邱锡鹏nndl-chap3-逻辑回归&softmax
提前安装ffmpeg,参考https://www.cnblogs.com/Neeo/articles/11677715.html
1.逻辑回归解决二分类问题
1.1生成数据集
1 import tensorflow as tf 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 4 from matplotlib import animation, rc 5 from IPython.display import HTML 6 import matplotlib.cm as cm 7 import numpy as np 8 9 10 dot_num = 100 11 x_p = np.random.normal(3., 1, dot_num) 12 y_p = np.random.normal(6., 1, dot_num) 13 y = np.ones(dot_num) #Y标签为1 14 C1 = np.array([x_p, y_p, y]).T 15 16 x_n = np.random.normal(6., 1, dot_num) 17 y_n = np.random.normal(3., 1, dot_num) 18 y = np.zeros(dot_num) #Y标签为0 19 C2 = np.array([x_n, y_n, y]).T 20 21 plt.scatter(C1[:, 0], C1[:, 1], c='b', marker='+') #高斯分布采样(X, Y) ~ N(3, 6, 1, 1, 0). 22 plt.scatter(C2[:, 0], C2[:, 1], c='g', marker='o') #高斯分布采样 (X, Y) ~ N(6, 3, 1, 1, 0). 23 24 data_set = np.concatenate((C1, C2), axis=0) 25 np.random.shuffle(data_set)
1.2建立模型
逻辑函数的交叉熵损失函数: $=-\sum _{i=1}^{n}y_ilog(p_i)+(1-y_i)log(1-p_i)$ $y_i$指i的真实值,$p_i$指i的预测值。
下面loss函数中在预测值pred后面加上了epsilon。
1 epsilon = 1e-12 2 class LogisticRegression(): 3 def __init__(self): 4 self.W = tf.Variable(shape=[2, 1], dtype=tf.float32, 5 initial_value=tf.random.uniform(shape=[2, 1], minval=-0.1, maxval=0.1)) 6 self.b = tf.Variable(shape=[1], dtype=tf.float32, initial_value=tf.zeros(shape=[1])) 7 8 self.trainable_variables = [self.W, self.b] 9 10 @tf.function 11 def __call__(self, inp): 12 logits = tf.matmul(inp, self.W) + self.b #shape(N, 1) 13 pred = tf.nn.sigmoid(logits) 14 return pred 15 16 @tf.function 17 def compute_loss(pred, label): 18 if not isinstance(label, tf.Tensor): 19 label = tf.constant(label, dtype=tf.float32) 20 pred = tf.squeeze(pred, axis=1) 21 22 '''=============================''' 23 #输入label shape(N,), pred shape(N,) 24 #输出 losses shape(N,) 每一个样本一个loss 25 #todo 填空一,实现sigmoid的交叉熵损失函数(不使用tf内置的loss 函数) 26 27 #losses = -label*tf.math.log(pred) - (1-label)* tf.math.log(1-pred) 28 losses = -label*tf.math.log(pred+epsilon) - (1.-label)* tf.math.log(1.-pred+epsilon) 29 '''=============================''' 30 31 loss = tf.reduce_mean(losses) 32 33 pred = tf.where(pred>0.5, tf.ones_like(pred), tf.zeros_like(pred)) #大于0.5预测正确,否则预测错误,形成判定矩阵 34 accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(label, pred), dtype=tf.float32)) #计算正确率 35 return loss, accuracy 36 37 38 @tf.function 39 def train_one_step(model, optimizer, x, y): 40 with tf.GradientTape() as tape: 41 pred = model(x) 42 loss, accuracy = compute_loss(pred, y) 43 44 grads = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables) 45 optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model.trainable_variables)) 46 return loss, accuracy, model.W, model.b
1.3实例化一个模型,进行训练
1 if __name__ == '__main__': 2 model = LogisticRegression() 3 opt = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=0.01) #SGD优化器 4 x1, x2, y = list(zip(*data_set)) 5 x = list(zip(x1, x2)) 6 animation_fram = [] 7 8 for i in range(200): 9 loss, accuracy, W_opt, b_opt = train_one_step(model, opt, x, y) 10 animation_fram.append((W_opt.numpy()[0, 0], W_opt.numpy()[1, 0], b_opt.numpy(), loss.numpy())) 11 if i%20 == 0: 12 print(f'loss: {loss.numpy():.4}\t accuracy: {accuracy.numpy():.4}')
1.4展示动态结果
1 f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,4)) #f是图像对象,ax是坐标轴对象 2 f.suptitle('Logistic Regression Example', fontsize=15) 3 plt.ylabel('Y') 4 plt.xlabel('X') 5 ax.set_xlim(0, 10) 6 ax.set_ylim(0, 10) 7 8 line_d, = ax.plot([], [], label='fit_line') 9 C1_dots, = ax.plot([], [], '+', c='b', label='actual_dots') 10 C2_dots, = ax.plot([], [], 'o', c='g' ,label='actual_dots') 11 12 13 frame_text = ax.text(0.02, 0.95,'',horizontalalignment='left',verticalalignment='top', transform=ax.transAxes) 14 15 def init(): 16 line_d.set_data([],[]) 17 C1_dots.set_data([],[]) 18 C2_dots.set_data([],[]) 19 return (line_d,) + (C1_dots,) + (C2_dots,) 20 21 def animate(i): 22 xx = np.arange(10, step=0.1) 23 a = animation_fram[i][0] 24 b = animation_fram[i][1] 25 c = animation_fram[i][2] 26 yy = a/-b * xx +c/-b 27 line_d.set_data(xx, yy) 28 29 C1_dots.set_data(C1[:, 0], C1[:, 1]) 30 C2_dots.set_data(C2[:, 0], C2[:, 1]) 31 32 frame_text.set_text('Timestep = %.1d/%.1d\nLoss = %.3f' % (i, len(animation_fram), animation_fram[i][3])) 33 34 return (line_d,) + (C1_dots,) + (C2_dots,) 35 36 37 #FuncAnimation函数绘制动图,f是画布,animate是自定义动画函数,init_func自定义开始帧,即传入init初始化函数, 38 #frames动画长度,一次循环包含的帧数,在函数运行时,其值会传递给函数animate(i)的形参“i”,interval更新频率,以ms计,blit选择更新所有点,还是仅更新产生变化的点。 39 anim = animation.FuncAnimation(f, animate, init_func=init, frames=len(animation_fram), interval=30, blit=True) 40 HTML(anim.to_html5_video())
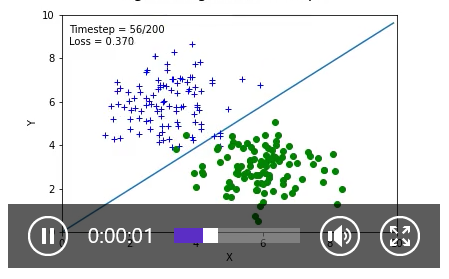
动态截图:
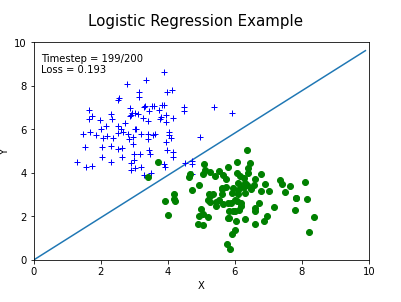
最终结果:
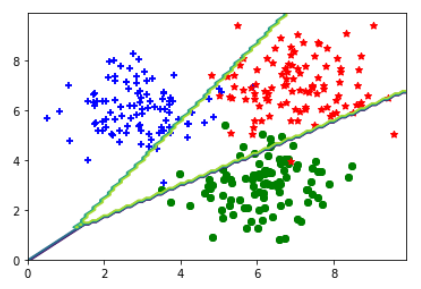
2.softmax回归解决多分类问题
2.1生成数据集
1 import tensorflow as tf 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 4 from matplotlib import animation, rc 5 from IPython.display import HTML 6 import matplotlib.cm as cm 7 import numpy as np 8 9 10 dot_num = 100 11 x_p = np.random.normal(3., 1, dot_num) 12 y_p = np.random.normal(6., 1, dot_num) 13 y = np.ones(dot_num) #Y标签为1 14 C1 = np.array([x_p, y_p, y]).T 15 16 x_n = np.random.normal(6., 1, dot_num) 17 y_n = np.random.normal(3., 1, dot_num) 18 y = np.zeros(dot_num) #Y标签为0 19 C2 = np.array([x_n, y_n, y]).T 20 21 x_b = np.random.normal(7., 1, dot_num) 22 y_b = np.random.normal(7., 1, dot_num) 23 y = np.ones(dot_num)*2 #Y标签为2 24 C3 = np.array([x_b, y_b, y]).T 25 26 plt.scatter(C1[:, 0], C1[:, 1], c='b', marker='+') 27 plt.scatter(C2[:, 0], C2[:, 1], c='g', marker='o') 28 plt.scatter(C3[:, 0], C3[:, 1], c='r', marker='*') 29 30 data_set = np.concatenate((C1, C2, C3), axis=0) 31 np.random.shuffle(data_set)

2.2建立模型
softmax的交叉熵损失函数:$-\frac{1}{N}\sum _{n=1}^{N}\sum _{c=1}^{C}y_{c}^{(n)}logp_{c}^{n}=-\frac{1}{N}\sum _{n=1}^{N}(y^{n})^{T}logp^{n}$ $y$指真实值,$p$指预测值。
下面loss函数中在预测值pred后面加上了epsilon。
1 epsilon = 1e-12 2 #建立模型类 3 class SoftmaxRegression(): 4 def __init__(self): 5 '''=============================''' 6 #todo 填空一,构建模型所需的参数 self.W, self.b 可以参考logistic-regression-exercise 7 self.W = tf.Variable(shape=[2, 3], dtype=tf.float32, initial_value=tf.random.uniform(shape=[2, 3], minval=-0.1, maxval=0.1)) 8 self.b = tf.Variable(shape=[1, 3], dtype=tf.float32, initial_value=tf.zeros(shape=[1, 3])) 9 '''=============================''' 10 11 self.trainable_variables = [self.W, self.b] 12 @tf.function 13 def __call__(self, inp): 14 logits = tf.matmul(inp, self.W) + self.b #shape(N, 3) 15 pred = tf.nn.softmax(logits) 16 return pred 17 18 #定义loss函数 19 @tf.function 20 def compute_loss(pred, label): 21 label = tf.one_hot(tf.cast(label, dtype=tf.int32), dtype=tf.float32, depth=3) 22 '''=============================''' 23 #输入label shape(N, 3), pred shape(N, 3) 24 #输出 losses shape(N,) 每一个样本一个loss 25 #todo 填空二,实现softmax的交叉熵损失函数(不使用tf内置的loss 函数) 26 losses=-tf.reduce_mean(label*tf.math.log(pred+epsilon)) 27 '''=============================''' 28 loss = tf.reduce_mean(losses) 29 30 accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(tf.argmax(label,axis=1), tf.argmax(pred, axis=1)), dtype=tf.float32)) 31 return loss, accuracy 32 33 #定义一步梯度下降过程函数 34 @tf.function 35 def train_one_step(model, optimizer, x, y): 36 with tf.GradientTape() as tape: 37 pred = model(x) 38 loss, accuracy = compute_loss(pred, y) 39 40 grads = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables) 41 optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model.trainable_variables)) 42 return loss, accuracy 43 44 45 model = SoftmaxRegression() 46 opt = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=0.01) 47 x1, x2, y = list(zip(*data_set)) 48 x = list(zip(x1, x2)) 49 for i in range(1000): 50 loss, accuracy = train_one_step(model, opt, x, y) 51 if i%50==49: 52 print(f'loss: {loss.numpy():.4}\t accuracy: {accuracy.numpy():.4}')
loss: 0.3311 accuracy: 0.36
loss: 0.2889 accuracy: 0.6433
loss: 0.2595 accuracy: 0.81
loss: 0.238 accuracy: 0.8667
loss: 0.2216 accuracy: 0.8767
loss: 0.2085 accuracy: 0.89
loss: 0.1979 accuracy: 0.8967
loss: 0.1889 accuracy: 0.9
loss: 0.1814 accuracy: 0.9033
loss: 0.1748 accuracy: 0.9067
loss: 0.1691 accuracy: 0.9067
loss: 0.164 accuracy: 0.9067
loss: 0.1595 accuracy: 0.9067
loss: 0.1554 accuracy: 0.9067
loss: 0.1517 accuracy: 0.9067
loss: 0.1484 accuracy: 0.9067
loss: 0.1453 accuracy: 0.9067
loss: 0.1425 accuracy: 0.9067
loss: 0.1398 accuracy: 0.9067
loss: 0.1374 accuracy: 0.9067
2.3展示结果
1 plt.scatter(C1[:, 0], C1[:, 1], c='b', marker='+') 2 plt.scatter(C2[:, 0], C2[:, 1], c='g', marker='o') 3 plt.scatter(C3[:, 0], C3[:, 1], c='r', marker='*') 4 5 x = np.arange(0., 10., 0.1) 6 y = np.arange(0., 10., 0.1) 7 8 X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y) #生成网格点坐标矩阵(可形成100*100=10000个点坐标) 9 10 inp = np.array(list(zip(X.reshape(-1), Y.reshape(-1))), dtype=np.float32) 11 print(inp.shape) #(10000, 2),inp相当于10000个点坐标 12 13 Z = model(inp) #Z.shape=(10000,3) 14 Z = np.argmax(Z, axis=1) #(10000,)选出三个类别中的最可能类别 15 Z = Z.reshape(X.shape) #(100,100) 16 plt.contour(X,Y,Z) #绘制等高线,Z看成关于X,Y的函数 17 plt.show()