Spring学习(四)ApplicationContext
The ApplicationContext
beans包提供了以编程的方式管理和操控bean的基本功能,而context包下的ApplicationContext以一种更加面向框架的方式增强了BeanFactory的功能。多数用户可以采用声明的方式来使用ApplicationContext,甚至不用手动创建它,而通过ContextLoader这样的支持类,把它作为J2EE web应用的一部分自动启动。当然,我们仍然可以采用编程的方式创建一个ApplicationContext。
context包的核心是ApplicationContext接口。它由BeanFactory接口派生而来,因而提供了BeanFactory所有的功能。为了以一种更向面向框架的方式工作以及对上下文进行分层和实现继承,context包还提供了以下的功能:
-
MessageSource, 提供国际化的消息访问 -
资源访问,如URL和文件
-
事件传播,实现了
ApplicationListener接口的bean -
载入多个(有继承关系)上下文 ,使得每一个上下文都专注于一个特定的层次,比如应用的web层
3.8.1. BeanFactory 还是 ApplicationContext?
简单的说:除非你有更好的理由,否则尽量使用ApplicationContext,下面是对于哪些"为什么"等等更深入的建议
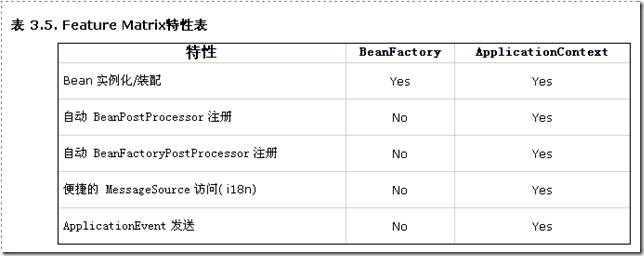
ApplicationContext包含BeanFactory的所有功能。通常建议比BeanFactory优先,除非有一些限制的场合如字节长度对内存有很大的影响时(Applet)。然后,绝大多数"典型的"企业应用和系统,ApplicationContext就是你需要使用的。Spring2.0及以上版本,大量使用了link linkend="beans-factory-extension-bpp">BeanPostProcessor扩展(以便应用代理等功能),如果你选择BeanFactory则无法使用相当多的支持功能,如事务和AOP,这可能会导致混乱,因为配置并没有错误。
下面的功能矩阵列出了BeanFactory提供的功能和ApplicationContext提供的功能(包括其实现)。(下一节更深度的描述了ApplicationContext比BeanFactory更强的功能。)
3.8.2. 利用MessageSource实现国际化
ApplicationContext接口扩展了MessageSource接口,因而提供了消息处理的功能(i18n或者国际化)。与HierarchicalMessageSource一起使用,它还能够处理嵌套的消息,这些是Spring提供的处理消息的基本接口。让我们快速浏览一下它所定义的方法:
-
String getMessage(String code, Object[] args, String default, Locale loc):用来从MessageSource获取消息的基本方法。如果在指定的locale中没有找到消息,则使用默认的消息。args中的参数将使用标准类库中的MessageFormat来作消息中替换值。 -
String getMessage(String code, Object[] args, Locale loc):本质上和上一个方法相同,其区别在:没有指定默认值,如果没找到消息,会抛出一个NoSuchMessageException异常。 -
String getMessage(MessageSourceResolvable resolvable, Locale locale):上面方法中所使用的属性都封装到一个MessageSourceResolvable实现中,而本方法可以指定MessageSourceResolvable实现。
当一个ApplicationContext被加载时,它会自动在context中查找已定义为MessageSource类型的bean。此bean的名称须为messageSource。如果找到,那么所有对上述方法的调用将被委托给该bean。否则ApplicationContext会在其父类中查找是否含有同名的bean。如果有,就把它作为MessageSource。如果它最终没有找到任何的消息源,一个空的StaticMessageSource将会被实例化,使它能够接受上述方法的调用。
Spring目前提供了两个MessageSource的实现:ResourceBundleMessageSource和StaticMessageSource。它们都继承NestingMessageSource以便能够处理嵌套的消息。StaticMessageSource很少被使用,但能以编程的方式向消息源添加消息。ResourceBundleMessageSource会用得更多一些,为此提供了一下示例:
<beans> <bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource"> <property name="basenames"> <list> <value>format</value> <value>exceptions</value> <value>windows</value> </list> </property> </bean> </beans>
这段配置假定在你的classpath中有三个资源文件(resource bundle),它们是format, exceptions和windows。通过ResourceBundle,使用JDK中解析消息的标准方式,来处理任何解析消息的请求。出于示例的目的,假定上面的两个资源文件的内容为…
# in 'format.properties' message=Alligators rock!
# in 'exceptions.properties'
argument.required=The '{0}' argument is required.
下面是测试代码。因为ApplicationContext实现也都实现了MessageSource接口,所以能被转型为MessageSource接口
public static void main(String[] args) { MessageSource resources = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); String message = resources.getMessage("message", null, "Default", null); System.out.println(message); } 上述程序的输出结果将会是... Alligators rock!
总而言之,我们在'beans.xml'的文件中(在classpath根目录下)定义了一个messageSource bean,通过它的basenames属性引用多个资源文件;而basenames属性值由list元素所指定的三个值传入,它们以文件的形式存在并被放置在classpath的根目录下(分别为format.properties,exceptions.properties和windows.properties)。
再分析个例子,这次我们将着眼于传递参数给查找的消息,这些参数将被转换为字符串并插入到已查找到的消息中的占位符(译注:资源文件中花括号里的数字即为占位符)。
<beans> <!-- this MessageSource is being used in a web application --> <bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource"> <property name="baseName" value="WEB-INF/test-messages"/> </bean> <!-- let's inject the above MessageSource into this POJO --> <bean id="example" class="com.foo.Example"> <property name="messages" ref="messageSource"/> </bean> </beans>
public class Example { private MessageSource messages; public void setMessages(MessageSource messages) { this.messages = messages; } public void execute() { String message = this.messages.getMessage("argument.required", new Object [] {"userDao"}, "Required", null); System.out.println(message); } }
调用execute()方法的输出结果是...
The 'userDao' argument is required.
对于国际化(i18n),Spring中不同的MessageResource实现与JDK标准ResourceBundle中的locale解析规则一样。比如在上面例子中定义的messageSource bean,如果你想解析British (en-GB) locale的消息,那么需要创建format_en_GB.properties,exceptions_en_GB.properties和windows_en_GB.properties三个资源文件。
Locale解析通常由应用程序根据运行环境来指定。出于示例的目的,我们对将要处理的(British)消息手工指定locale参数值。
# in 'exceptions_en_GB.properties'
argument.required=Ebagum lad, the '{0}' argument is required, I say, required.
public static void main(final String[] args) {
MessageSource resources = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
String message = resources.getMessage("argument.required",
new Object [] {"userDao"}, "Required", Locale.UK);
System.out.println(message);
}
上述程序运行时的输出结果是...
Ebagum lad, the 'userDao' argument is required, I say, required.
MessageSourceAware接口还能用于获取任何已定义的MessageSource引用。任何实现了MessageSourceAware接口的bean将在创建和配置的时候与MessageSource一同被注入。
3.8.3. 事件
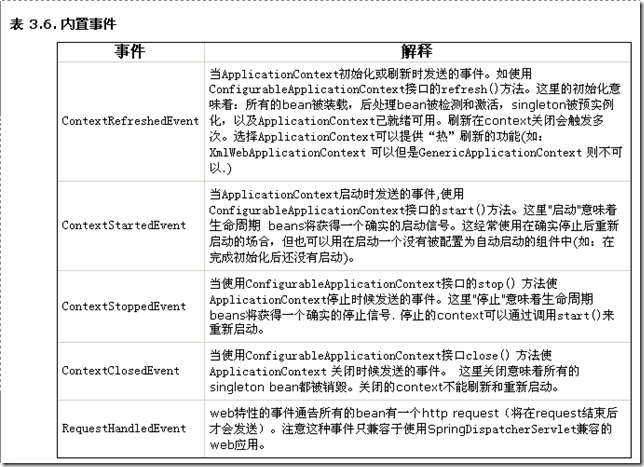
ApplicationContext中的事件处理是通过ApplicationEvent类和ApplicationListener接口来提供的。如果在上下文中部署一个实现了ApplicationListener接口的bean,那么每当一个ApplicationEvent发布到ApplicationContext时,这个bean就得到通知。实质上,这是标准的Observer设计模式。Spring提供了三个标准事件:
只要在ApplicationContext调用publishEvent()方法可以很方便的实现自定义事件,将一个实现了ApplicationEvent的自定义事件类作为参数就可以了。事件监听器同步的接收事件。这意味着publishEvent()方法将被阻塞,直到所有的监听器都处理完事件(可以通过一个ApplicationEventMulticaster的实现提供可选的事件发送策略)。此外,如果事务context可用,监听器会接收到一含有发送者事务context的事件。
看一个例子,首先是ApplicationContext:
<bean id="emailer" class="example.EmailBean"> <property name="blackList"> <list> <value>black@list.org</value> <value>white@list.org</value> <value>john@doe.org</value> </list> </property> </bean> <bean id="blackListListener" class="example.BlackListNotifier"> <property name="notificationAddress" value="spam@list.org"/> </bean> 再看一下实际的类:
public class EmailBean implements ApplicationContextAware { private List blackList; private ApplicationContext ctx; public void setBlackList(List blackList) { this.blackList = blackList; } public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext ctx) { this.ctx = ctx; } public void sendEmail(String address, String text) { if (blackList.contains(address)) { BlackListEvent event = new BlackListEvent(address, text); ctx.publishEvent(event); return; } // send email... } } public class BlackListNotifier implements ApplicationListener { private String notificationAddress; public void setNotificationAddress(String notificationAddress) { this.notificationAddress = notificationAddress; } public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { if (event instanceof BlackListEvent) { // notify appropriate person... } } }
当然,这个例子可以使用更好的方法实现(如采用AOP特性) ,但应该足以说明事件的基本机制。
3.8.4. 底层资源的访问
为了更好的使用和理解应用上下文,通常用户应当对Spring的Resource有所了解,详见第 4 章 资源
应用上下文同时也是个资源加载器(ResourceLoader),能被用来加载多个Resource。一个Resource实质上可以当成一个java.net.URL,可被用来从大多数位置以透明的方式获取底层的资源,包括从classpath、文件系统位置、任何以标准URL描述的位置以及其它一些变种。如果资源位置串是一个没有任何前缀的简单路径,这些资源来自何处取决于实际应用上下文的类型。
为了让bean能访问静态资源,可以象其它属性一样注入Resource。被注入的Resource属性值可以是简单的路径字符串,ApplicationContext会使用已注册的PropertyEditor,来将字符串转换为实际的Resource对象。
ApplicationContext构造器的路径就是实际的资源串,根据不同的上下文实现,字符串可视为不同的形式(例如:ClassPathXmlApplicationContext会把路径字符串看作一个classpath路径)。然而,它也可以使用特定的前缀来强制地从classpath或URL加载bean定义文件,而不管实际的上下文类型。
3.8.5. ApplicationContext在WEB应用中的实例化
与BeanFactory通常以编程的方式被创建不同的是,ApplicationContext能以声明的方式创建,如使用ContextLoader。当然你也可以使用ApplicationContext的实现之一来以编程的方式创建ApplicationContext实例。首先,让我们先分析ContextLoader接口及其实现。
ContextLoader机制有两种方式,ContextLoaderListener 和ContextLoaderServlet,他们功能相同但是listener不能在Servlet2.3容器下使用。Servlet2.4规范中servlet context listeners需要在web应用启动并能处理初始请求时立即运行。(servlet context listener关闭的时候也是相同的)。servlet context listener是初始化Spring ApplicationContext理想的方式。你可能愿意选择ContextLoaderListener,虽然是一样的,但决定权在于你。你可以查看ContextLoaderServlet的Javadoc来获得更详细的信息。
可以象下面所示例的一样使用ContextLoaderListener注册一个ApplicationContext
<context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/daoContext.xml /WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <!-- or use the ContextLoaderServlet instead of the above listener <servlet> <servlet-name>context</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> -->
监听器首先检查contextConfigLocation参数,如果它不存在,它将使用/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml作为默认值。如果已存在,它将使用分隔符(逗号、冒号或空格)将字符串分解成应用上下文件位置路径。可以支持ant-风格的路径模式,如/WEB-INF/*Context.xml(WEB-INF文件夹下所有以"Context.xml"结尾的文件)。或者/WEB-INF/**/*Context.xml(WEB-INF文件夹及子文件夹下的以"Context.xml"结尾的文件)。
ContextLoaderServlet同ContextLoaderListener一样使用'contextConfigLocation'参数。