Mybatis源码3 CachingExecutor, 二级缓存,缓存的实现
Mybatis CachingExecutor, 二级缓存,缓存的实现
一丶二级缓存概述
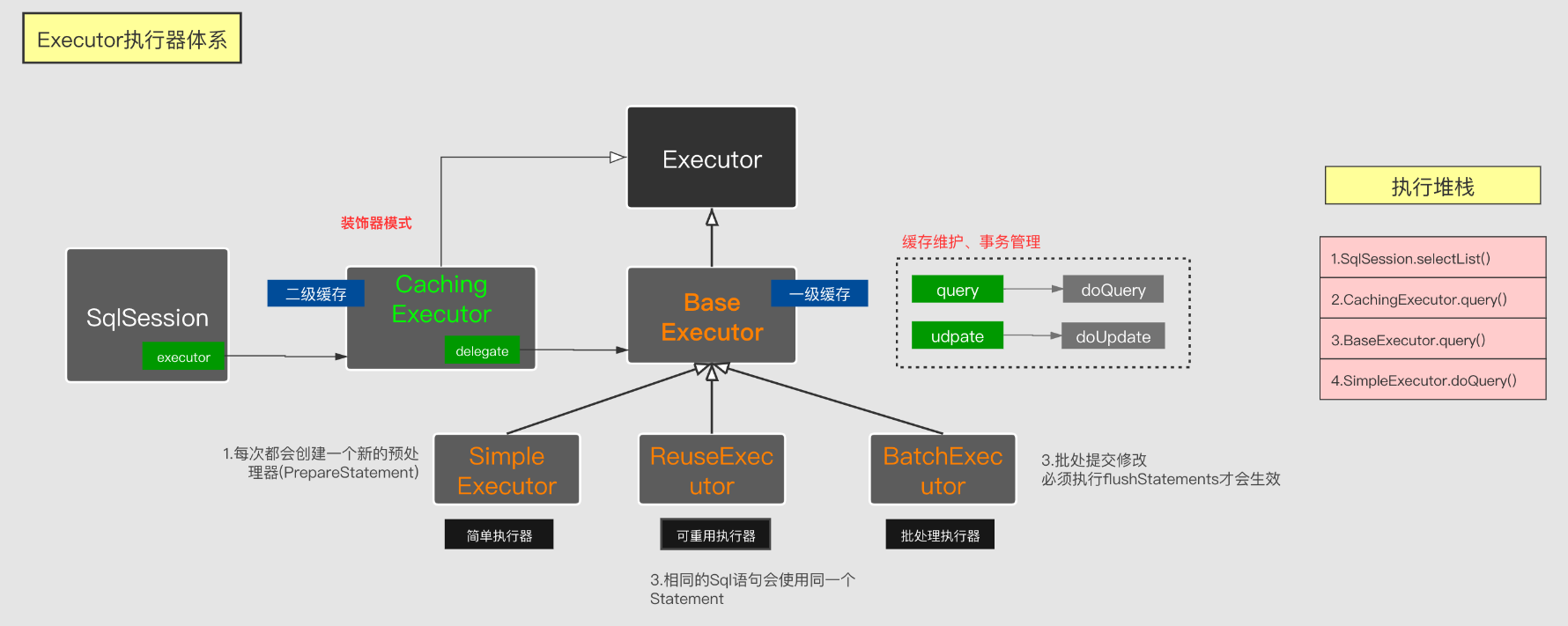
上一章节,我们知道mybaits在构造SqlSession的时候,需要让SqlSession持有一个执行器,如果配置了缓存开启,那么在Configuration.newExecutor的时候,会使用CachingExecutor对执行器进行装饰(被装饰可能是SimpleExecutor,ReuseExecutor,BatchExecutor)
//如果要求缓存,生成另一种CachingExecutor(默认就是有缓存),装饰者模式,所以默认都是返回CachingExecutor
if (cacheEnabled) {
//上面根据配置的ExecutorType 生成了executor==> SimpleExecutor or ReuseExecutor or BatchExecutor
//这里的开启不意味着一定开启二级缓存,而是说通过CachingExecutor装饰,可能用到二级缓存,为什么这么说,见 CachingExecutor 代码学习
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
二丶为什么需要二级缓存
一级缓存是SqlSession级别的(SqlSession持有一个Excutor,一个Excutor对于一个一级缓存)
所以SqlSesion的生命周期等于一级缓存的生命周期,且不同SqlSession的一级缓存不共用
不同session进行相同SQL查询的时候,是查询两次数据库的。显然这是一种浪费,既然SQL查询相同,就没有必要再次查库了,直接利用缓存数据即可,这种思想就是MyBatis二级缓存的初衷。如果开启二级缓存,关闭sqlsession后,会把该sqlsession一级缓存中的数据添加到mapper namespace的二级缓存中。这样,缓存在sqlsession关闭之后依然存在。
三丶Cache的实现类和缓存管理器
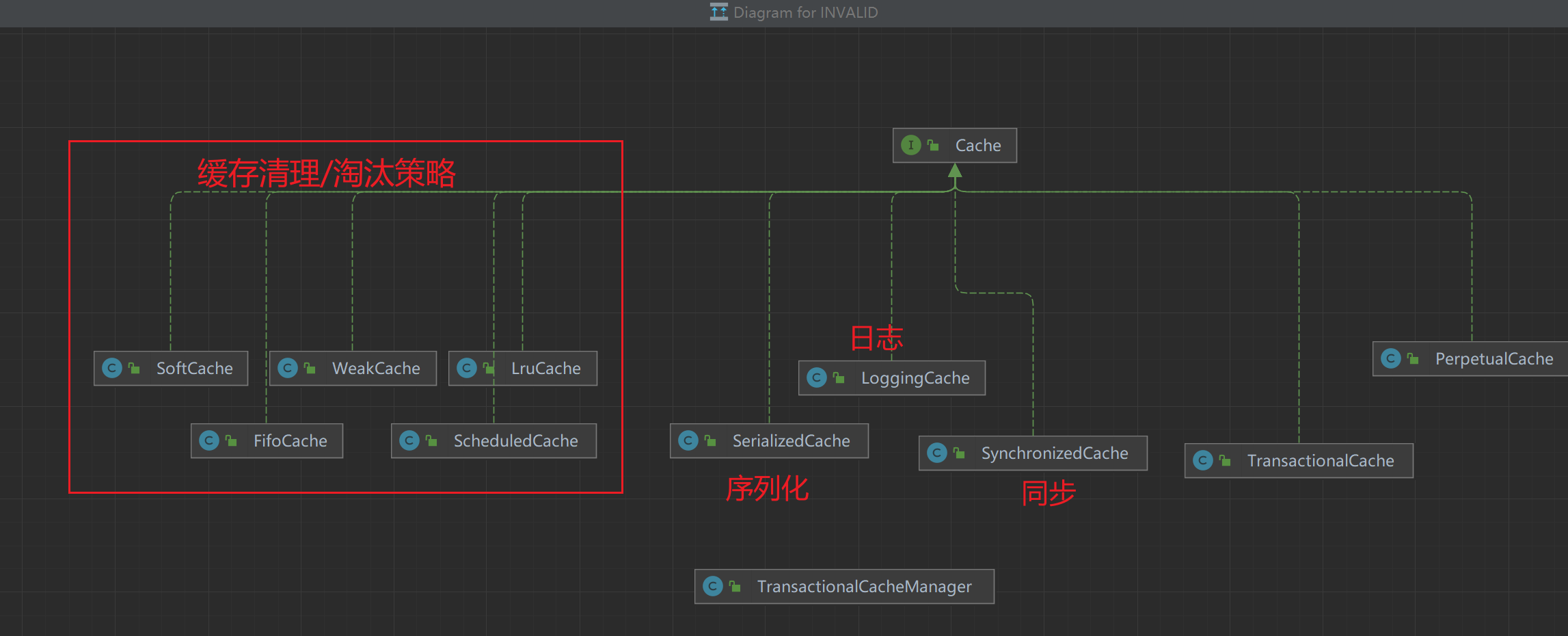
其实还有一个BlockingCache,但是我的idea画图有点问题
-
PerpetualCache mybatis 提供的缓存默认实现,基于hashMap
-
TransactionalCache,事务缓存,持有以下字段
//装饰器模式,真正的缓存操作将交由此执行
private Cache delegate;
//是否因为commit而清空了缓存 避免脏读
private boolean clearOnCommit;
//commit时要添加的元素 二级缓存变更的数据都将存储在 entriesToAddOnCommit中,后续同步到真正的缓存空间 //有点类似于git的本地代码 commit之后经过push才提交到云端服务器,只不过mybatis的push是commit操作
private Map<Object, Object> entriesToAddOnCommit;
//缓存未命中的key 避免缓存穿透
private Set<Object> entriesMissedInCache;
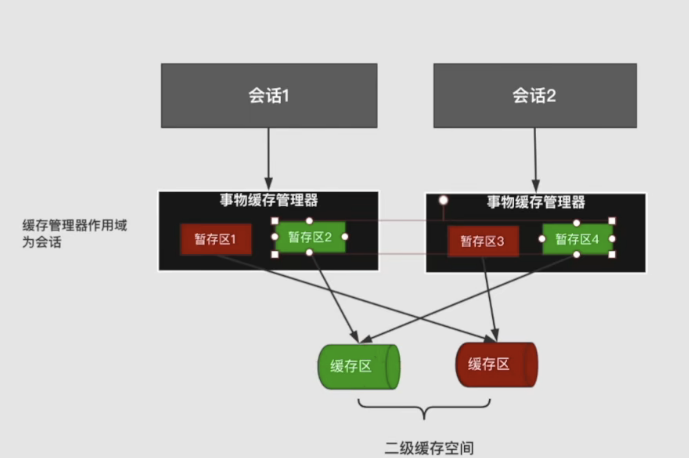
- TransactionalCacheManager 事务缓存管理器,没有实现cache接口,持有以下字段
//管理了许多TransactionalCache
//二级缓存是和nameSpace相关的,map的key对应一个mapperStatement
// map的value 是上面讲到的事务缓存,事务缓存持有 Cache delegate指向真正的二级缓存数据存储区域
private Map<Cache, TransactionalCache> transactionalCaches = new HashMap<Cache, TransactionalCache>();
每一个Sqlsession对应一个CachingExecutor,每一个CachingExcutor对应一个事务缓存管理器,每一个事务缓存管理器有多个value,value中的TransactionalCache 中的delegate是真正的二级缓存缓存区,entriesToAddOnCommit是其暂存区
四丶CachingExcutor源码学习
1.查询
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
//二级缓存适合MappedStatement 绑定的 MappedStatement是和mapper的nameSpace一对一的
//这里的cache是属于这个mapper的暂存区
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
//默认情况下是没有开启缓存的(二级缓存).要开启二级缓存,
// 你需要在你的 SQL 映射文件中添加一行: <cache/> or使用注解
//先查CacheKey,查不到再委托给实际的执行器去查
if (cache != null) {
//如果需要刷新缓存 对应flushCache的配置
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
// 如果配置了使用 二级缓存 useCach配置
//<select ... flushCache="false" useCache="true"/>
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
//确定是存储过程的时候没有out类型的参数 如果有抛出异常
//二级缓存不支持有输出的存储过程
ensureNoOutParams(ms, parameterObject, boundSql);
//根据暂存区的cache从缓存区取值
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
//没有那么调用被装饰着去查询 还会走到BaseExecutor的一级缓存
list = delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
//存到暂存区
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
//没有使用二级缓存 那么被装饰者执行
return delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
为什么说是提交到暂存区了
//TransactionalCacheManager的
public void putObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key, Object value) {
getTransactionalCache(cache).putObject(key, value);
}
// TransactionalCache 的 putObject
//其实是加到了 TransactionalCache的entriesToAddOnCommit中了 等commit的时候再加入到二级缓存,从而保证二级缓存中的数据是提交后的避免造成脏读
//假设发生了一个写操作,执行完成后另外一个请求查询到了该数据直接放置到二级缓存区域,但是此时这条数据执行了回滚操作,那么此时就会造成一个脏读!
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object object) {
entriesToAddOnCommit.put(key, object);
}
2.更新
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException {
//刷新缓存完再update
//这里的刷新缓存并不是立马将二级缓存中的数据进行清空
//而是TransactionalCache中的clearOnCommit 置为了true
//如果更新的时候直接清空二级缓存 那么发生回滚的时候,二级缓存的数据回不来了,降低了二级缓存的命中率
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
return delegate.update(ms, parameterObject);
}
3.commit
@Override
public void (boolean required) throws SQLException {
delegate.commit(required);
tcm.commit();
}
//tcm.commit(); 多了commit方法,提供事务功能
public void commit() {
//提交是先清空缓存,避免被缓存和数据库不一致
if (clearOnCommit) {
delegate.clear();
}
//把待提交的数据 加入到二级缓存
flushPendingEntries();
//重置属性 clearOnCommit = false;entriesToAddOnCommit清空,entriesMissedInCache清空
reset();
}
private void flushPendingEntries() {
//待提交的数据 加入到二级缓存
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : entriesToAddOnCommit.entrySet()) {
delegate.putObject(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
//没有命中的数据赋值为null “这样可以避免缓存穿透么?”
for (Object entry : entriesMissedInCache) {
if (!entriesToAddOnCommit.containsKey(entry)) {
delegate.putObject(entry, null);
}
}
}
4.rollback
@Override
public void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException {
try {
delegate.rollback(required);
} finally {
if (required) {
tcm.rollback();
}
}
}
//tcm.rollback
public void rollback() {
unlockMissedEntries();
reset();
}
private void unlockMissedEntries() {
for (Object entry : entriesMissedInCache) {
delegate.putObject(entry, null);
}
}
五丶Mybatis是如何把众多Cache的装饰器串联起来组成责任链模式的
mybatis构建一个二级缓存使用的是CacheBuilder(建造者模式)
//对应mapperStateMent的id
private String id;
//二级缓存的具体实现 也就是说可以通过配置进行自定义的二级缓存,甚至是基于第三方如redis的缓存
private Class<? extends Cache> implementation;
//装饰器,通过配置 可以选择使用那些进行装饰增强
private List<Class<? extends Cache>> decorators;
//缓存的大小
private Integer size;
//缓存自动清楚间隔
private Long clearInterval;
//读写锁
private boolean readWrite;
//是否阻塞
private boolean blocking;
public Cache build() {
//如果用户没有自定义的缓存 那么使用PerpetualCache 如果用户没有指定的淘汰策略 那么使用LruCache 最近最少使用的原则进行淘汰
setDefaultImplementations();
//先new一个base的cache(PerpetualCache) 没有指定 那么就是反射生成PerpetualCache
Cache cache = newBaseCacheInstance(implementation, id);
//设额外属性
setCacheProperties(cache);
// issue #352, do not apply decorators to custom caches
//装饰器 只对默认的二级缓存PerpetualCache 生效,也就是说自定义的cache不被装饰,淘汰策略,锁等等要自己实现
if (PerpetualCache.class.equals(cache.getClass())) {
for (Class<? extends Cache> decorator : decorators) {
//装饰者模式一个个包装cache 反射构造函数 把被装饰者作为入参
cache = newCacheDecoratorInstance(decorator, cache);
//又要来一遍设额外属性
setCacheProperties(cache);
}
//最后附加上标准的装饰者
cache = setStandardDecorators(cache);
} else if (!LoggingCache.class.isAssignableFrom(cache.getClass())) {
//如果是custom缓存,且没有日志装饰,要加日志
cache = new LoggingCache(cache);
}
return cache;
}
//最后附加上标准的装饰者
private Cache setStandardDecorators(Cache cache) {
try {
MetaObject metaCache = SystemMetaObject.forObject(cache);
if (size != null && metaCache.hasSetter("size")) {
//反射设置缓存大小
metaCache.setValue("size", size);
}
if (clearInterval != null) {
//刷新缓存间隔,怎么刷新呢,用ScheduledCache来刷,还是装饰者模式
cache = new ScheduledCache(cache);
((ScheduledCache) cache).setClearInterval(clearInterval);
}
if (readWrite) {
//如果readOnly=false,可读写的缓存 会返回缓存对象的拷贝(通过序列化) 。这会慢一些,但是安全,因此默认是 false。
cache = new SerializedCache(cache);
}
//日志缓存
cache = new LoggingCache(cache);
//同步缓存
cache = new SynchronizedCache(cache);
if (blocking) {
cache = new BlockingCache(cache);
}
return cache;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CacheException("Error building standard cache decorators. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号