student { 2 private int id; 3 private String name; 4 private int age; 5 private double grade; 6 public Student(){ 7 8 } 9 public Student(int id, String name, int age, double grade) { 10 this.id = id; 11 this.setName(name); 12 this.setAge(age); 13 this.setGrade(grade); 14 } 15 public int getId() { 16 return id; 17 } 18 public void setId(int id) { 19 this.id = id; 20 } 21 public String getName() { 22 return name; 23 } 24 public void setName(String name) { 25 if (name.length()>10){ 26 throw new IllegalArgumentException("name's length should <=10 "+name.length()); 27 } 28 this.name = name; 29 } 30 public int getAge() { 31 return age; 32 } 33 public void setAge(int age) { 34 if (age<=0){ 35 throw new IllegalArgumentException("age should >0 "+age); 36 } 37 this.age = age; 38 } 39 public double getGrade() { 40 return grade; 41 } 42 public void setGrade(double grade) { 43 if (grade<0 || grade >100){ 44 throw new IllegalArgumentException("grade should be in [0,100] "+grade); 45 } 46 this.grade = grade; 47 } 48 @Override 49 public String toString() { 50 return "Student [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", grade=" + grade + "]"; 51 } 52 53 } 54 public class Main { 55 public static void main(String[] args) 56 { 57 58 String fileName="d:\\student.data"; 59 try(DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(fileName))) 60 { 61 Student[] stu=new Student[3]; 62 stu[0]=new Student(1,"zhangsan",19,65.0); 63 stu[1]=new Student(2,"lisi",19,75.0); 64 stu[2]=new Student(3,"wangwu",20,85.0); 65 for(Student stu1:stu) { 66 dos.writeInt(stu1.getId()); 67 dos.writeUTF(stu1.getName()); 68 dos.writeInt(stu1.getAge()); 69 dos.writeDouble(stu1.getGrade()); 70 } 71 72 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 73 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 74 e.printStackTrace(); 75 System.out.println("1"); 76 } catch (IOException e) { 77 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 78 e.printStackTrace(); 79 System.out.println("2"); 80 } 81 try(DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(fileName))) 82 { 83 while(dis!=null) { 84 int id=dis.readInt(); 85 String name=dis.readUTF(); 86 int age=dis.readInt(); 87 double grade=dis.readDouble(); 88 Student stu=new Student(id,name,age,grade); 89 System.out.println(stu); 90 } 91 92 93 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 94 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 95 e.printStackTrace(); 96 System.out.println("3"); 97 } catch (IOException e) { 98 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 99 e.printStackTrace(); 100 System.out.println("4"); 101 } 102 103 }
我的总结
在读取文件数据时while循环会报错,加入测试点后发现while循环多读了一次,
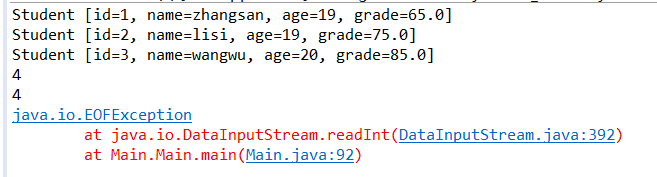
后将while(dis!=null)改成while(dis.available()!=0),问题解决
1. 字符流与文本文件:使用 PrintWriter(写),BufferedReader(读)
任务:
- 使用BufferedReader从编码为UTF-8的文本文件中读出学生信息,并组装成对象然后输出。
- 中文乱码问题(FileReader使用系统默认编码方式读取文件,会产生乱码,可使用InputStreamReader解决)
- String的split方法使用
\\s+可以使用多个空格作为分隔符。 - 进阶:修改Students.txt文件,在正确的数据行中间增加一些错误行(如,每行只有3个数据,或者应该是数字的地方放入其他字符),修改自己的程序,让起可以处理出错的行(报错但可以继续运行)。
- 编写public static ListreadStudents(String fileName);从fileName指定的文本文件中读取所有学生,并将其放入到一个List中
- 使用PrintWriter将Student对象写入文本文件,基础代码见后。注意:缓冲区问题。
- 使用ObjectInputStream/ObjectOutputStream读写学生对象。
我的代码
1.
1 public class Main { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 3 { 4 String FileName="D:\\TSBrowserDownloads\\Students.txt"; 5 BufferedReader br = null; 6 try { 7 br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(FileName),"UTF-8")); 8 String line = null; 9 while((line=br.readLine())!=null) 10 System.out.println(line); 11 } finally{ 12 if (br!=null){ 13 br.close(); 14 } 15 } 16 } 17 18 }
我的总结
默认方法打开读取会产生乱码

将模式读取方式改成"UTF-8"后显示正常

2.
1 public static void ListreadStudents(String fileName){ 2 ArrayList<Student> StudentList=new ArrayList<Student>(); 3 BufferedReader br = null; 4 try { 5 br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(fileName),"UTF-8")); 6 while(br!=null) { 7 String line=br.readLine(); 8 String[] stu=line.split("\\s+"); 9 int id=Integer.parseInt(stu[0]); 10 String name=stu[1]; 11 int age=Integer.parseInt(stu[2]); 12 double grade=Double.parseDouble(stu[3]); 13 Student Stu=new Student(id,name,age,grade); 14 StudentList.add(Stu); 15 } 16 } finally{ 17 if (br!=null){ 18 br.close(); 19 } 20 } 21 }
实验调试
刚开始本来想用和DataInputStream一样直接读,发现BufferedReader只用read和ReadLine方法,得用实验提到的"\\s+"的方法将读到的一整行用分隔符来分开,再用类型转换来读。
3.
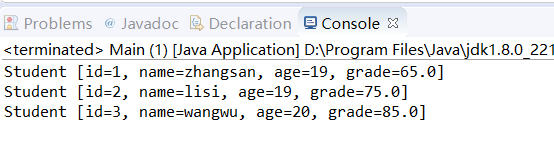
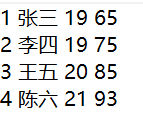
2 String FileName="D:\\TSBrowserDownloads\\Students.txt"; 3 PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(FileName,true),"UTF-8")); 4 pw.print("4 陈六 21 93"); 5 pw.close();
我的总结
正确写入文件
4.
1 String FileName="D:\\TSBrowserDownloads\\student.dat"; 2 try( 3 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(FileName); 4 ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(fos)) 5 { 6 Student ts=new Student(5,"asd",14,60); 7 oos.writeObject(ts); 8 } 9 catch (Exception e) { 10 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 11 e.printStackTrace(); 12 } 13 try( 14 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(FileName); 15 ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(fis)) 16 { 17 Student newStudent =(Student)ois.readObject(); 18 System.out.println(newStudent); 19 } catch (IOException e) { 20 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { 23 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 }
2. 缓冲流(结合使用JUint进行测试)
使用PrintWriter往文件里写入1千万行随机整数,范围在[0,10]。随机数种子设置为100.
然后从文件将每行读取出来转换成整数后相加。然后依次输出“个数 和 平均值(保留5位小数)”。
对比使用BufferedReader与使用Scanner从该文件中读取数据(只读取,不输出),使用哪种方法快?
- 使用junit对比
BufferedReader与Scanner读文件的效率 - 格式化输出:System.out.format。
- 要使用Scanner的hasNextXXX方法来判断是否到文件尾,否则会抛异常。
- Scanner的asNextXXX方法应与相对应的nextXXX方法配合使用,否则容易出。
- 请删除
fail("Not yet implemented");;并且在需要测试的方法上使用@Test进行标注。
写入文件代码
1 String FILENAME = "test.txt"; 2 double sum=0,aver; 3 PrintWriter pw=null; 4 try { 5 pw = new PrintWriter(FILENAME); 6 for(int i = 0;i<10000000;i++){//写入1千万行 7 int r=new Random().nextInt(10); 8 sum+=r; 9 pw.println(r); 10 //System.out.println(r); 11 } 12 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 }finally{ 15 pw.close(); 16 } 17 aver=sum/10000000; 18 System.out.format("%.5f", aver); 19 }
使用JUint的代码
1 public class test { 2 @Test 3 public void test() { 4 String FILENAME = "test.txt"; 5 long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); 6 Scanner scanner=null; 7 try { 8 scanner = new Scanner(new File(FILENAME)); 9 while(scanner.hasNextLine()){//只是读出每一行,不做任何处理 10 scanner.nextLine(); 11 } 12 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 }finally{ 15 scanner.close(); 16 } 17 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 18 System.out.println("last "+(end-begin)); 19 System.out.println("read using Scanner done"); 20 } 21 @Test 22 public void Bufftest() { 23 String FILENAME = "test.txt"; 24 long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); 25 BufferedReader br = null; 26 try { 27 br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(FILENAME))); 28 while(br.readLine()!=null){};//只是读出,不进行任何处理 29 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 } catch (IOException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 }finally{ 34 try { 35 br.close(); 36 } catch (IOException e) { 37 e.printStackTrace(); 38 } 39 } 40 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 41 System.out.println("last "+(end-begin)); 42 System.out.println("read using BufferedReader done"); 43 } 44 }
我的总结
可以明显对比出缓冲流BufferedReader的方法要比Scanner的方法快很多
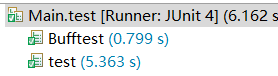
不使用JUint也可以在循环开始前后定义时间变量,最后相减也能得到运行所用时间
第2次实验
3. 字节流之对象流
结合使用ObjectOutputStream、ObjectInputStream与FileInputStream、FileOuputStream实现对Student对象的读写。
编写如下两个方法:
- public static void writeStudent(List stuList)
- public static List readStudents(String fileName)
我的代码
1 public static void writeStudent(List<Student> stuList) 2 { 3 String fileName="D:\\Student.dat"; 4 try ( FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(fileName); 5 ObjectOutputStream ois=new ObjectOutputStream(fos)) 6 { 7 ois.writeObject(stuList); 8 9 } 10 catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 11 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 12 e.printStackTrace(); 13 } catch (IOException e1) { 14 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 15 e1.printStackTrace(); 16 } 17 } 18 public static List<Student> readStudents(String fileName) 19 { 20 List<Student> stuList=new ArrayList<>(); 21 try ( FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(fileName); 22 ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(fis)) 23 { 24 stuList=(List<Student>)ois.readObject(); 25 } 26 catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 27 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 } catch (IOException e1) { 30 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 31 e1.printStackTrace(); 32 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { 33 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } 36 return stuList; 37 }
5. 文件操作
编写一个程序,可以根据指定目录和文件名,搜索该目录及子目录下的所有文件,如果没有找到指定文件名,则显示无匹配,否则将所有找到的文件名与文件夹名显示出来。
- 编写
public static void findFile(Path dir,String fileName)方法.
以dir指定的路径为根目录,在其目录与子目录下查找所有和filename
相同的文件名,一旦找到就马上输出到控制台。
我的代码
1 if (args.length == 0) args = new String[] { ".." }; 2 try 3 { 4 File pathName = new File(args[0]); 5 String[] fileNames = pathName.list(); 6 7 // enumerate all files in the directory 8 for (int i = 0; i < fileNames.length; i++) 9 { 10 File f = new File(pathName.getPath(), fileNames[i]); 11 12 // if the file is again a directory, call the main method recursively 13 if (f.isDirectory()) 14 { 15 if(f.getName().contains(fileName)) { 16 System.out.println(f.getCanonicalPath()); 17 main(new String[] { f.getPath() }); 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 catch (IOException e) 23 { 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 }
我的总结
用了参考代码稍加修改,若文件名字包含fileName,则输出该文件的路径
6. 正则表达式
- 如何判断一个给定的字符串是否是10进制数字格式?尝试编程进行验证。
- 修改HrefMatch.java
- 尝试匹配网页中的数字字符串
- 尝试匹配网页中的图片字符串
1.
1 Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); 2 Pattern pattern=Pattern.compile("^-?[0-9]\\d*(\\.\\d+)?$"); 3 Matcher matcher=null; 4 while(sc.hasNext()) 5 { 6 String str=sc.next(); 7 matcher=pattern.matcher(str); 8 System.out.println(matcher.matches()); 9 } 10 sc.close();
2.
1 try 2 { 3 // get URL string from command line or use default 4 String urlString; 5 if (args.length > 0) urlString = args[0]; 6 else urlString = "http://cec.jmu.edu.cn"; 7 8 // open reader for URL 9 InputStreamReader in = new InputStreamReader(new URL(urlString).openStream()); 10 //InputStreamReader in = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("集美大学-计算机工程学院.htm")); 11 // read contents into string builder 12 StringBuilder input = new StringBuilder(); 13 int ch; 14 while ((ch = in.read()) != -1) 15 input.append((char) ch); 16 17 // search for all occurrences of pattern 18 String patternString = "<a\\s+href\\s*=\\s*(\"[^\"]*\"|[^\\s>]*)\\s*>"; 19 String patternImgString = "[+-]?[0-9]+"; 20 //String patternString = "[\u4e00-\u9fa5]"; //匹配文档中的所有中文 21 Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(patternString, Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE); 22 Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(input); 23 24 while (matcher.find()) 25 { 26 int start = matcher.start(); 27 int end = matcher.end(); 28 String match = input.substring(start, end); 29 System.out.println(match); 30 } 31 } 32 catch (IOException e) 33 { 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } 36 catch (PatternSyntaxException e) 37 { 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 }

总结:这次实验内容较多,花费了大量的时间,总的来说IO流是java中很重要的一部分,涉及面很广,还会和今后的网络编程牵扯关系,应该好好学。正值表达式的内容较难理解





