.Net 进程间通信
一、前言:
在项目开发中经常会遇到,多个进程间进行通信调用的需求。
常用的方式有:
- 管道:包括命名管道和匿名管道
- 内存映射文件:借助文件和内存空间之间的映射关系,应用(包括多个进程)能够直接对内存执行读取和写入操做,从而实现进程间通讯
Socket:使用套接字在不一样的进程间通讯,这种通讯方式下,须要占用系统至少一个端口SendMessage:经过窗口句柄的方式来通讯,此通讯方式基于Windows消息WM_COPYDATA来实现- 消息队列:在对性能要求不高的状况下,咱们可使用
Msmq。但在实际项目中,通常使用ActiveMQ、Kafka、RocketMQ、RabbitMQ等这些针对特定场景优化的消息中间件,以得到最大的性能或可伸缩性优点
其中,管道、内存映射文件、SendMessage的方式,通常用于单机上进程间的通讯,在单机上使用这三种方式,比使用 Socket 要相对高效,且更容易控制网络。
本篇将介绍采用.Net 管道方式实现多进程间通信。
二、管道
管道为进程间通信提供了平台。 管道分为两种类型:
- 匿名管道:
匿名管道在本地计算机上提供进程间通信。 与命名管道相比,虽然匿名管道需要的开销更少,但提供的服务有限。
匿名管道是单向的,不能通过网络使用。 仅支持一个服务器实例。
匿名管道可用于线程间通信,也可用于父进程和子进程之间的通信,因为管道句柄可以轻松传递给所创建的子进程。
- 命名管道:
命名管道在管道服务器和一个或多个管道客户端之间提供进程间通信。
命名管道可以是单向的,也可以是双向的。 它们支持基于消息的通信,并允许多个客户端使用相同的管道名称同时连接到服务器进程。
命名管道还支持模拟,这样连接进程就可以在远程服务器上使用自己的权限。
三、应用
1、匿名管道:实现效果:服务端将输入内容传递给客户端输出。
- 服务端:创建输出匿名管道,将控制台输入内容通过管道传递到子进程中
using System; using System.Diagnostics; using System.IO; using System.IO.Pipes; namespace IpcServer { class AonymousPipeServer { public static void Run() { //客户端进程 Process pipeClient = new Process(); pipeClient.StartInfo.FileName = "IpcClient.exe"; //创建输出匿名管道、指定句柄由子进程继承 using (AnonymousPipeServerStream pipeServer = new AnonymousPipeServerStream(PipeDirection.Out, HandleInheritability.Inheritable)) { Console.WriteLine("[SERVER] 管道传输模式: {0}.", pipeServer.TransmissionMode); //将客户端进程的句柄传递给服务器。 pipeClient.StartInfo.Arguments = pipeServer.GetClientHandleAsString(); pipeClient.StartInfo.UseShellExecute = false; pipeClient.Start(); pipeServer.DisposeLocalCopyOfClientHandle(); try { // 读取服务端输入内容,发送到客户端进程 using (StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(pipeServer)) { sw.AutoFlush = true; // 发送“同步消息”并等待客户端接收。 sw.WriteLine("SYNC"); //等待客户端读取所有内容 pipeServer.WaitForPipeDrain(); // 发送控制台数据到子进程 Console.Write("[SERVER] 输入文本: "); sw.WriteLine(Console.ReadLine()); } } catch (IOException e) { Console.WriteLine("[SERVER] 异常: {0}", e.Message); } } pipeClient.WaitForExit(); pipeClient.Close(); Console.WriteLine("[SERVER] 客户端退出,服务端终止."); } } }
- 客户端:创建输入管道,从管道中获取服务端传入的数据并输出
using System; using System.IO; using System.IO.Pipes; namespace IpcClient { class AonymousPipeClient { public static void Run(string[] args) { if (args.Length > 0) { //创建输入类型匿名管道 using (PipeStream pipeClient = new AnonymousPipeClientStream(PipeDirection.In, args[0])) { Console.WriteLine("[CLIENT] 当前管道传输模式: {0}.", pipeClient.TransmissionMode); //创建读取流,从管道中读取 using (StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(pipeClient)) { string temp; // 等待来着服务器的消息 do { Console.WriteLine("[CLIENT] 同步等待..."); temp = sr.ReadLine(); } while (!temp.StartsWith("SYNC")); // Read the server data and echo to the console. while ((temp = sr.ReadLine()) != null) { Console.WriteLine("[CLIENT] 响应: " + temp); } } } } Console.Write("[CLIENT] 任意键退出..."); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
示例效果:
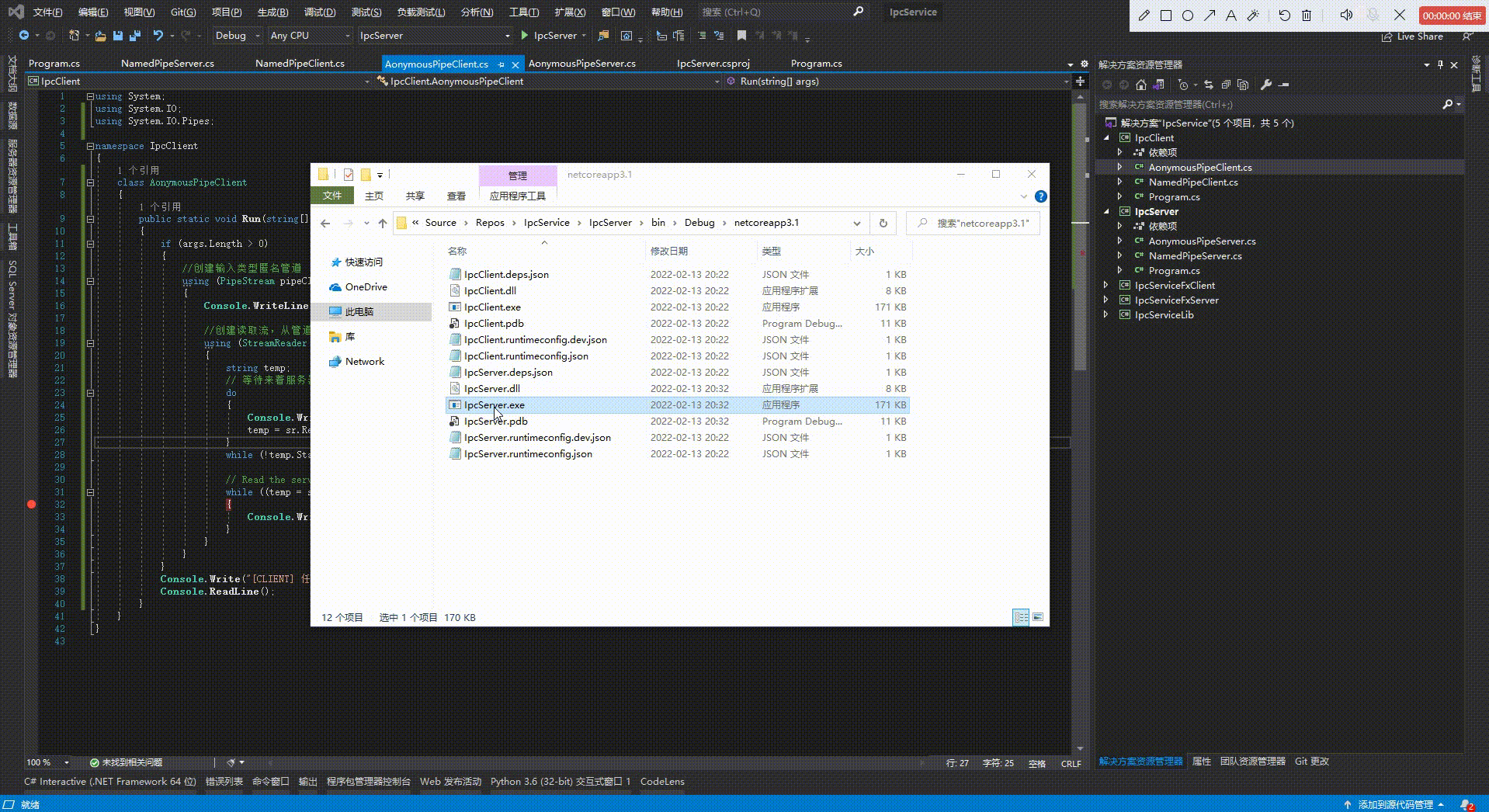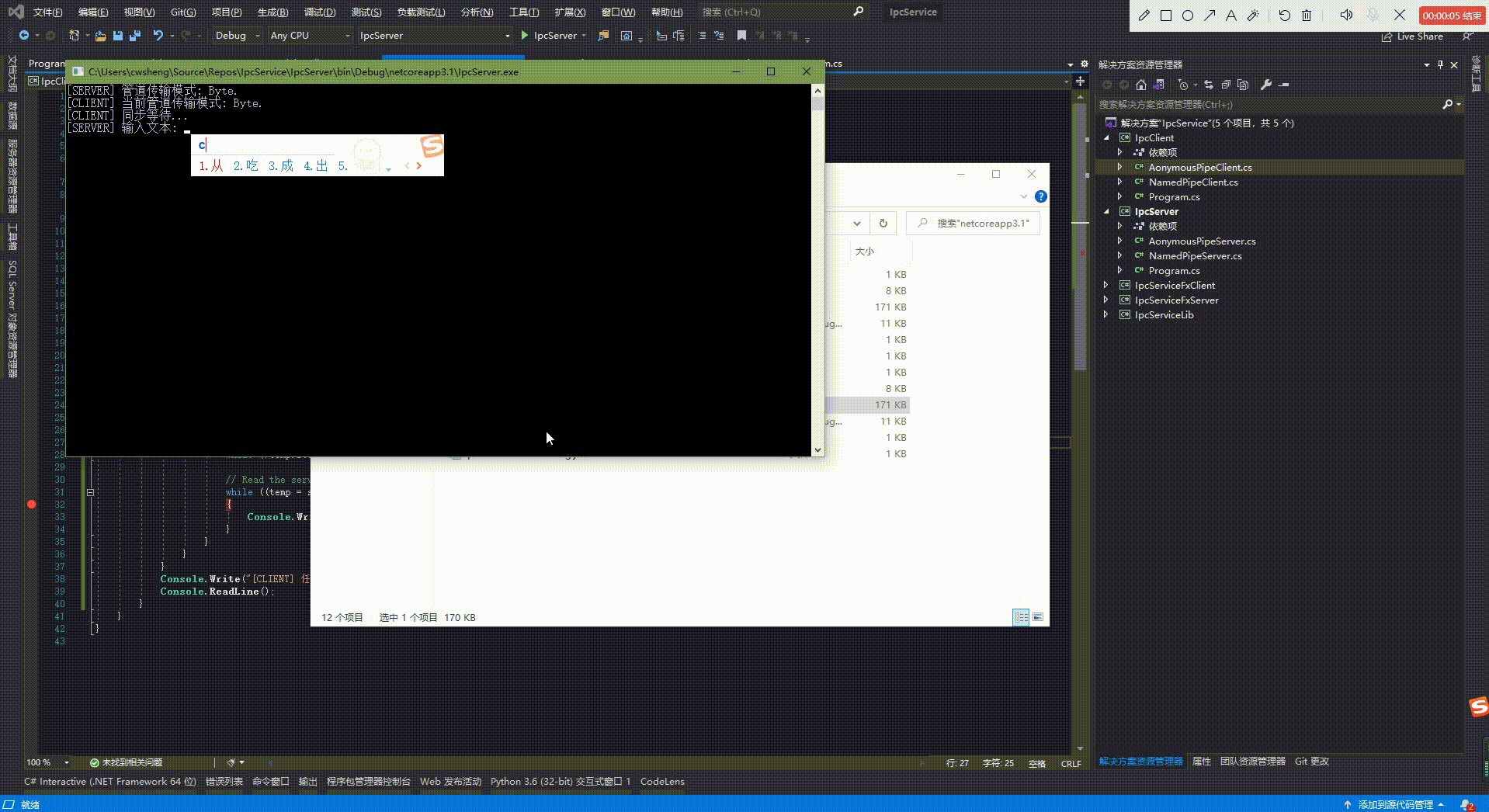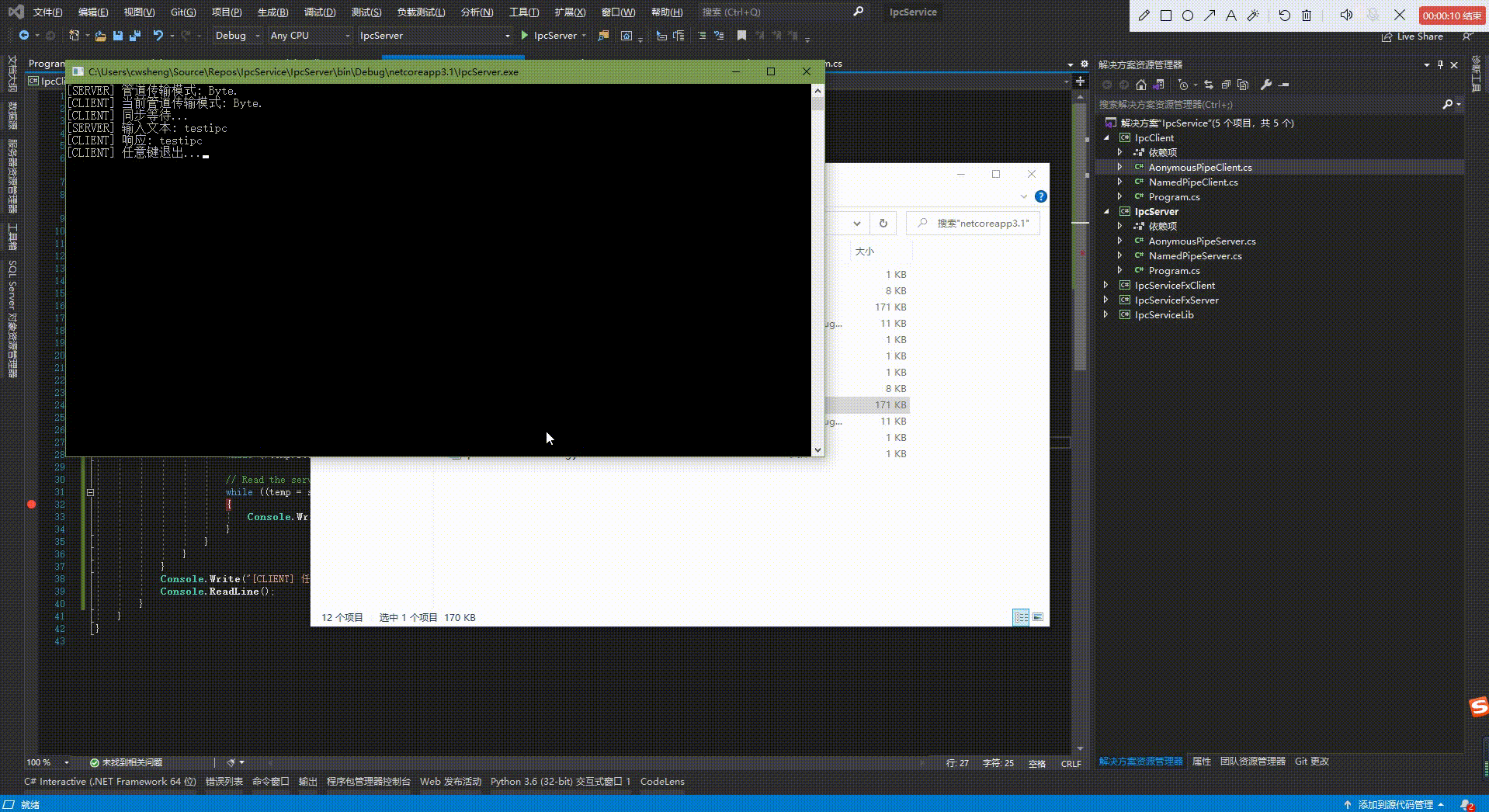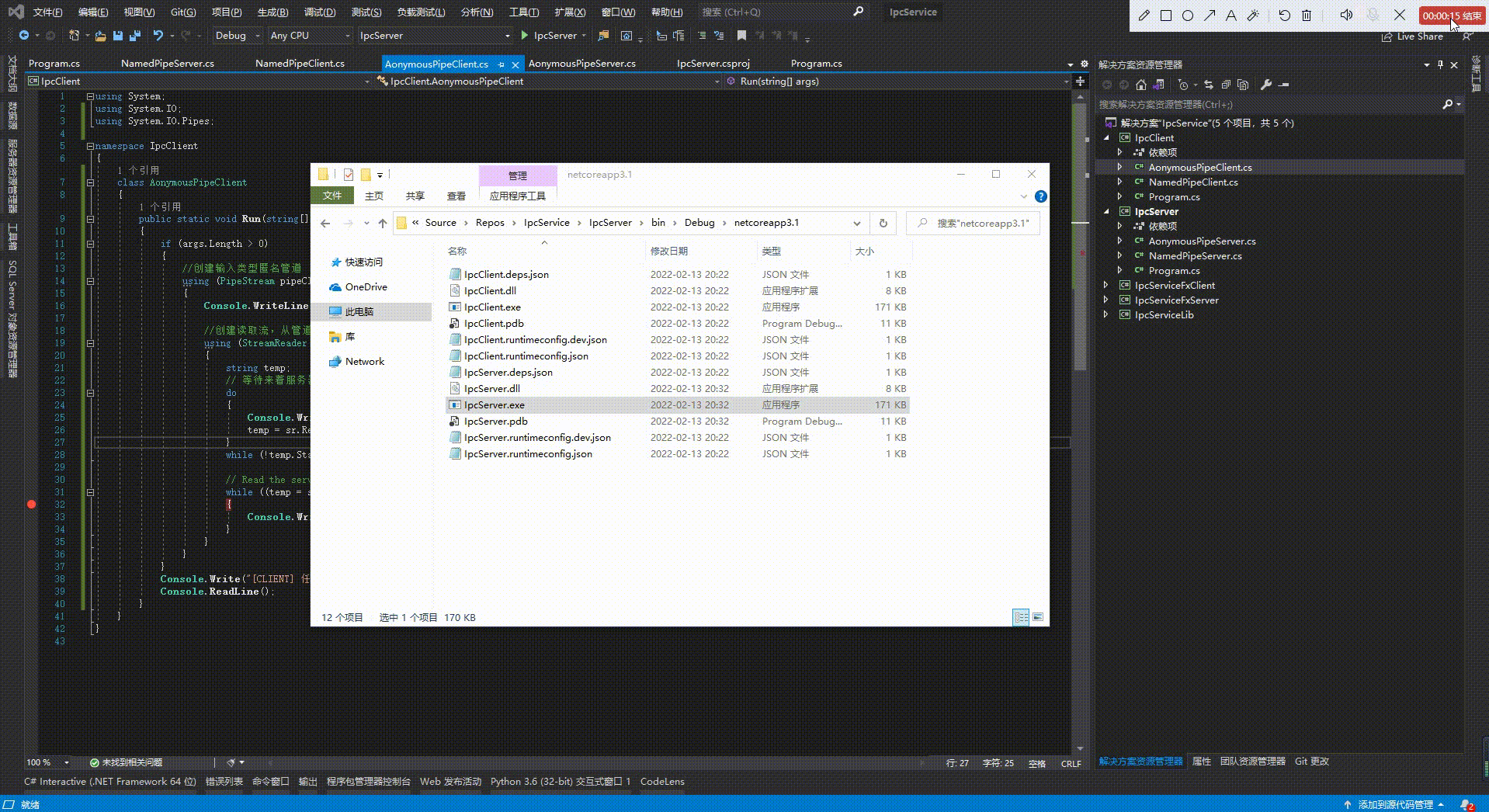
2、命名管道:
- 服务端:通过管道读取客户端发送的文件地址,在服务端中读取后返回给客户端
using System; using System.IO; using System.IO.Pipes; using System.Text; using System.Threading; namespace IpcServer { public class NamedPipeServer { private static int numThreads = 4; public static void Run() { int i; Thread[] servers = new Thread[numThreads]; Console.WriteLine("\n*** 命名管道服务端示例 ***\n"); Console.WriteLine("等待客户端连接...\n"); for (i = 0; i < numThreads; i++) { servers[i] = new Thread(ServerThread); servers[i].Start(); } Thread.Sleep(250); while (i > 0) { for (int j = 0; j < numThreads; j++) { if (servers[j] != null) { if (servers[j].Join(250)) { Console.WriteLine("Server thread[{0}] 结束.", servers[j].ManagedThreadId); servers[j] = null; i--; // 减少线程数量 } } } } Console.WriteLine("\n服务器线程已完成,正在退出."); Console.ReadLine(); } private static void ServerThread(object data) { //管道名称、管道方向 NamedPipeServerStream pipeServer = new NamedPipeServerStream("testpipe", PipeDirection.InOut, numThreads); int threadId = Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId; // 等待客户端连接 pipeServer.WaitForConnection(); Console.WriteLine("客户端连接成功 thread[{0}].", threadId); try { //读取客户的请求。客户端写入管道后,其安全令牌将可用 StreamString ss = new StreamString(pipeServer); //使用客户端预期的字符串向连接的客户端验证我们的身份。 ss.WriteString("I am the one true server!"); string filename = ss.ReadString(); //在模拟客户端时读入文件的内容。 ReadFileToStream fileReader = new ReadFileToStream(ss, filename); Console.WriteLine("读取文件: {0} 线程[{1}] 管道用户: {2}.", filename, threadId, pipeServer.GetImpersonationUserName()); pipeServer.RunAsClient(fileReader.Start); } catch (IOException e) { Console.WriteLine("异常: {0}", e.Message); } pipeServer.Close(); } } //定义用于在流上读取和写入字符串的数据协议 public class StreamString { private Stream ioStream; private UnicodeEncoding streamEncoding; public StreamString(Stream ioStream) { this.ioStream = ioStream; streamEncoding = new UnicodeEncoding(); } public string ReadString() { int len = 0; len = ioStream.ReadByte() * 256; len += ioStream.ReadByte(); byte[] inBuffer = new byte[len]; ioStream.Read(inBuffer, 0, len); return streamEncoding.GetString(inBuffer); } public int WriteString(string outString) { byte[] outBuffer = streamEncoding.GetBytes(outString); int len = outBuffer.Length; if (len > UInt16.MaxValue) { len = (int)UInt16.MaxValue; } ioStream.WriteByte((byte)(len / 256)); ioStream.WriteByte((byte)(len & 255)); ioStream.Write(outBuffer, 0, len); ioStream.Flush(); return outBuffer.Length + 2; } } // 包含在模拟用户的上下文中执行的方法 public class ReadFileToStream { private string fn; private StreamString ss; public ReadFileToStream(StreamString str, string filename) { fn = filename; ss = str; } public void Start() { string contents = File.ReadAllText(fn); ss.WriteString(contents); } } }
- 客户端:连接服务端命名管道后,发送要读取的文件路径;读取服务端返回文件内容并输出
using System; using System.Diagnostics; using System.IO; using System.IO.Pipes; using System.Security.Principal; using System.Text; using System.Threading; namespace IpcClient { class NamedPipeClient { private static int numClients = 4; public static void Run(string[] args) { if (args.Length > 0) { if (args[0] == "spawnclient") { //.代表本机(可替换为具体IP) var pipeClient = new NamedPipeClientStream(".", "testpipe", PipeDirection.InOut, PipeOptions.None, TokenImpersonationLevel.Impersonation); Console.WriteLine("连接服务端...\n"); pipeClient.Connect(); var ss = new StreamString(pipeClient); // Validate the server's signature string. if (ss.ReadString() == "I am the one true server!") { //发送文件路径,服务端读取后返回 ss.WriteString(Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "namedpipeTxt.txt")); //输出文件内容 Console.Write($"文件内容:{ss.ReadString()}\r\n"); } else { Console.WriteLine("服务端未验证通过"); } pipeClient.Close(); Console.ReadLine(); } } else { Console.WriteLine("\n*** 命名管道客户端示例 ***\n"); StartClients(); } } // 启动客户端 private static void StartClients() { string currentProcessName = Environment.CommandLine; currentProcessName = currentProcessName.Trim('"', ' '); currentProcessName = Path.ChangeExtension(currentProcessName, ".exe"); Process[] plist = new Process[numClients]; Console.WriteLine("生成客户端进程...\n"); if (currentProcessName.Contains(Environment.CurrentDirectory)) { currentProcessName = currentProcessName.Replace(Environment.CurrentDirectory, String.Empty); } //兼容处理 currentProcessName = currentProcessName.Replace("\\", String.Empty); currentProcessName = currentProcessName.Replace("\"", String.Empty); int i; for (i = 0; i < numClients; i++) { //启动客户端进程,使用同一个命名管道 plist[i] = Process.Start(currentProcessName, "spawnclient"); } while (i > 0) { for (int j = 0; j < numClients; j++) { if (plist[j] != null) { if (plist[j].HasExited) { Console.WriteLine($"客户端进程[{plist[j].Id}]已经退出."); plist[j] = null; i--; } else { Thread.Sleep(250); } } } } Console.WriteLine("\n客户端进程完成,退出中"); } } //定义用于在流上读取和写入字符串的数据协议 public class StreamString { private Stream ioStream; private UnicodeEncoding streamEncoding; public StreamString(Stream ioStream) { this.ioStream = ioStream; streamEncoding = new UnicodeEncoding(); } public string ReadString() { int len; len = ioStream.ReadByte(); len = len * 256; len += ioStream.ReadByte(); var inBuffer = new byte[len]; ioStream.Read(inBuffer, 0, len); return streamEncoding.GetString(inBuffer); } public int WriteString(string outString) { byte[] outBuffer = streamEncoding.GetBytes(outString); int len = outBuffer.Length; if (len > UInt16.MaxValue) { len = (int)UInt16.MaxValue; } ioStream.WriteByte((byte)(len / 256)); ioStream.WriteByte((byte)(len & 255)); ioStream.Write(outBuffer, 0, len); ioStream.Flush(); return outBuffer.Length + 2; } } }
四、总结:
若使用管道来实现进程间的通讯,可按如下方式选择:
- 若是只须要单向通讯,且两个进行间的关系为父子进程,则可使用匿名管道
- 若是须要双向通讯,则使用命名管道
- 若是咱们没法决定到底该选择什么,那就选择命名管道的双向通讯方式。在如今的电脑上,命名管道于匿名管道性能的差异咱们能够忽略不记。而双向通讯的命名管道,既可单向,又可双向,更加灵活
源码:IpcService






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(1)