红黑树原理与实现
红黑树
红黑树的性质
-
根节点必须是黑色
-
每个结点必须是黑色或者红色
-
叶子节点 (nil) 是黑色
-
如果一个结点是红色,则它的两个子节点都是黑色的
-
从根结点出发到所有叶节点的路径上,黑色节点数量相同
#define K(n) ((n)->key) #define C(n) ((n)->color) #define L(n) ((n)->lchild) #define R(n) ((n)->rchild) //定义红黑树结点 typedef struct node { int key; int color; //红色0 黑色1 双重黑2 struct node *lchild, rchild; } node; //定义nil结点 node __nil; #define nil (&__nil) __attribute__((constructor)) void init_nil() { nil->key = 0; nil->color = 1; nil->lchild = nil->rchild = nil; } //建立新节点 node *getNewNode(int key) { node *p = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node)); p->key = key; p->lchild = p->rchild = nil; p->color = 0; //默认插入红色结点 return p; } //红黑树的删除 void clear(node *root) { if (root == nil) return; clear(root->lchild); clear(root->rchild); free(root); return; } //辅助函数 //是否有红色孩子结点 int hasRed(node *root) { return C(L(root)) == 0 || C(R(root)) == 0; } //找到前驱节点 node *predecessor(node *root) { node *p = root->lchild; while (p->rchild != nil) p = p->rchild; return p; }
红黑树的调整策略
- 插入调整站在祖父结点看
- 删除调整站在父结点看
- 插入和删除的情况处理一共五种
红黑树结点的插入
情况一
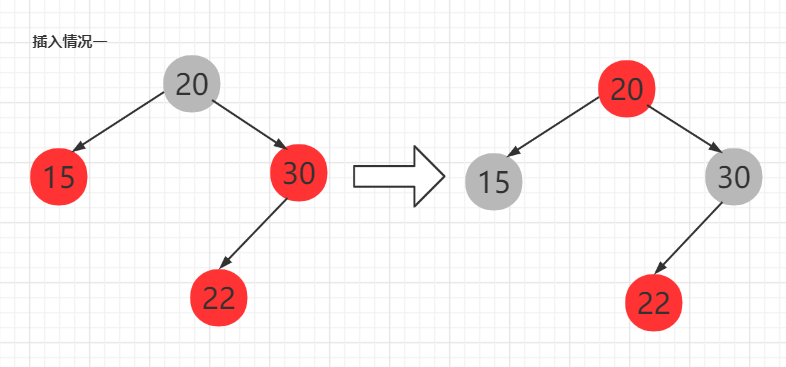
两个孩子结点均为红色,孩子的孩子结点有红色。把孩子改为黑色,自己改为红色(所谓的红色上顶)
情况二
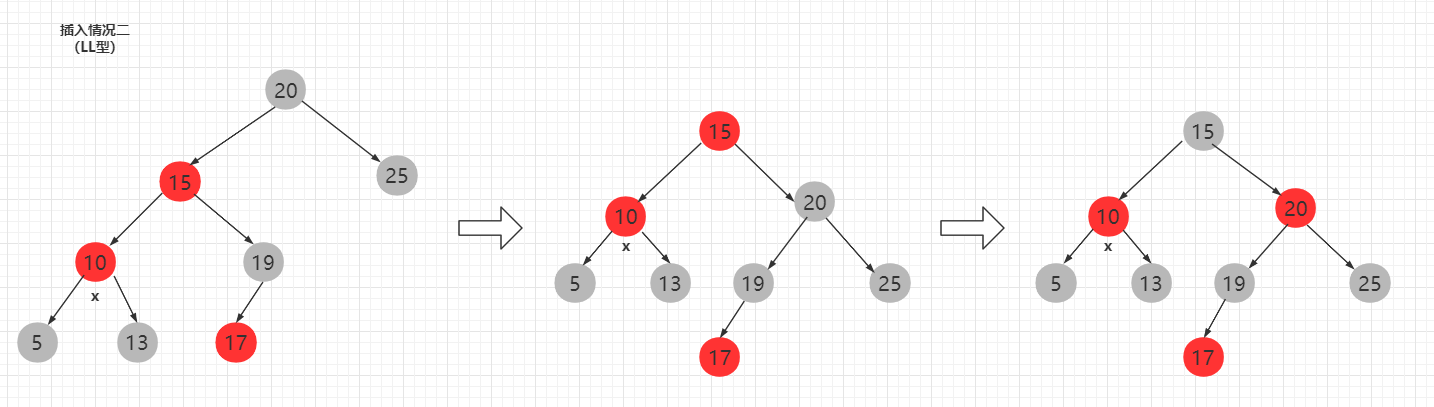
LL型调整先进行大右旋,然后有两种变色方案(只需要保证这两层的黑色结点为一就可以),上黑下红(原来的结点变为黑色,父结点变为红色),或者上红下黑(左孩子结点变为黑色)。
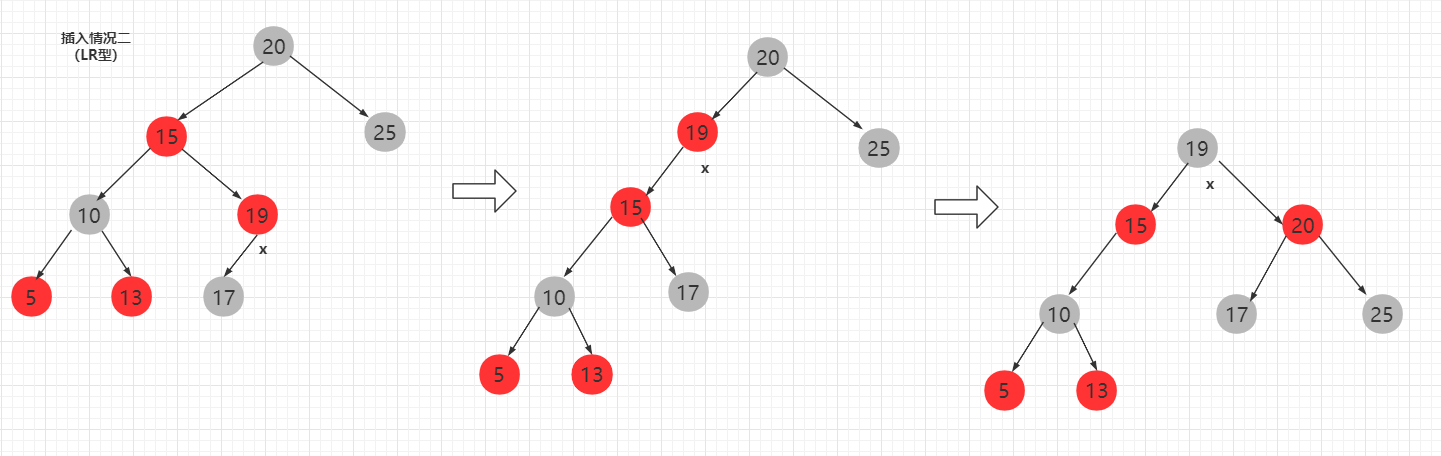
LR型调整先进行局部小左旋,然后就变为LL型的情况。
RR型和RL型类似于LL型与LR型,不多赘述。
//左旋
node *left_rot(node *root) {
node *p = root->rchild;
root->rchild = p->lchild;
p->lchild = root;
return p;
}
//右旋
node *right_rot(node *root) {
node *p = root->lchild;
root->lchild = p->rchild;
p->rchild = root;
return p;
}
node *insert_maintain(node *root) {
if (!hasRed(root)) return root; //不可能出现双红
int flag = 0;
if (C(L(root)) == 0 && hasRed(L(root))) flag = 1;
else if (C(R(root)) == 0 && hasRed(R(root))) flag = 2;
if (!flag) return root;
if (flag == 1 && C(R(root)) == 1) { //第二种情况
if (C(R(L(root)))) == 0) {
root->lchild = left_rot(root->lchild);
}
root = right_rot(root);
} else {
if (C(L(R(root)))) == 0) {
root->rchild = right_rot(root->rchild);
}
root = left_rot(root);
}
C(root) = 0; //这里采用红色上顶方案,两种情况最终变色方案一样
C(L(root)) = C(R(root)) = 1;
return root;
}
node *__insert(node *root, int key) {
if (root == nil) return getNewNode(key); //创建新节点
if (root->key == key) return root;
if (root->key > key) L(root) = __insert(L(root), key); //在左子树中插入key
else R(root) = __insert(R(root), key);
return insert_maintain(root); //进行插入调整
}
node *insert(node *root, int key) {
__insert(root, key);
C(root) = 1; //插入之后根节点变为黑色,保证根节点为黑色,否则可能为红色
return root;
}
一个栗子
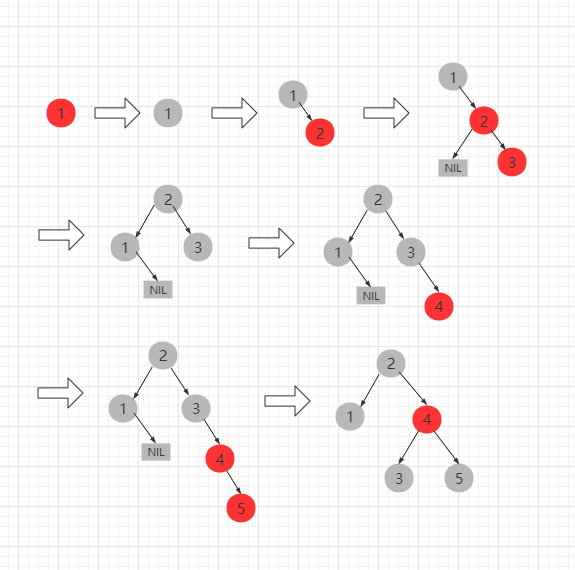
红黑树结点的删除
删除的结点度为1
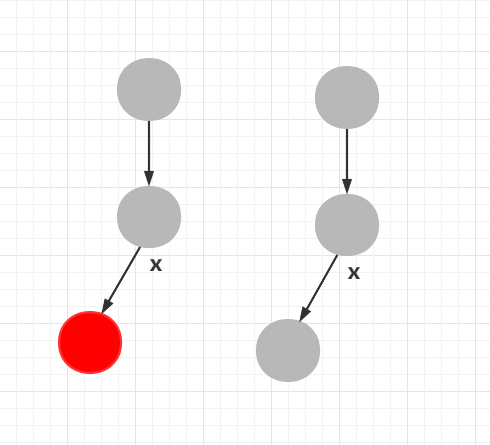
由于红黑树的性质,从任意节点到叶子结点经过的黑色节点数目相同,可以得知,度为1的结点一定是黑色结点。如果一个红色结点的度为1,那么它的孩子一定是黑色结点,这样就不符合红黑树的性质。
删除的结点度为0
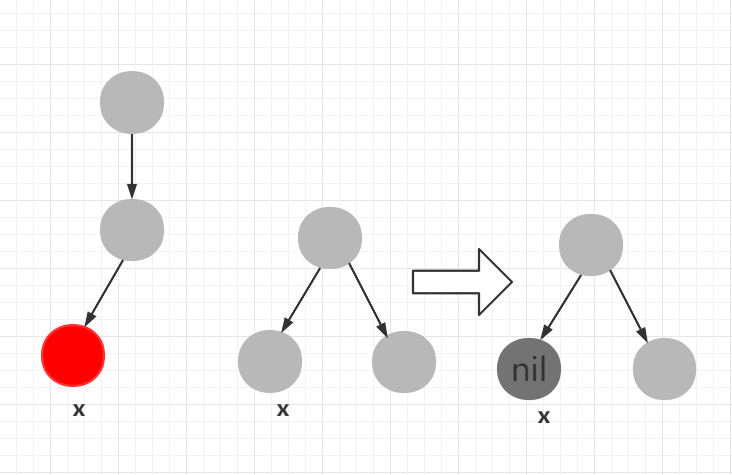
第一种情况:直接删除红色结点即可。
第二种情况:删除x结点会造成红黑树的不平衡,这时候引入双重黑的概念,在nil结点上增加一层黑色,相当于两个黑结点,然后再调整双重黑结点即可。
双重黑结点的删除
情况一
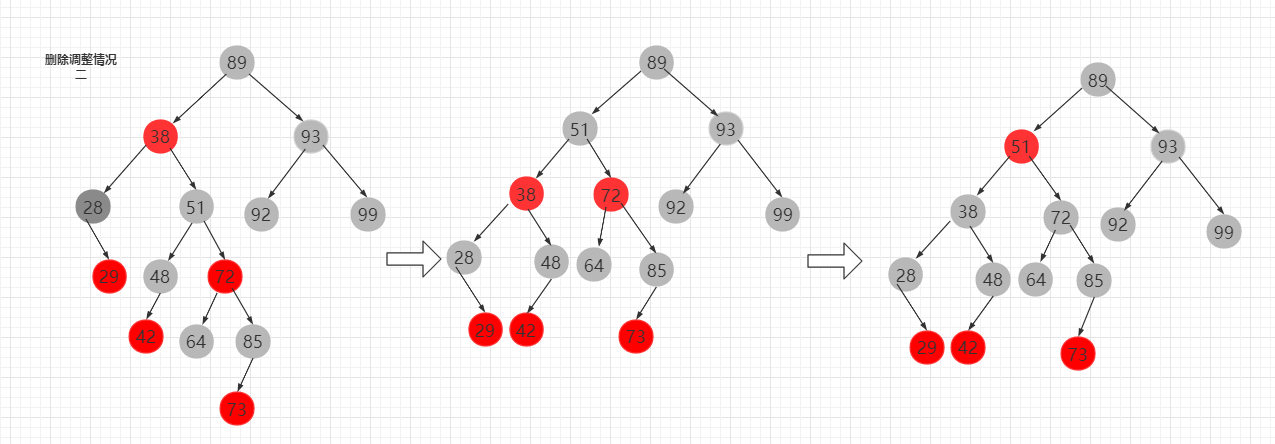
双重黑结点的兄弟结点为黑色,兄弟节点的孩子全为黑色。这时候把兄弟节点和自己黑色减一,父结点黑色加一即可。
情况二
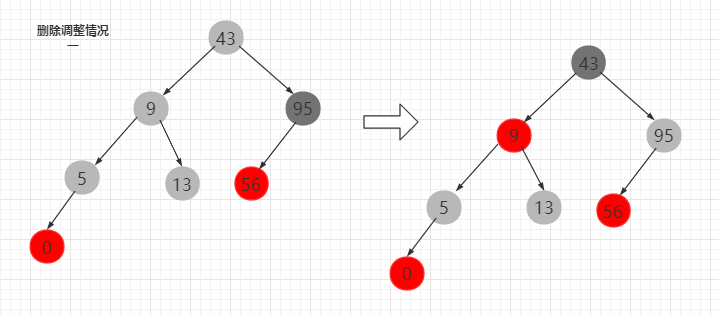
RR型,先对38结点进行左旋,把28颜色改为正常,这时候由于48结点的颜色不确定,需要把38设置为黑色,72设置为黑色,51设置为38的颜色。
情况三
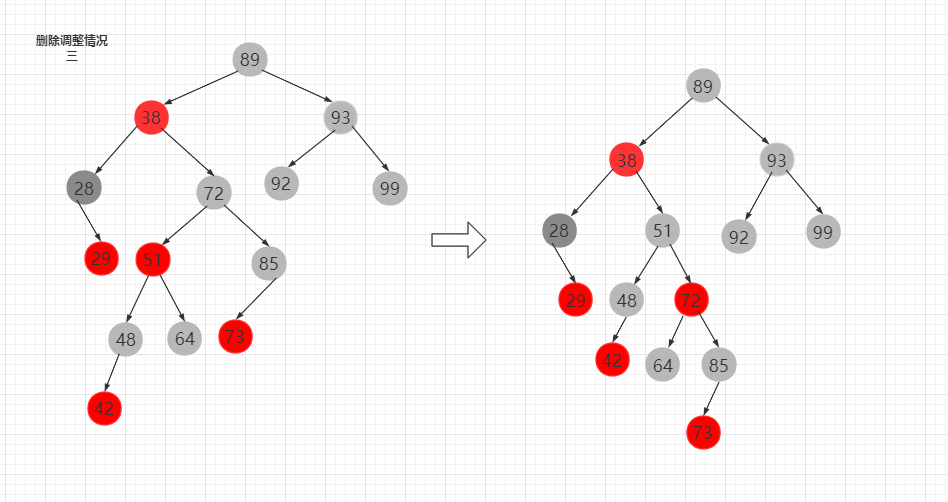
RL型,对72结点进行右旋,72变为红色,51变为黑色,然后按照情况二处理
情况四
双重黑结点兄弟结点为红色时,左孩子为红色则右旋,右孩子为红色则左旋,原来的根节点变为红色,旋转后的根节点变为黑色。然后进入相应的子树中处理二重黑结点。(假装这里有图)
node *erase_maintain(root) {
if (C(L(root)) != 2 && C(R(root)) != 2) return root;
if (hasRed(root)) { //情况四
int flag = 0;
root->color = 0;
if (C(L(root)) == 0) root = right_rot(root), flag = 1;
else if (C(R(root)) == 0) root = left_rot(root), flag = 2;
root->color = 1;
if (flag == 1) root->rchild = erase_maintain(root->rchild);
else root->lchild = erase_maintain(root->lchild);
return root;
}
if (C(L(root)) == 1) {
C(R(root)) = 1;
if (!hasRed(L(root))) {
C(root) += 1;
C(L(root)) -= 1;
return root;
}
if (C(L(L(root))) != 0) {
C(L(root)) = 0;
root->lchild = left_rot(root->lchild);
C(L(root)) = 1;
}
C(L(root)) = C(root);
root = right_rot(root);
C(L(root)) = 1;
C(R(root)) = 1;
} else {
C(L(root)) = 1;
if (!hasRed(R(root))) {
root->color += 1;
C(R(root)) -= 1;
return root;
}
if (C(R(R(root))) != 0) {
C(R(root)) = 0;
root->rchild = right_rot(root->rchild);
C(R(root)) = 1;
}
C(R(root)) = C(root);
root = left_rot(root);
C(L(root)) = 1;
C(R(root)) = 1;
}
return root;
}
node *__erase(node *root, int key) {
if (root == nil) return root;
if (root->key > key) root->lchild = __erase(root, key);
else if (root->key < key) root->rchild = __erase(root, key);
else {
if (root->lchild == nil || root->rchild == nil) {
node *p = root->lchild == nil ? root->rchild : root->rchild;
p->color += root->color; //here
free(root);
return p;
} else {
node *p = decessor(root);
root->key = p->key;
root->lchild = __erase(root->lchild, p->key);
}
}
return erase_maintain(root);
}
node *erase(node *root, int key) {
root = __erase(root, key);
root->color = 1;
return root;
}
总结



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号