神经网络和深度学习-week3编程题(具有一个隐藏层的平面数据分类)

建立神经网络的步骤:
1.定义模型结构(eg输入特征的数量)
2.初始化模型的参数
3.循环求解最终参数:
- 计算当前损失(正向传播)
- 计算当前梯度(反向传播)
- 更新参数(梯度下降)
4.预测
提前加载和查看数据
1 import numpy as np 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 from testCases import * 4 import sklearn 5 import sklearn.datasets 6 import sklearn.linear_model 7 from planar_utils import plot_decision_boundary, sigmoid, load_planar_dataset, load_extra_datasets 8 9 10 np.random.seed(1) # set a seed so that the results are consistent 11 X, Y = load_planar_dataset() #X(2,400)数据点数值 Y(1,400)对应X的标签0或1 12 m=X.shape[1] #400个数据 13 14 # Visualize the data: 15 plt.scatter(X[0, :], X[1, :], c=np.squeeze(Y), s=40, cmap = plt.cm.Spectral)
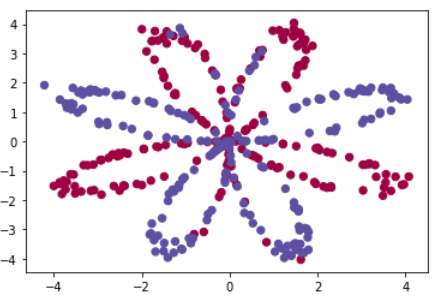
定义神经网络结构
输入:X,Y是数据集和标签
返回:n_x,n_h,n_y分别表示输入层、隐藏层(规定为4)和输出层的数量
1 def layer_sizes(X, Y): 2 3 n_x=X.shape[0] 4 n_h=4 5 n_y=Y.shape[0] 6 7 return (n_x, n_h, n_y)
初始化模型参数
输入:n_x,n_h,n_y分别表示输入层、隐藏层(规定为4)和输出层的数量
返回:参数(W1,b1,W2,b2)
1 def initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y): 2 3 np.random.seed(2) 4 5 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code) 6 W1=np.random.randn(n_h, n_x)*0.01 7 W2=np.random.randn(n_y,n_h)*0.01 8 9 b1=np.zeros((n_h,1)) 10 b2=np.zeros((n_y,1)) 11 ### END CODE HERE ### 12 13 assert (W1.shape == (n_h, n_x)) 14 assert (b1.shape == (n_h, 1)) 15 assert (W2.shape == (n_y, n_h)) 16 assert (b2.shape == (n_y, 1)) 17 18 parameters = {"W1": W1, 19 "b1": b1, 20 "W2": W2, 21 "b2": b2} 22 23 return parameters
Forward propagation 前向传播
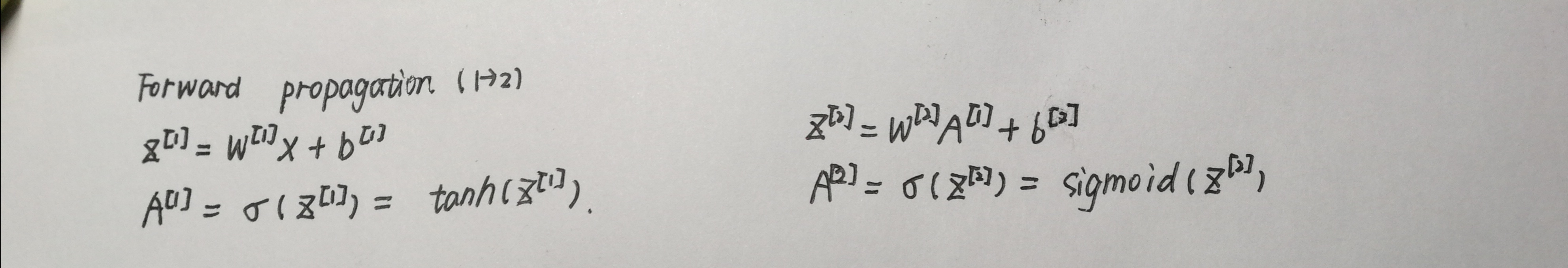
输入:数据集X,初始化得到的参数parameters(包含W1,b1,W2,b2)
返回:包含Z1,A1,Z2,A2的cache值(用来作为反向传输的输入)
1 def forward_propagation(X, parameters): 2 3 # Retrieve each parameter from the dictionary "parameters" 4 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code) 5 W1=parameters['W1'] 6 b1=parameters['b1'] 7 W2=parameters['W2'] 8 b2=parameters['b2'] 9 ### END CODE HERE ### 10 11 # Implement Forward Propagation to calculate A2 (probabilities) 12 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code) 13 Z1=np.dot(W1,X)+b1 14 A1=np.tanh(Z1) 15 16 Z2=np.dot(W2,A1)+b2 17 A2=sigmoid(Z2) 18 ### END CODE HERE ### 19 20 assert(A2.shape == (1, X.shape[1])) 21 22 cache = {"Z1": Z1, 23 "A1": A1, 24 "Z2": Z2, 25 "A2": A2} 26 27 return A2, cache
计算损失
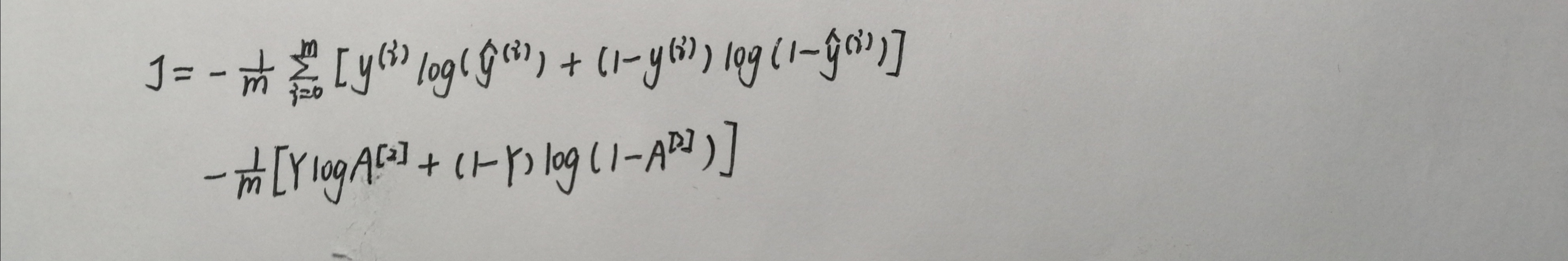
输入:A2表示二次激活后的数值,Y表示数据标签(1,400),参数parameters(包含W1,b1,W2,b2)
返回:计算得到的成本
1 def compute_cost(A2, Y, parameters): 2 3 m = Y.shape[1] # number of example 4 5 # Retrieve W1 and W2 from parameters 6 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code) 7 W1=parameters['W1'] 8 W2=parameters['W2'] 9 ### END CODE HERE ### 10 11 # Compute the cross-entropy cost 12 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code) 13 logprobs = np.multiply(np.log(A2),Y) + np.multiply((1 - Y), np.log(1 - A2)) 14 cost = - np.sum(logprobs) / m 15 ### END CODE HERE ### 16 17 cost = float(np.squeeze(cost)) # makes sure cost is the dimension we expect. 18 # E.g., turns [[17]] into 17 19 assert(isinstance(cost, float)) 20 21 return cost
Backward propagation反向传播

输入:参数parameters(包含W1,b1,W2,b2),参数cache(包含Z1,A1,Z2,A2),X表示数据集,Y表示数据标签
返回:包含dW1,db1,dW2,db2的grads
1 def backward_propagation(parameters, cache, X, Y): 2 3 m = X.shape[1] 4 5 # First, retrieve W1 and W2 from the dictionary "parameters". 6 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code) 7 W1=parameters['W1'] 8 W2=parameters['W2'] 9 ### END CODE HERE ### 10 11 # Retrieve also A1 and A2 from dictionary "cache". 12 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code) 13 A1=cache['A1'] 14 A2=cache['A2'] 15 ### END CODE HERE ### 16 17 # Backward propagation: calculate dW1, db1, dW2, db2. 18 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 6 lines of code, corresponding to 6 equations on slide above) 19 dZ2=A2-Y 20 dW2=np.dot(dZ2,A1.T)/m 21 db2=np.sum(dZ2,axis=1,keepdims=True)/m 22 23 dZ1=np.multiply(np.dot(W2.T, dz2), 1 - np.power(A1, 2)) 24 dW1=np.dot(dZ1,X.T)/m 25 db1=np.sum(dZ1,axis=1,keepdims=True)/m 26 ### END CODE HERE ### 27 28 grads = {"dW1": dW1, 29 "db1": db1, 30 "dW2": dW2, 31 "db2": db2} 32 33 return grads
更新参数
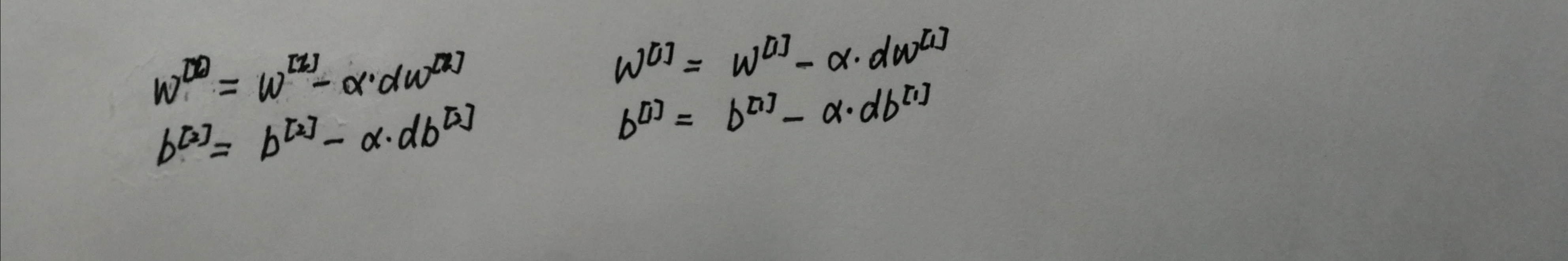
输入:参数parameters(包含W1,b1,W2,b2),参数grads(包含dW1,db1,dW2,db2),学习速率learning_rate
返回:参数parameters(包含W1,b1,W2,b2)
1 def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate=1.2): 2 3 # Retrieve each parameter from the dictionary "parameters" 4 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code) 5 W1=parameters['W1'] 6 b1=parameters['b1'] 7 W2=parameters['W2'] 8 b2=parameters['b2'] 9 ### END CODE HERE ### 10 11 # Retrieve each gradient from the dictionary "grads" 12 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code) 13 dW1=grads['dW1'] 14 db1=grads['db1'] 15 dW2=grads['dW2'] 16 db2=grads['db2'] 17 ## END CODE HERE ### 18 19 # Update rule for each parameter 20 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code) 21 W1=W1-learning_rate*dW1 22 W2=W2-learning_rate*dW2 23 b1=b1-learning_rate*db1 24 b2=b2-learning_rate*db2 25 26 ### END CODE HERE ### 27 28 parameters = {"W1": W1, 29 "b1": b1, 30 "W2": W2, 31 "b2": b2} 32 33 return parameters
封装函数
输入:X表示数据集,Y表示数据标签,n_h表示隐藏层层数,num_iterations表示迭代次数
返回:最终参数parameters(包含W1,b1,W2,b2)
def nn_model(X, Y, n_h, num_iterations=10000, print_cost=False): np.random.seed(3) n_x = layer_sizes(X, Y)[0] n_y = layer_sizes(X, Y)[2] # Initialize parameters, then retrieve W1, b1, W2, b2. Inputs: "n_x, n_h, n_y". Outputs = "W1, b1, W2, b2, parameters". ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 5 lines of code) parameters=initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y) W1=parameters['W1'] b1=parameters['b1'] W2=parameters['W2'] b2=parameters['b2'] ### END CODE HERE ### # Loop (gradient descent) for i in range(0, num_iterations): ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code) # Forward propagation. Inputs: "X, parameters". Outputs: "A2, cache". A2,cache=forward_propagation(X, parameters) # Cost function. Inputs: "A2, Y, parameters". Outputs: "cost". cost=compute_cost(A2, Y, parameters) # Backpropagation. Inputs: "parameters, cache, X, Y". Outputs: "grads". grads=backward_propagation(parameters, cache, X, Y) # Gradient descent parameter update. Inputs: "parameters, grads". Outputs: "parameters". parameters=update_parameters(parameters, grads) ### END CODE HERE ### # Print the cost every 1000 iterations if print_cost and i % 1000 == 0: print ("Cost after iteration %i: %f" % (i, cost)) return parameters
预测
输入:从nn_model函数返回的参数parameters(包含W1,b1,W2,b2),X为数据集
返回:仅含有0和1的数组
1 def predict(parameters, X): 2 3 # Computes probabilities using forward propagation, and classifies to 0/1 using 0.5 as the threshold. 4 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code) 5 A2 , cache = forward_propagation(X,parameters) 6 predictions = np.round(A2) 7 ### END CODE HERE ### 8 9 return predictions
1 parameters = nn_model(X, Y, n_h = 4, num_iterations=10000, print_cost=True) 2 3 #绘制边界 4 plot_decision_boundary(lambda x: predict(parameters, x.T), X, Y) 5 plt.title("Decision Boundary for hidden layer size " + str(4)) 6 7 predictions = predict(parameters, X)8 print ('准确率: %d' % float((np.dot(Y, predictions.T) + np.dot(1 - Y, 1 - predictions.T)) / float(Y.size) * 100) + '%')
运行结果:
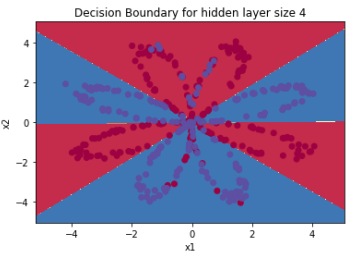
不同隐藏层节点数量的预测准确率
1 plt.figure(figsize=(16, 32)) 2 hidden_layer_sizes = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 20, 50] 3 for i, n_h in enumerate(hidden_layer_sizes): 4 plt.subplot(5, 2, i + 1) 5 plt.title('Hidden Layer of size %d' % n_h) 6 parameters = nn_model(X, Y, n_h, num_iterations=5000) 7 plot_decision_boundary(lambda x: predict(parameters, x.T), X, Y) 8 predictions = predict(parameters, X) 9 accuracy = float((np.dot(Y, predictions.T) + np.dot(1 - Y, 1 - predictions.T)) / float(Y.size) * 100) 10 print ("Accuracy for {} hidden units: {} %".format(n_h, accuracy))

